Green technology, also known as environmental or eco-technology, plays a crucial role in addressing global environmental challenges. It focuses on sustainable practices and products that reduce ecological footprints, conserve resources, and promote ecological balance. Green technologies range from renewable energy sources to sustainable construction practices, all aiming for a cleaner, healthier planet. In recent years, entities like Tesla, as well as cities and corporations worldwide, have embraced green technology, working to mitigate climate change and foster sustainability.
1. Carbon Capture, Utilization, and Storage (CCUS)
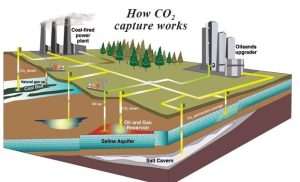
CCUS is a technology that captures carbon dioxide emissions from industrial sources and stores them underground or uses them in other processes, preventing CO2 from entering the atmosphere. This innovation is essential in carbon-intensive industries, as it helps lower greenhouse gas emissions and aligns with global climate goals.
Case Study:
Boundary Dam Power Station The Boundary Dam Power Station in Canada was one of the first large-scale CCUS projects. It captures approximately 1 million tons of CO2 annually, equivalent to removing over 250,000 cars from the road each year. This project showcases how CCUS can be implemented effectively in coal-fired power plants to reduce carbon emissions significantly.
Benefits of CCUS
- Mitigates carbon emissions in heavy industries
- Supports a transition to a low-carbon economy
- Helps achieve climate targets
2. Energy-Efficient Building Designs
Energy-efficient building design focuses on reducing energy consumption and utilizing resources effectively within buildings. This approach integrates sustainable building materials, advanced insulation, LED lighting, and smart thermostats to create eco-friendly structures.
Example:
The Edge in Amsterdam The Edge in Amsterdam is known as one of the most sustainable office buildings worldwide. It uses energy-efficient lighting, smart sensors, and a climate control system to reduce energy consumption by almost 70%. This building’s sustainable design proves that green architecture can enhance employee comfort while significantly lowering energy costs.
Benefits of Energy-Efficient Buildings
- Reduces utility costs and energy consumption
- Lowers carbon footprint for urban areas
- Enhances occupant health and productivity
3. Electric Vehicles (EVs)

Electric vehicles (EVs) have revolutionized the transportation sector by offering an alternative to fossil fuel-powered cars. EVs help reduce greenhouse gas emissions and minimize pollution, contributing to cleaner air and a healthier environment.
Case Study:
Tesla’s Impact on EV Adoption Tesla has become a global leader in EV manufacturing, with models like the Tesla Model 3 and Model S setting new standards for range and performance. By 2020, there were over 10 million electric cars worldwide, largely due to Tesla’s innovation and advocacy for sustainable transportation. The company’s advancements in battery technology and expansion of the Supercharger network have driven widespread EV adoption and emission reductions.
Benefits of Electric Vehicles
- Reduces air pollution and greenhouse gases
- Lowers dependence on fossil fuels
- Promotes energy-efficient transportation
4. Smart Grid Technology
Smart grid technology enhances the efficiency and reliability of electricity distribution by allowing real-time monitoring and control of energy usage. Smart grids integrate renewable energy sources, optimize distribution, and balance supply and demand, making power systems more sustainable.
Example:
Chattanooga’s Smart Grid Transformation Chattanooga, Tennessee, implemented a smart grid system that dramatically improved its energy resilience. The city’s smart grid has helped reduce power outages and energy costs while supporting renewable energy integration. Chattanooga’s success demonstrates the potential of smart grids in modernizing energy infrastructure and improving sustainability.
Benefits of Smart Grids
- Increases energy efficiency and reduces costs
- Enhances power reliability and stability
- Facilitates the integration of renewable energy sources
5. Vertical Farming

Vertical farming involves growing crops in vertically stacked layers, often in controlled indoor environments. This approach uses less water and land than traditional farming, making it an innovative solution for urban areas with limited agricultural space.
Case Study:
AeroFarms
AeroFarms, a New Jersey-based company, operates one of the world’s largest vertical farms. By using up to 95% less water than conventional farming, AeroFarms has achieved high crop yields with minimal environmental impact. This farming method has proven effective in urban areas and can address food security issues sustainably.
Benefits of Vertical Farming
- Saves water and land resources
- Increases food production in urban settings
- Reduces transportation emissions by growing food locally
6. Biomimicry in Green Design
Biomimicry, the practice of emulating natural processes in design, has become increasingly popular in green technology. Innovations inspired by nature are often energy-efficient and environmentally friendly.
Example:
The Lotus Effect Inspired by the lotus leaf’s water-repellent properties, scientists have developed self-cleaning building materials that repel dirt and reduce maintenance needs. This example of biomimicry reduces water usage and cleaning chemicals, contributing to more sustainable urban infrastructure.
Benefits of Biomimicry
- Promotes energy-efficient and sustainable designs
- Encourages eco-friendly materials and processes
- Reduces resource consumption and waste
7. Plant-Based Packaging Solutions

Plant-based packaging, an eco-friendly alternative to traditional plastic, is made from renewable biological sources. These materials are compostable, reducing landfill waste and pollution caused by single-use plastics.
Example:
Notpla’s Seaweed-Based Packaging Notpla, a London-based company, has developed plant-based packaging using seaweed and other natural materials. Their products are biodegradable and serve as sustainable alternatives to plastic packaging, helping companies reduce their environmental impact.
Benefits of Plant-Based Packaging
- Reduces reliance on petroleum-based plastics
- Decreases waste in landfills and oceans
- Lowers pollution and conserves resources
8. Renewable Energy Sources
Renewable energy, derived from natural sources such as solar, wind, hydro, and geothermal power, is at the forefront of the green technology movement. These energy sources produce little to no emissions, offering a sustainable alternative to fossil fuels.
Case Study:
Solar Energy in Germany Germany’s Energiewende, or energy transition, is a pioneering example of a large-scale shift toward renewable energy. As of 2020, renewable sources provided over 40% of Germany’s electricity, reducing the country’s carbon footprint and dependence on coal and nuclear power.
Benefits of Renewable Energy
- Provides clean, emission-free energy
- Reduces dependency on non-renewable resources
- Supports climate change mitigation efforts
Challenges in Green Technology
While green technology has many benefits, several challenges still hinder its widespread adoption. High initial costs, technological limitations, regulatory obstacles, and market acceptance are notable barriers.
Case Study:
Petra Nova’s Carbon Capture Costs The Petra Nova project in Texas was one of the largest carbon capture facilities in the world but faced high operational costs. Despite capturing over 1.6 million tons of CO2, the project was put on hold in 2020 due to financial constraints. This highlights the challenge of making green technologies economically viable.
Future Outlook on Green Technology
The future of green technology looks promising as global awareness of climate change grows. Key trends include advancements in renewable energy, smart grids, energy storage, and green hydrogen. For example, green hydrogen has potential in decarbonizing industries and transport sectors, while innovations in battery technology will improve energy storage capacity for renewable sources.
Governments worldwide, including the European Union’s Green Deal and the U.S. rejoining the Paris Agreement, have committed to green initiatives. These policies, combined with private sector investments, are accelerating the transition toward sustainable solutions. As innovation continues, green technology will undoubtedly be a cornerstone of our journey toward a more sustainable future.
Final Thought
Green technology innovations are transforming industries, promoting sustainability, and addressing climate change. From carbon capture to renewable energy sources, these advancements showcase the potential for a cleaner, healthier planet. While challenges like high costs and regulatory barriers remain, ongoing research, supportive policies, and private sector involvement are paving the way for a sustainable future. With continued investment and global commitment, green technology will play a pivotal role in creating a greener, more resilient world for generations to come.












