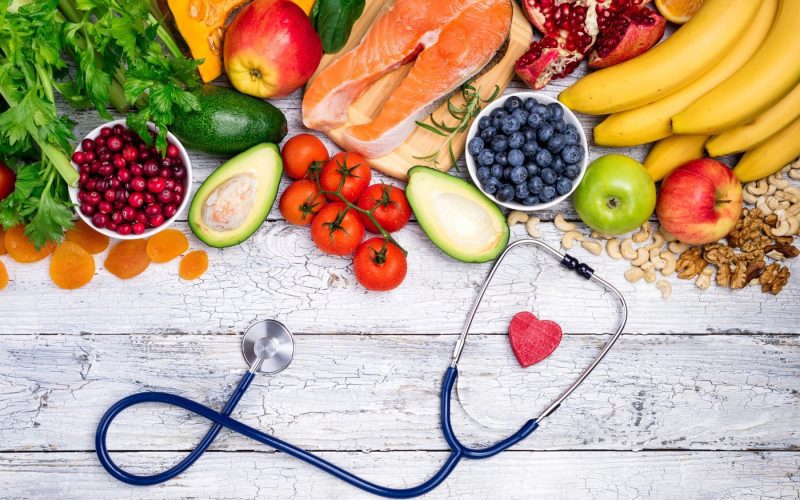
In recent years, the relationship between nutrition and chronic diseases has garnered significant attention from both the scientific community and the general public. Chronic diseases, such as heart disease, diabetes, and certain cancers, are among the leading causes of morbidity and mortality worldwide. Understanding the role of nutrition in preventing these conditions is crucial for promoting public health and enhancing the quality of life. This article delves into the intricate connection between nutrition and chronic diseases, highlighting the importance of a balanced diet in disease prevention.
The Link Between Nutrition and Chronic Diseases
Chronic diseases are long-lasting conditions that often progress slowly over time. They can result from a combination of genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors. Among these, nutrition stands out as a modifiable risk factor that can significantly influence the onset and progression of chronic diseases. A poor diet, characterized by high intake of processed foods, sugars, and unhealthy fats, can lead to obesity, inflammation, and metabolic imbalances, which are precursors to many chronic conditions.
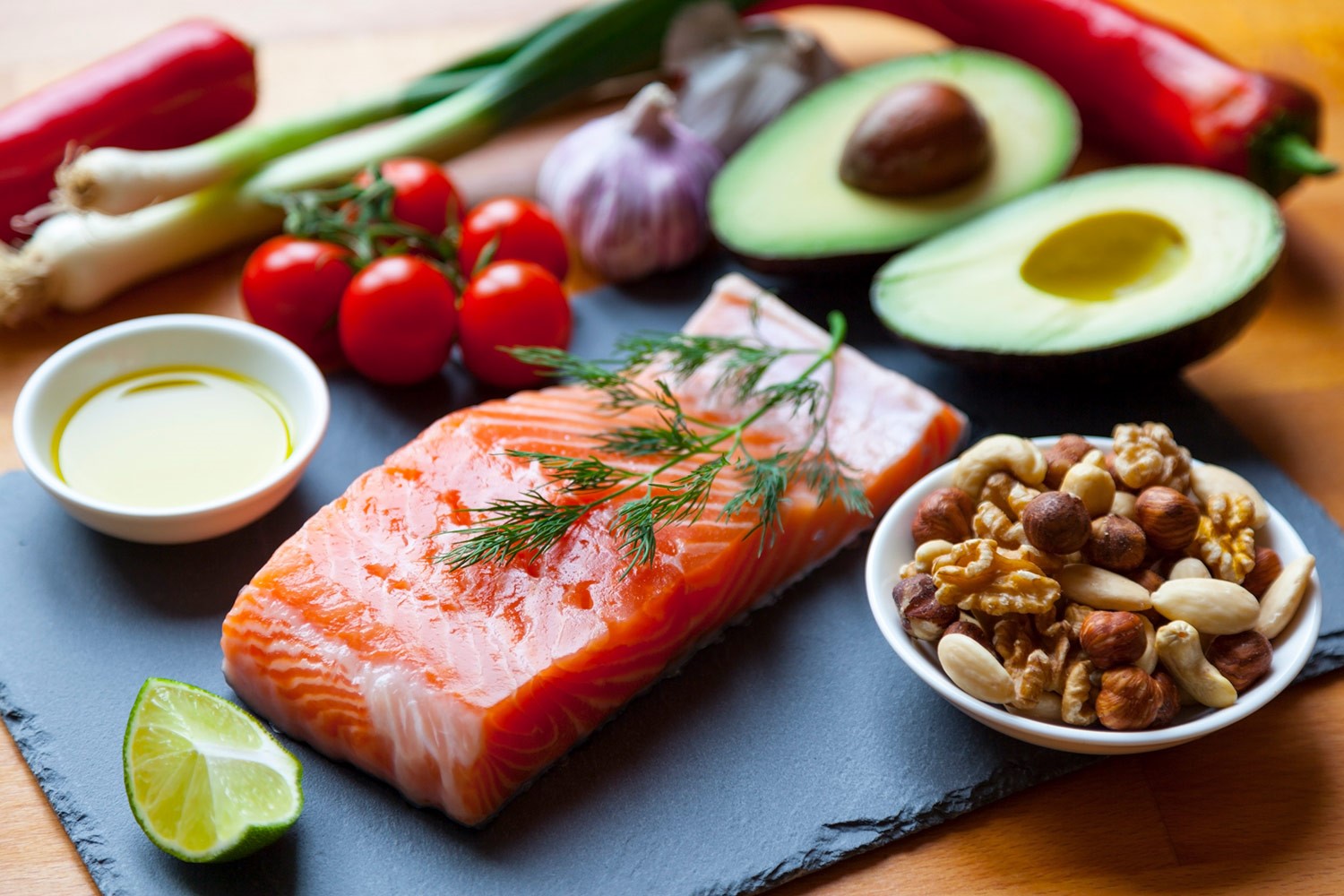

Heart Disease
Heart disease is the leading cause of death globally, and nutrition plays a pivotal role in its prevention. Diets high in saturated fats, trans fats, and cholesterol can lead to the development of atherosclerosis, a condition characterized by the buildup of plaque in the arteries. This can result in heart attacks and strokes. Conversely, a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and healthy fats (such as those found in olive oil and fatty fish) can help reduce the risk of heart disease. These foods are high in antioxidants, fiber, and essential nutrients that promote cardiovascular health.
Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes is another chronic disease that is closely linked to diet. Consuming excessive amounts of refined sugars and carbohydrates can lead to insulin resistance, a condition where the body’s cells do not respond effectively to insulin. This can result in elevated blood sugar levels and, eventually, type 2 diabetes. A balanced diet that includes a variety of whole foods, such as lean proteins, whole grains, and non-starchy vegetables, can help maintain stable blood sugar levels and reduce the risk of developing diabetes.
Cancer
Certain types of cancer, such as colorectal, breast, and prostate cancer, have been associated with dietary factors. Diets high in red and processed meats, as well as low in fruits and vegetables, have been linked to an increased risk of cancer. On the other hand, a diet rich in plant-based foods, which are high in fiber, vitamins, and phytochemicals, can help protect against cancer. These compounds have been shown to have anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties, which can help prevent the cellular damage that leads to cancer.
Obesity
Obesity is a major risk factor for many chronic diseases, including heart disease, diabetes, and certain cancers. It is often the result of an imbalance between calorie intake and energy expenditure. Consuming high-calorie, nutrient-poor foods can lead to weight gain and obesity. A diet that emphasizes nutrient-dense foods, such as fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains, can help maintain a healthy weight and reduce the risk of obesity-related chronic diseases.
The Role of Specific Nutrients
Certain nutrients have been identified as particularly beneficial in preventing chronic diseases. For example:
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Found in fatty fish, flaxseeds, and walnuts, omega-3 fatty acids have anti-inflammatory properties and can help reduce the risk of heart disease.
- Fiber: High-fiber foods, such as fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, can help regulate blood sugar levels, lower cholesterol, and promote digestive health.
- Antioxidants: Foods rich in antioxidants, such as berries, nuts, and leafy greens, can help protect against oxidative stress and inflammation, which are linked to chronic diseases.
- Vitamins and Minerals: Adequate intake of vitamins and minerals, such as vitamin D, calcium, and potassium, is essential for maintaining overall health and preventing chronic conditions.

The Mediterranean Diet: A Model for Chronic Disease Prevention
The Mediterranean diet is often cited as a prime example of a healthy eating pattern that can help prevent chronic diseases. This diet emphasizes the consumption of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, nuts, and olive oil, with moderate intake of fish and poultry and limited intake of red meat and sweets. Numerous studies have shown that adherence to the Mediterranean diet is associated with a lower risk of heart disease, diabetes, and certain cancers. The diet’s emphasis on plant-based foods, healthy fats, and lean proteins makes it an effective strategy for chronic disease prevention.
Practical Tips for a Healthy Diet
Adopting a healthy diet to prevent chronic diseases does not have to be complicated. Here are some practical tips to help you get started:
- Eat a Variety of Foods: Include a wide range of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats in your diet to ensure you get all the essential nutrients.
- Limit Processed Foods: Reduce your intake of processed and packaged foods, which are often high in unhealthy fats, sugars, and sodium.
- Choose Whole Foods: Opt for whole foods over refined and processed options. For example, choose whole grains like brown rice and quinoa instead of white rice and pasta.
- Watch Your Portions: Be mindful of portion sizes to avoid overeating and maintain a healthy weight.
- Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water throughout the day to stay hydrated and support overall health.
- Plan Your Meals: Plan your meals and snacks ahead of time to ensure you have healthy options available and avoid impulsive, unhealthy choices.
Conclusion
The role of nutrition in preventing chronic diseases cannot be overstated. A balanced diet that emphasizes whole, nutrient-dense foods can help reduce the risk of heart disease, diabetes, cancer, and obesity. By making informed dietary choices and adopting healthy eating patterns, individuals can take proactive steps to protect their health and enhance their quality of life. As research continues to uncover the complex relationship between nutrition and chronic diseases, it becomes increasingly clear that what we eat plays a crucial role in our long-term health and well-being.