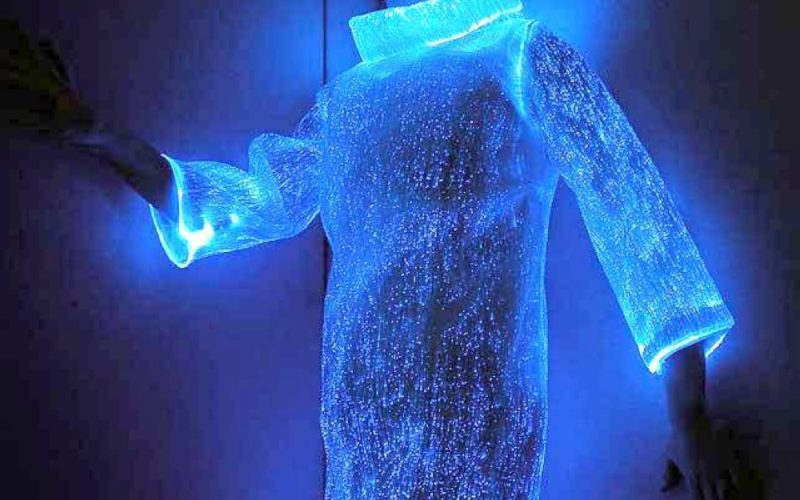
The textile industry is undergoing significant changes, driven by innovation, sustainability, and technology. From sustainable materials to smart fabrics, new technologies are reshaping how textiles are produced, consumed, and disposed of. This article explores key trends, their benefits, and relevant case studies in the field of textiles.
Sustainable Materials in Textiles

Overview
As awareness about environmental issues grows, the textile industry is increasingly turning to sustainable materials. These eco-friendly fabrics are designed to reduce the environmental impact of textile production. Materials such as organic cotton, hemp, bamboo, and recycled fibers are gaining popularity due to their lower ecological footprint.
Benefits
- Reduced chemical use: Organic cotton, for example, is grown without harmful pesticides, making it safer for the environment.
- Lower water consumption: Hemp and bamboo require far less water compared to traditional cotton.
- Biodegradability: Many sustainable fabrics break down naturally, reducing landfill waste.
Examples
- Hemp: Hemp is one of the oldest cultivated plants, used for textiles for thousands of years. Modern innovations have brought hemp back into the spotlight due to its strength, low water usage, and minimal need for pesticides.
- Bamboo: Companies like Bamboo Textiles create soft, breathable fabrics from bamboo fibers. The bamboo plant grows quickly, requiring little water, and is highly renewable.
Case Study: Patagonia
Patagonia, known for its commitment to environmental sustainability, uses recycled polyester in many of its products. It also partners with textile companies to improve its use of sustainable materials. The company’s Recycled Wool Jacket is an example of how recycled materials can be used effectively in high-performance outdoor gear.
Textile Recycling and Waste Reduction

Overview
Textile waste is a major environmental issue. According to the EPA, the textile industry generates millions of tons of waste every year. To combat this, many companies are investing in textile recycling technologies to repurpose old garments into new products.
Benefits
- Reduced landfill waste: Recycling textiles prevents clothes from ending up in landfills, where they take years to decompose.
- Conserves resources: Recycling fabrics reduces the need for virgin materials like cotton and synthetic fibers, conserving resources.
- Energy savings: The recycling process uses less energy compared to producing new fabrics.
Examples
- Recycled Polyester: Brands like Nike and Adidas have incorporated recycled polyester in their products, turning waste plastics and textiles into new fabric. This reduces the environmental impact of both textile production and plastic waste.
- Secondhand Clothing: Online platforms like ThredUp and Poshmark facilitate the reuse and recycling of clothes, giving old garments a second life.
Case Study: H&M’s Garment Collecting Program
H&M has launched an in-store garment collection program to encourage customers to recycle their old clothes. The program offers discounts in exchange for used clothing, which is then either recycled into new fabrics or repurposed into other products, such as cleaning cloths or insulation materials.
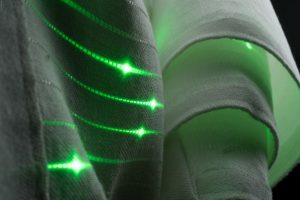
Smart Fabrics and Wearable Technology

Overview
Smart textiles or e-textiles incorporate electronics and sensors into the fabric itself. These textiles can interact with the wearer’s body or environment, providing a range of practical applications, from health monitoring to interactive fashion.
Benefits
- Health monitoring: Smart fabrics can track vital signs, such as heart rate, body temperature, and respiration rate.
- Increased comfort: Fabrics can adjust to the wearer’s body temperature, making them more comfortable in varying conditions.
- Enhanced functionality: Textiles can be used to control devices or provide feedback to users.
Examples
- Health Monitoring Clothing: The company Hexoskin produces smart shirts that track heart rate, breathing, and activity level, helping users monitor their health.
- Self-Healing Fabrics: Researchers have developed fabrics that can repair themselves when torn or damaged. This innovation is particularly useful for military or outdoor gear.
Case Study:
The Use of Smart Fabrics in Sportswear Under Armour has introduced performance-enhancing clothing, such as the UA Rush line, which includes minerals embedded in the fabric that absorb the body’s energy and reflect it back to help improve endurance and strength. This is an example of how smart textiles can boost athletic performance.
Circular Economy in Textiles
Overview
The circular economy model is designed to keep products and materials in use for as long as possible. In textiles, this means designing products that can be reused, recycled, or repurposed, rather than discarded after use.
Benefits
- Extended product life cycle: Garments are designed to last longer and can be repaired or refurbished, reducing the need for new clothes.
- Reduced environmental impact: By reusing materials, fewer resources are needed to produce new textiles.
- Economic opportunities: The circular economy creates new business models, such as repair shops and recycling facilities.
Examples
- Patagonia’s Worn Wear Program: Patagonia encourages customers to buy secondhand products and trade in their old gear. This reduces waste and gives clothing a longer lifespan.
- Levi’s: Levi’s promotes the concept of “buy better, wear longer,” offering repair services for customers’ jeans to prolong their life cycle.
Case Study: The Ellen MacArthur Foundation
The Ellen MacArthur Foundation has been advocating for a circular economy in textiles for several years. They have worked with major fashion brands like Burberry and H&M to implement circular design principles, focusing on product durability, recyclability, and waste reduction.
Digital Textile Printing
Overview
Digital textile printing allows for the direct printing of designs onto fabric, eliminating the need for traditional methods like screen printing. This technology is revolutionizing garment design and production, offering new possibilities for customization and rapid prototyping.
Benefits
- Customization: Designers can create highly personalized designs on demand, reducing overproduction.
- Waste reduction: Traditional printing methods generate excess dye and fabric waste. Digital printing is much more precise and efficient.
- Faster production: Digital printing reduces the time it takes to create samples and prototypes, speeding up the overall production process.
Examples
- Custom Printed Apparel: Brands like Spoonflower allow customers to design and print custom fabrics at home, making it easier to create one-of-a-kind garments.
- Nike’s Digital Print Technology: Nike uses digital printing to create customized, on-demand shoes, allowing customers to design their own footwear.
Case Study: Digital Fabric Printing at Fabric.co.uk
Fabric.co.uk has embraced digital textile printing, allowing customers to print their own designs on a variety of fabrics. This has opened up new opportunities for designers and manufacturers to create bespoke garments without the need for large-scale production runs.
Eco-Friendly Dyeing Technologies
Overview
Traditional textile dyeing processes consume large amounts of water and chemicals. New eco-friendly dyeing technologies aim to reduce water usage, eliminate harmful chemicals, and minimize environmental impact.
Benefits
- Water conservation: Waterless dyeing technologies can eliminate the need for vast amounts of water, which is particularly crucial in water-scarce regions.
- Reduced chemical use: Eco-friendly dyes are often plant-based, avoiding harmful chemicals that can pollute waterways.
- Faster drying times: Modern dyeing methods reduce the time fabrics need to dry, improving energy efficiency.
Examples
- Waterless Dyeing by DyeCoo: DyeCoo, a company based in the Netherlands, developed a waterless dyeing technology that uses supercritical CO2 instead of water to dye textiles. This process reduces water usage by up to 90%.
- Plant-Based Dyes: Companies like Stella McCartney use plant-based dyes, such as indigo and safflower, for their sustainable collections.
Case Study: Adidas’ Sustainable Dyeing Techniques
Adidas has partnered with the textile innovation company Colorifix to develop a more sustainable dyeing process. The method uses microorganisms to fix colors into the fabric, significantly reducing the environmental impact of traditional dyeing methods.
Performance Fabrics for Activewear
Overview
Activewear has become a significant segment in the textile industry, with performance fabrics designed for enhanced comfort, durability, and functionality. These textiles offer moisture-wicking properties, breathability, and UV protection, making them ideal for athletes and outdoor enthusiasts.
Benefits
- Moisture-wicking: Fabrics that wick away sweat keep the wearer dry and comfortable during intense physical activity.
- Breathability: Lightweight and breathable fabrics allow for air circulation, reducing overheating.
- UV protection: Some fabrics offer built-in protection against harmful UV rays.
Examples
- Nike Dri-FIT: Nike’s Dri-FIT technology is one of the most popular moisture-wicking fabrics used in athletic apparel. It draws moisture away from the skin and to the fabric’s surface, where it can evaporate.
- Lululemon’s Luon Fabric: Lululemon’s signature fabric is a blend of nylon and Lycra, offering excellent stretch, support, and comfort for activewear.
Case Study: Under Armour’s Performance Fabrics
Under Armour has built its brand around high-performance fabrics. The company’s HeatGear and ColdGear lines offer temperature-regulating properties, ensuring athletes stay comfortable in both hot and cold conditions.
Textile Innovations in Outdoor Gear
Overview
Outdoor apparel and gear are benefitting from advances in textile technology. Fabrics are being designed to provide better insulation, weather resistance, and durability in harsh conditions.
Benefits
- Enhanced weather resistance: Fabrics are engineered to be waterproof, windproof, and resistant to wear and tear.
- Lightweight and durable: Modern outdoor fabrics are lightweight yet strong, making them easier to carry and wear for extended periods.
- Temperature regulation: New materials help regulate body temperature, providing warmth without excessive bulk.
Examples
- Gore-Tex: This waterproof and breathable fabric is widely used in outdoor gear, ensuring that athletes and adventurers stay dry while remaining comfortable.
- The North Face’s ThermoBall: This lightweight insulation technology provides warmth without the bulk of traditional down.
Case Study: Arc’teryx and Advanced Fabrics
Arc’teryx, a high-end outdoor brand, uses advanced materials like GORE-TEX Pro and Coreloft to create durable, weather-resistant clothing. Their gear is popular among mountaineers, skiers, and other outdoor enthusiasts.
Recyclability of Fabrics and Product Lifecycle

Overview
Textile companies are increasingly focusing on designing products with the end-of-life stage in mind. Recyclability is becoming a key factor in the production of textiles, aiming to create closed-loop systems where garments can be recycled infinitely.
Benefits
- Waste reduction: Designing for recyclability helps minimize waste and the consumption of natural resources.
- Sustainability: Closed-loop recycling ensures that materials are reused, reducing the need for new raw materials.
- Product longevity: Textiles designed for recyclability are often more durable, extending the lifespan of the garment.
Examples
- Levi’s Water<Less: Levi’s uses innovative technologies to reduce water usage during the production of its jeans. Additionally, the company designs its garments to be easily recyclable at the end of their life.
Case Study: The North Face’s “Clothes the Loop”
The North Face encourages customers to recycle their old gear through its “Clothes the Loop” program. Clothes collected are repurposed into new products, such as insulation materials for jackets, extending the life cycle of textiles.
Technological Advances in Fabric Production
Overview
The textile production process has been revolutionized by technology. From 3D printing to automated weaving machines, modern innovations are making fabric production faster, more precise, and less wasteful.
Benefits
- Faster production: Automation and advanced manufacturing techniques reduce production times.
- Customization: Technologies like 3D printing enable the creation of custom fabrics and garments.
- Reduced waste: Automated systems are more efficient, minimizing fabric waste during production.
Examples
- 3D Printed Fabrics: Companies like Iris van Herpen are using 3D printing to create intricate and custom garments, pushing the boundaries of textile design.
- Automated Weaving Machines: Brands like Shima Seiki use advanced automated looms to create highly intricate designs with minimal waste.
Case Study: Adidas and 3D-Printed Shoes
Adidas has pioneered the use of 3D printing in footwear. The company’s Futurecraft 4D shoes are produced using a 3D-printed midsole, providing personalized comfort and reducing waste during production.












