In recent years, self-driving cars, also known as autonomous vehicles, have transformed from science fiction to a tangible reality. This technology is poised to revolutionize the transportation industry by reducing accidents, optimizing fuel efficiency, and improving mobility for all. However, while the excitement around driverless cars is high, challenges related to safety, cost, and ethics remain significant hurdles. Let’s delve into the details of how these vehicles work, their benefits, and what the future holds for them.
What Is an Autonomous Vehicle?
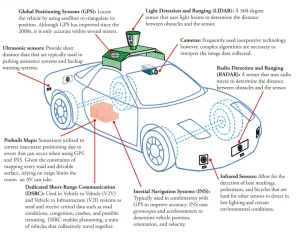
An autonomous vehicle is a car equipped with technology that enables it to sense its surroundings—such as traffic, pedestrians, and obstacles—without human intervention. These cars use sensors, cameras, and advanced algorithms to adjust their speed, route, and actions in real time.
The Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE) defines self-driving cars using a six-level system, where:
- Level 0: No automation; the driver is fully in control.
- Level 1: Basic driver assistance, such as adaptive cruise control.
- Level 2: Partial automation, allowing the car to steer or accelerate with the driver monitoring.
- Level 3: Conditional automation, where the car can handle certain conditions but requires human intervention.
- Level 4: High automation, where the car is almost entirely self-driving but may require assistance in unusual circumstances.
- Level 5: Fully autonomous, with no human input required.
How Do Self-Driving Cars Work?
The magic behind self-driving cars lies in the complex network of sensors, processors, and artificial intelligence (AI) systems that interact with the physical world.
- Sensors: Autonomous vehicles rely on several sensors to “see” their surroundings. The primary technologies include radar, LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging), and cameras. LiDAR uses lasers to measure the distance between the car and other objects, while cameras provide visual data on lane markings, pedestrians, and other vehicles.
- Data Processing: The data from these sensors is processed by sophisticated software that uses machine learning algorithms. These algorithms can interpret data, identify obstacles, and determine the safest driving path.
- Actuators: The processed data instructs the car’s actuators, which control steering, braking, and acceleration, allowing the car to react in real time to changes in the environment.
- AI and Machine Learning: Self-driving cars use AI to make decisions. For instance, when navigating through traffic, the vehicle’s AI will predict the behavior of surrounding vehicles and adjust accordingly.
The Pros and Cons of Driverless Cars

Like any emerging technology, self-driving cars offer both advantages and challenges.
Benefits of Self-Driving Cars
- Increased Safety: Human error is responsible for around 90% of traffic accidents. Self-driving cars, which don’t get distracted, tired, or drunk, can significantly reduce accident rates. Automated Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS), like emergency braking and lane departure warnings, already help to prevent crashes.
- Improved Mobility: Autonomous cars can offer freedom to people who are unable to drive, including the elderly and those with disabilities. Self-driving taxis, like those operated by Waymo and Cruise, provide a new level of independence for these groups.
- Reduced Traffic Congestion: With better coordination between vehicles, self-driving technology can help reduce traffic jams. When fewer accidents occur, roadways stay clearer. Moreover, cars can communicate with one another to optimize flow.
- Fuel Efficiency: Autonomous cars can reduce fuel consumption by using efficient driving patterns. Research from the University of Michigan shows that self-driving vehicles can lower fuel consumption by up to 9%, contributing to reduced greenhouse gas emissions.
- Cost Savings: For businesses, autonomous trucks and delivery services reduce the need for human drivers, which translates to lower labor costs and increased operational efficiency. Companies like Kodiak Robotics and Gatik are already deploying autonomous trucks for commercial deliveries.
Challenges of Self-Driving Cars
Despite the numerous benefits, self-driving cars face several challenges:
- Safety Concerns: While autonomous cars are designed to reduce accidents, they are not infallible. Incidents, such as the fatal accidents involving Uber’s self-driving vehicle and Cruise’s robotaxi, highlight that this technology still requires refinement.
- Cost: Developing and producing fully autonomous vehicles is expensive. The McKinsey & Company report estimates that only 12% of new cars sold in 2030 will have Level 3 or higher autonomy, largely due to cost concerns.
- Legal and Ethical Issues: Autonomous cars introduce ethical dilemmas. For instance, should a car prioritize the safety of its passengers over pedestrians? Germany has passed legislation mandating that self-driving cars must prioritize human life in all situations. Additionally, varying legal frameworks globally make it hard to develop a unified set of rules for these vehicles.
- Weather Conditions: Adverse weather, such as snow or heavy rain, can obscure road markings and limit the effectiveness of sensors, posing a significant challenge for fully autonomous vehicles.
Case Studies and Real-World Examples
Waymo’s Robotaxi Service
One of the most well-known examples of self-driving cars in action is Waymo’s robotaxi service. Operating in cities like San Francisco and Phoenix, Waymo offers Level 4 autonomous vehicles that navigate complex urban environments. Passengers can summon a Waymo car via an app, and the car drives them to their destination without human intervention. Despite some operational challenges, such as dealing with construction zones and pedestrian-heavy areas, Waymo has been largely successful and is expanding to cities like Los Angeles and Austin.
Kodiak Robotics and Gatik

In the realm of logistics, Kodiak Robotics and Gatik have pioneered the use of autonomous trucks for goods delivery. Kodiak Robotics has integrated self-driving technology into long-haul semi-trucks, reducing the need for rest stops and improving delivery times. Gatik, meanwhile, focuses on middle-mile deliveries (between warehouses and stores), with a special emphasis on efficiency and safety. These companies highlight how self-driving technology can be adapted for commercial use, cutting costs and boosting efficiency.
Cruise’s Setbacks
Not all self-driving car companies have had smooth success. Cruise, a subsidiary of General Motors, faced significant backlash after a robotaxi accident in San Francisco. Despite the incident, Cruise continues to push for improvements in its technology. This serves as a reminder of the complexities involved in creating safe, reliable autonomous vehicles for public use.
The Future of Self-Driving Cars
As automakers continue to develop self-driving technology, it’s clear that we’re moving toward a future where autonomous vehicles will play a significant role in transportation. However, full autonomy—Level 5—remains elusive, with even the most advanced cars on the market still requiring some level of human oversight.
Consumer interest is high, with many willing to pay a premium for ADAS and other automation features. McKinsey predicts that self-driving technology could generate between $300 billion and $400 billion in the passenger car market by 2035.
While it’s unlikely that we’ll see a world dominated by driverless cars in the immediate future, significant progress is expected in areas such as autonomous logistics, robotaxis, and safety features in personal vehicles. Commercial applications, like those pioneered by Waymo, Gatik, and Kodiak Robotics, will likely lead the way, with consumer vehicles slowly catching up.
Final Thought
Self-driving cars are on the verge of becoming a permanent fixture in both commercial and personal transportation. With benefits ranging from enhanced safety to reduced emissions, the technology promises to revolutionize how we move people and goods. However, significant challenges, including safety concerns, cost, and legal issues, must be addressed before fully autonomous vehicles become a common sight on our roads.
The future may not be here yet, but the wheels are certainly in motion. Whether it’s in the form of robotaxis in urban centers, autonomous trucks hauling goods, or ADAS features in your next car, self-driving technology is shaping the future of mobility.












