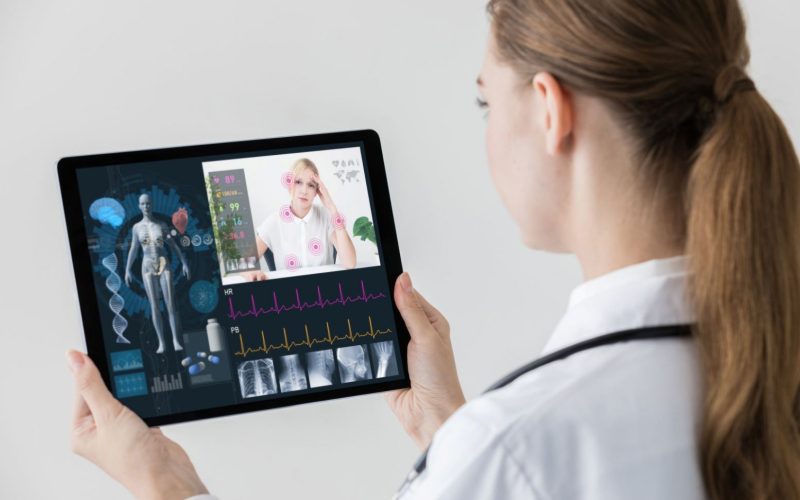
In recent years, telemedicine has emerged as a transformative force in healthcare, offering unprecedented opportunities for remote patient monitoring and care delivery. As we step into 2024, the landscape of telemedicine for cardiac patients is evolving rapidly, driven by technological advancements and an increasing emphasis on patient-centric care. This article explores the latest developments in telemedicine for cardiac care, highlighting innovations that promise to enhance patient outcomes and streamline healthcare delivery.

The Evolution of Telemedicine in Cardiac Care
Telemedicine, the use of digital communication technologies to deliver healthcare services remotely, has been a game-changer for cardiac care. Traditionally, cardiac patients required frequent visits to healthcare facilities for monitoring and follow-up consultations. However, telemedicine allows for continuous monitoring and timely interventions without the need for physical visits, thus offering convenience and reducing healthcare costs.
The COVID-19 pandemic accelerated the adoption of telemedicine, highlighting its potential in managing chronic conditions like heart disease. As we move into 2024, telemedicine is no longer seen as a temporary solution but as an integral component of cardiac care.
Key Innovations in 2024
Advanced Wearable Devices
Wearable technology has seen significant advancements, with new devices capable of monitoring a range of cardiac parameters in real-time. In 2024, these devices are more sophisticated, offering features such as continuous ECG monitoring, blood pressure tracking, and even early detection of arrhythmias. These wearables are integrated with telemedicine platforms, allowing healthcare providers to receive real-time data and make informed decisions about patient care.
AI-Driven Predictive Analytics
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is playing a crucial role in enhancing telemedicine for cardiac patients. AI-driven predictive analytics can analyze vast amounts of data collected from wearables and electronic health records to identify patterns and predict potential cardiac events. This proactive approach allows for early intervention, potentially preventing severe cardiac episodes and improving patient outcomes.
Personalized Treatment Plans
The integration of AI and machine learning in telemedicine platforms enables the creation of personalized treatment plans for cardiac patients. By analyzing individual patient data, these platforms can recommend specific lifestyle changes, medication adjustments, and other interventions tailored to the patient’s unique needs. This level of personalization enhances the effectiveness of cardiac care and improves patient adherence to treatment plans.
Virtual Cardiac Rehabilitation
Cardiac rehabilitation is a critical component of recovery for heart patients. In 2024, virtual cardiac rehabilitation programs are becoming more prevalent, offering patients the opportunity to participate in rehabilitation exercises from the comfort of their homes. These programs are designed to be interactive and engaging, using video conferencing and digital platforms to guide patients through exercises and monitor their progress. This approach not only improves accessibility but also encourages greater participation in rehabilitation programs.
Enhanced Patient-Provider Communication
Effective communication between patients and healthcare providers is essential for successful cardiac care. Telemedicine platforms in 2024 are equipped with advanced communication tools, including secure messaging, video consultations, and instant notifications. These tools facilitate timely communication, enabling patients to report symptoms, ask questions, and receive guidance without delay. Enhanced communication leads to better patient engagement and satisfaction.
Challenges and Considerations
While the advancements in telemedicine for cardiac care are promising, several challenges must be addressed to fully realize its potential.
Data Security and Privacy
The collection and transmission of sensitive health data raise concerns about data security and privacy. It is crucial for telemedicine platforms to implement robust security measures to protect patient information and comply with regulatory standards.

Access and Equity
Despite the growth of telemedicine, disparities in access to technology and internet connectivity persist. Ensuring equitable access to telemedicine services for all cardiac patients, regardless of their geographical location or socioeconomic status, remains a priority.
Integration with Traditional Care
Telemedicine should complement, not replace, traditional in-person care. Integrating telemedicine with existing healthcare systems and ensuring seamless transitions between virtual and in-person care are essential for comprehensive cardiac care.
The Future of Telemedicine in Cardiac Care
As we look to the future, the potential of telemedicine in cardiac care is vast. Continued advancements in technology, coupled with a focus on patient-centered care, will drive further innovations in this field. The integration of telemedicine with other emerging technologies, such as blockchain for secure data sharing and virtual reality for immersive patient education, holds promise for enhancing cardiac care delivery.
Moreover, the ongoing development of global standards and guidelines for telemedicine will facilitate its widespread adoption and ensure consistent quality of care across different regions.
Conclusion
The year 2024 marks a significant milestone in the evolution of telemedicine for cardiac patients. With advancements in wearable technology, AI-driven analytics, personalized treatment plans, virtual rehabilitation, and enhanced communication tools, telemedicine is poised to revolutionize cardiac care. However, addressing challenges related to data security, access, and integration with traditional care is essential to maximize its benefits.
As healthcare providers, patients, and policymakers continue to embrace telemedicine, the future of cardiac care looks promising, with the potential to improve patient outcomes, reduce healthcare costs, and enhance the overall quality of life for cardiac patients worldwide.