Introduction
A healthy smile is more than just an aesthetic feature; it is a reflection of overall well-being and oral health. Maintaining strong gums is essential, yet for many people, particularly women, hormonal fluctuations can create unique challenges. Hormones influence blood flow, immune response, and tissue sensitivity, all of which directly impact the gums.
Awareness of these changes and their effects is crucial for preventing long-term damage and maintaining a confident, healthy smile. This article explores how hormonal shifts affect oral health, identifies periods of heightened risk, and outlines strategies for prevention and treatment.
What is Gum Disease?
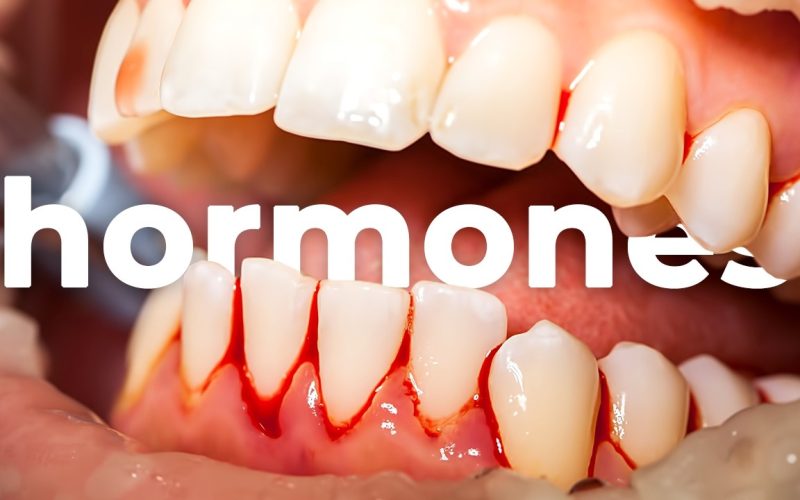
Gum disease, or periodontal disease, begins as gingivitis with red, swollen, bleeding gums. If untreated, it can progress to periodontitis, weakening bone and tissue support, potentially causing loose teeth or tooth loss.
Healthy gums are essential for:
- Forming a protective seal around each tooth to prevent bacterial invasion
- Anchoring teeth firmly in place
- Supporting the jawbone and maintaining oral structure
During periods of hormonal change, these protective mechanisms can be compromised, making gums more susceptible to infections such as gum disease Nottingham.
Stages of Gum Disease:
- Gingivitis: Mild gum inflammation causing redness, swelling and bleeding.
- Periodontitis: Advanced bone infection leading to gum recession, loose teeth, and persistent bad breath.
How Hormones Affect Gum Health
Hormones, particularly oestrogen and progesterone, play a crucial role in maintaining gum health. They regulate blood flow, tissue repair, and the inflammatory response. Fluctuations in these hormone levels can increase gum sensitivity and susceptibility to infections.
Key Effects of Hormonal Changes:
- Increased Blood Flow: Hormones can enlarge blood vessels in the gums, making tissues more reactive to plaque and bacteria.
- Heightened Inflammatory Response: Even small amounts of plaque can trigger pronounced gum inflammation.
Life Stages Affected by Hormonal Shifts:
- Puberty: Rising hormones often cause swollen, tender gums.
- Menstrual Cycle: Hormonal fluctuations may trigger mild inflammation and sensitivity.
- Pregnancy: Hormonal surges can lead to pregnancy gingivitis and bleeding gums.
- Menopause: Reduced oestrogen may cause dryness, recession, and sensitivity.
Understanding these life stages helps explain why gum infections often appear or worsen during specific periods.
Why Hormonal Fluctuations Increase Gum Disease Risk
Hormonal changes can increase the risk of gum disease through several mechanisms:
- Enhanced Gum Inflammation: Hormonal surges make gums more prone to irritation and swelling.
- Slower Tissue Repair: Fluctuating hormone levels can impair the body’s natural healing capacity.
- Altered Oral Environment: Hormonal changes may affect saliva composition, allowing bacteria to thrive.
These factors can contribute to the development or worsening of Gum Disease Nottingham, especially when combined with other risk factors.
Lifestyle Factors That Exacerbate Hormonal Gum Risks

Beyond hormones, lifestyle choices significantly impact gum health. Smoking, for example, can exacerbate gum vulnerability by:
- Reducing blood flow to gum tissues
- Weakening the immune system
- Altering saliva composition, creating an environment conducive to bacterial growth
This combination increases the likelihood of gum infections and can complicate treatments, including Dental Implant Nottingham, if gum disease is present.
Other Contributing Factors:
- Poor oral hygiene
- High sugar or acidic diets
- Chronic stress, which can reduce immune effectiveness
Recognising the Signs of Hormonal Gum Issues
Early detection is essential to prevent irreversible damage. Hormonal fluctuations may mask or exaggerate certain symptoms, making regular dental assessments critical.
Symptoms to Watch For:
- Red, swollen or tender gums
- Bleeding while brushing or flossing
- Gum recession, causing teeth to appear longer
- Persistent bad breath
- Loosened or shifting teeth
Because hormonal changes can hide early warning signs, proactive monitoring and routine dental visits are crucial.
Prevention Strategies
Maintaining gum health during hormonal shifts requires a combination of consistent oral hygiene, professional care, and lifestyle management.
Daily Oral Care:
- Brush twice daily using fluoride toothpaste
- Floss or use interdental brushes to remove plaque
- Rinse with antimicrobial or fluoride mouthwash if recommended
Professional Care:
- Schedule dental check-ups at least twice a year
- Have professional cleanings to remove tartar and plaque below the gum line
- Discuss fluoride treatments or medicated mouth rinses for extra protection
Lifestyle Support:
- Eat a nutrient-rich diet with vitamins C, D, and calcium
- Stay hydrated to promote saliva production
- Avoid smoking or exposure to tobacco
- Manage stress to support immune function
These steps significantly reduce the risk of hormonal-related gum infections and improve oral resilience.
Treatment Options for Hormonal Gum Issues
Even with preventive measures, some patients may experience gum infections. Early intervention ensures better outcomes and preserves oral health.
Non-Surgical Treatments:
- Scaling and Root Planing: Removes plaque and tartar below the gum line
- Medicated Mouth Rinses: Control bacterial growth
- Laser Therapy: Targets bacteria and stimulates tissue regeneration
Surgical Treatments:
- Flap surgery to access deep pockets
- Bone grafts to restore lost bone
- Soft tissue grafts to rebuild receded gums
Timing treatment around hormone cycles, especially for pregnant or menopausal women, can enhance results.
Hormones and Dental Implants

Hormonal fluctuations can also influence restorative procedures such as dental implant Nottingham.
- Sensitive and inflamed gums may affect healing after implant placement
- Maintaining optimal oral health before, during, and after surgery improves long-term success
- Professional guidance ensures treatment is timed appropriately during high-risk hormonal periods
Proper planning and care are essential for achieving stable, functional, and long-lasting dental implants.
Monitoring and Awareness
Being proactive about hormonal effects on gum health is key:
- Keep a diary of symptoms and correlate with menstrual or hormonal cycles
- Communicate changes in gum health to your dentist
- Schedule additional dental visits during high-risk periods
- Collaborate with healthcare providers for integrated care
Regular monitoring ensures gum issues are addressed promptly, improving both natural gum health and outcomes for restorative treatments.
Conclusion
Hormonal shifts can subtly but significantly impact gum health, increasing vulnerability to infections such as Gum Disease. Awareness, diligent oral hygiene, preventive care, and timely professional treatment are vital for maintaining a strong, healthy smile. Hormonal influences also affect the success of restorative treatments like Dental Implant, making planning and proactive care essential.
At Smilo Dental Implant Nottingham, we combine advanced technology with personalised care to support patients through hormonal changes, helping them achieve strong, resilient and confident smiles. Understanding and addressing these factors ensures long-term oral health for every patient.