Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) is a significant public health issue, with over 138 million people affected in India as of 2023. This long-term condition involves a gradual loss of kidney function, which can lead to severe health complications.
The kidneys are essential organs responsible for filtering blood, removing waste and excess fluid, regulating blood pressure, maintaining electrolyte balance, and producing red blood cells. When kidney function declines, the body’s ability to perform these vital tasks diminishes, potentially resulting in kidney failure, a life-threatening condition.
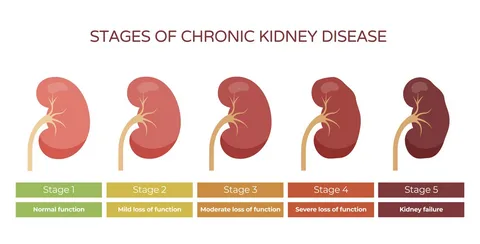
Common Symptoms of CKD
CKD is insidious in nature, often developing slowly over months or years. Early-stage symptoms may be subtle and go unnoticed until significant damage has occurred. As the disease progresses, waste products and toxins accumulate in the bloodstream, leading to various troubling symptoms.
In advanced stages of CKD, patients may experience:
- Nausea and Vomiting: Caused by the buildup of waste products in the blood.
- Loss of Appetite: Reduced interest in food due to illness.
- Fatigue: Persistent tiredness and lack of energy.
- Insomnia: Difficulty sleeping due to discomfort or other health issues.
- Hypertension: High blood pressure that may worsen over time.
- Shortness of Breath: Fluid buildup in the lungs or anemia can cause this symptom.
Recognizing these symptoms promptly can lead to early interventions that may slow the progression of the disease.
Causes of CKD
The causes of CKD vary widely and often involve multiple factors. The most common causes include:
- Diabetes: Both Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes can damage blood vessels in the kidneys, reducing their ability to filter waste effectively.
- Hypertension: Chronic high blood pressure can cause blood vessel damage in the kidneys, leading to a decline in function.
- Autoimmune Diseases: Conditions such as lupus or Sjogren syndrome can lead to kidney inflammation and damage.
- Obstructive Uropathy: An enlarged prostate or urinary retention can obstruct urine flow, leading to kidney damage.
- Infections: Recurrent urinary tract infections (UTIs) can contribute to kidney injury.
- Vesicoureteral Reflux: This condition causes urine to flow backward into the kidneys, potentially damaging them.
- Medications: Certain drugs, including lithium, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), and some antibiotics, can harm the kidneys, especially when taken long-term.
Understanding these risk factors is essential for prevention and early intervention.
Diagnosis of CKD
Diagnosing CKD typically involves a comprehensive assessment by healthcare professionals. Initial evaluations may include:
- Blood Tests: Measuring creatinine, urea, and electrolytes in the blood helps assess kidney function. The glomerular filtration rate (GFR) is a critical metric used to determine kidney health.
- Urine Tests: A urinalysis can reveal abnormalities, such as protein or blood, indicating kidney damage.
- Imaging Studies: Ultrasounds and CT scans visualize kidney structure and function, identifying any obstructions or abnormalities.
- Biopsy: In some cases, a kidney biopsy may be recommended to assess the extent of damage or determine specific underlying causes.
These diagnostic tests are crucial for developing appropriate treatment plans.
Conventional Treatment for CKD
The primary goal of CKD management is to slow disease progression and mitigate complications, as there is currently no cure. Standard treatment strategies include:
- Dietary Changes: A low-sodium diet is recommended, limiting intake to 2,000 mg per day to help manage blood pressure and reduce kidney strain.
- Blood Pressure Control: Medications such as angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors or angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs) are prescribed to maintain optimal blood pressure levels.
- Protein Management: Adopting a low-protein diet can reduce the kidneys’ workload, minimizing waste production.
- Dialysis: For those with end-stage renal disease, dialysis becomes necessary. There are two types: hemodialysis, which filters blood outside the body, and peritoneal dialysis, which uses the lining of the abdomen to filter waste.
- Kidney Transplantation: A surgical option for eligible patients involves receiving a healthy kidney from a donor.
Note: While these treatments can improve quality of life and longevity, they do not guarantee a complete cure, and complications may arise, especially in transplant cases, where rejection is a significant concern.
Stem Cell Treatment for Chronic Kidney Disease
Stem Cell Treatment for CKD presents a promising alternative that offers potential benefits beyond conventional therapies. Stem cells have unique regenerative properties and can differentiate into various cell types, making them a compelling option for repairing kidney tissue.
How Stem Cell Therapy Works in CKD Patients
The mechanisms through which stem cells can aid CKD treatment include:
- Regeneration of Kidney Cells: Stem cells can evolve into renal tubular cells and other kidney cell types, aiding in the repair of damaged nephrons.
- Anti-Inflammation: Stem cells can secrete anti-inflammatory agents that help alleviate inflammation in the kidneys.
- Immunomodulation: Stem cells have a unique ability to modulate the immune response, potentially reducing the risk of rejection when used alongside other treatments.
- Paracrine Effects: These cells release growth factors and cytokines that promote tissue repair and enhance cellular communication, ultimately improving kidney function.
Clinical Application and Research
Preclinical and clinical studies provide promising evidence on the effectiveness of stem cell therapy for CKD:
- Acute Kidney Injury (AKI): Research indicates that stem cells can stimulate tissue repair and reduce inflammation, demonstrating improved kidney function.
- Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD): Some studies show that stem cells can slow disease progression and stabilize renal function, making them a viable treatment option.
- Kidney Transplantation: Incorporating stem cells during kidney transplants may help decrease immune rejection and enhance long-term graft survival rates.
Advantages of Stem Cell Therapy for Renal Disorders in India
- Improvement in Kidney Function: Patients may experience a restoration of kidney abilities.
- Reduction in Inflammation and Fibrosis: This can slow the progression of kidney damage.
- Enhanced Quality of Life: Patients often report feeling better overall, with improved emotional well-being.
Challenges and Limitations
While stem cell treatment holds great promise, several challenges must be addressed:
- Regulatory Hurdles: Navigating the complex approval processes for new therapies can delay patient access.
- Cost and Accessibility: The high cost of stem cell therapies may limit access for many patients.
- Research Gaps: Continued investigation is necessary to refine techniques and validate the efficacy of stem cell treatments for CKD.
Conclusion
Chronic Kidney Disease is a significant health challenge affecting millions worldwide. While traditional treatments focus on managing symptoms and slowing progression, innovative approaches like stem cell therapy are emerging.
These therapies offer hope for regeneration, reduced inflammation, and improved quality of life. As research advances, stem cell treatments have the potential to revolutionize CKD care, paving the way for new, effective strategies to combat this life-altering condition.
By combining traditional and innovative treatment modalities, patients can look forward to a brighter future in managing CKD, emphasizing the need for continued awareness and research in this critical area of health.