The Future of Renewable Energy Technology
Renewable energy is no longer just an option—it is a necessity. With increasing global energy demands and the urgent need to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, renewable energy technologies are advancing rapidly to provide sustainable, reliable, and affordable power. These innovations are reshaping the energy landscape, offering solutions that are not only environmentally friendly but also economically viable.
In this article, we explore the cutting-edge advancements in renewable energy technologies, their benefits, real-world examples, and the transformative potential they hold for the future.
1. Advancements in Solar Energy

Perovskite Solar Cells: A Solar Revolution
Perovskite solar cells are at the forefront of solar energy advancements. Unlike traditional silicon-based cells, perovskites are cheaper to produce, highly efficient, and versatile. These materials can be manufactured using simpler methods like inkjet printing and can even be applied to flexible surfaces, opening up new possibilities for integrating solar power into everyday life.
Recent advancements have pushed the efficiency of perovskite solar cells beyond 30%, making them competitive with, and in some cases superior to, traditional photovoltaic cells.
Benefits:
- Cost-Effective: Lower manufacturing costs reduce barriers to entry for consumers and industries.
- Lightweight and Flexible: Ideal for applications in wearables, vehicles, and building-integrated photovoltaics (BIPV).
Case Study: Oxford PV, a leader in perovskite technology, partnered with commercial manufacturers to develop tandem solar cells that combine silicon and perovskite layers, achieving unprecedented efficiency and market viability.
Bifacial Solar Panels: Capturing More Sunlight
Bifacial solar panels represent a significant leap in efficiency by capturing sunlight on both sides. They are especially effective in reflective environments, such as snow-covered or sandy regions, where light bounces back to the underside of the panel.
Example: In Chile’s Atacama Desert, a solar farm utilizing bifacial panels reported a 20% increase in energy output compared to traditional panels, showcasing their potential to maximize energy yields in suitable climates.
Benefits:
- Higher Output: Generates more electricity with the same footprint.
- Durability: Designed to withstand harsh environmental conditions.
Solar Paint: Future Integration
Imagine painting your house and generating electricity. Solar paint, still in development, contains photovoltaic particles that convert sunlight into electricity. While it is not yet commercially available, its potential applications could revolutionize urban energy systems.
Future Vision: Buildings could become self-sustaining power generators, significantly reducing reliance on external grids.
2. Wind Energy Innovations
Floating Offshore Wind Farms
Floating offshore wind farms are unlocking wind energy potential in deep waters where traditional fixed-bottom turbines are impractical. Floating platforms tether turbines to the seabed, allowing them to operate in areas with stronger, more consistent winds.
Example: Hywind Scotland, the first floating wind farm, demonstrated higher capacity factors than traditional offshore turbines, generating enough energy to power over 36,000 homes annually.
Benefits:
- Access to Deeper Waters: Exploits untapped wind resources.
- Minimal Land Use: Keeps valuable coastal areas free for other uses.
Vertical Axis Wind Turbines (VAWTs)
Compact and efficient, VAWTs are designed for urban environments where wind patterns are unpredictable. Unlike traditional horizontal-axis turbines, they can generate power from any direction, making them ideal for cities.
Case Study: The Éole urban project in Paris installed VAWTs near landmarks like the Eiffel Tower to demonstrate their potential for urban renewable energy.
Benefits:
- Space-Saving: Ideal for crowded urban landscapes.
- Low Noise: Minimizes disturbance in residential areas.
Recyclable Wind Turbine Blades

Traditional turbine blades are challenging to recycle due to their composite materials. New technologies are developing fully recyclable blades, addressing one of the industry’s significant sustainability challenges.
Case Study: Vestas, a leading wind turbine manufacturer, announced fully recyclable blade technology in 2023, paving the way for a circular economy in wind energy.
3. Energy Storage Breakthroughs
Energy storage is critical for the reliable integration of renewable energy. Recent breakthroughs are making energy storage more efficient and accessible.
Solid-State Batteries
Solid-state batteries are a significant improvement over lithium-ion batteries. They use solid electrolytes instead of liquid ones, offering higher energy density, longer lifespans, and enhanced safety.
Case Study: Toyota’s development of solid-state batteries for electric vehicles demonstrates their transformative potential for both renewable energy storage and transportation.
Benefits:
- Longer Durability: Ideal for grid-scale applications.
- Safer Operation: Reduced risk of overheating or fires.
Grid-Scale Flow Batteries
Flow batteries store energy in liquid electrolytes, making them suitable for large-scale applications. Unlike traditional batteries, they can store energy for days or even weeks.
Example: The Dalian Flow Battery Energy Storage Project in China stores 400MWh of energy, helping stabilize the grid during peak demands and renewable intermittency.
Hydrogen as a Storage Medium
Green hydrogen, produced using renewable energy, acts as a versatile storage medium. It can be stored indefinitely and used in industries, transportation, and power generation.
Case Study: Germany’s “Hydrogen Valleys” are integrating green hydrogen with renewables, showcasing how hydrogen can support a carbon-neutral economy.
4. Artificial Intelligence and Smart Grids

AI and IoT technologies are transforming how renewable energy is managed and distributed.
Predictive Maintenance
AI systems analyze data from renewable energy infrastructure to predict potential failures, reducing downtime and maintenance costs.
Example: GE Renewable Energy uses AI to monitor wind turbines, improving their operational efficiency by 15%.
Smart Grids
Smart grids balance energy supply and demand in real-time, optimizing renewable energy usage and minimizing waste.
Case Study: California’s smart grid initiative has reduced blackouts by 30% and increased renewable energy integration.
Benefits:
- Enhanced Efficiency: Reduces energy loss during transmission.
- Consumer Control: Smart meters allow households to manage energy usage more effectively.
5. Emerging Renewable Technologies
Wave and Tidal Energy
Marine energy technologies, including wave and tidal systems, offer consistent and predictable energy generation.
Case Study: The MeyGen tidal energy project in Scotland has supplied enough electricity to power 4,000 homes annually, highlighting its reliability.
Enhanced Geothermal Systems (EGS)
EGS technology uses advanced drilling techniques to extract heat from deep within the Earth, making geothermal energy viable in areas without natural hot springs.
Example: Iceland’s deep-drilling project has achieved record-breaking geothermal energy output, powering over 90% of its homes sustainably.
6. Decentralized Energy Systems
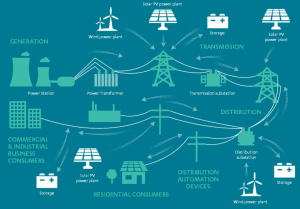
Microgrids
Microgrids are localized energy systems that enhance resilience and reduce reliance on centralized grids. They are particularly valuable in remote areas and disaster-prone regions.
Case Study: Puerto Rico adopted microgrids after Hurricane Maria, ensuring energy stability during subsequent hurricanes.
Peer-to-Peer Energy Sharing
Blockchain technology allows communities to trade excess energy directly, fostering energy independence.
Example: The Brooklyn Microgrid project enables residents to buy and sell solar energy within their community.
7. The Future Outlook
Fusion Energy
Fusion energy, often considered the “holy grail” of energy, offers the potential for limitless, clean power. While still in experimental stages, breakthroughs like ITER’s record plasma containment in 2023 signal significant progress.
Space-Based Solar Power (SBSP)
SBSP systems collect solar energy in space and transmit it to Earth via microwaves. This concept could revolutionize energy generation by bypassing the limitations of weather and daylight.
Conclusion
The future of renewable energy technology is both promising and transformative. From cutting-edge solar cells and offshore wind farms to AI-driven smart grids and hydrogen storage, these advancements promise a cleaner, more sustainable world. By investing in these innovations today, we are laying the foundation for a brighter, greener tomorrow.












