Introduction
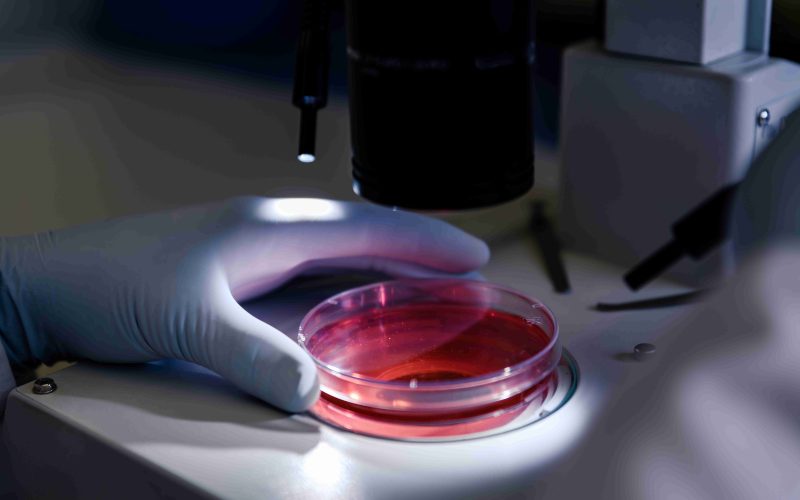
Human biospecimens biological samples such as blood, tissue, and saliva—are central to the development of new medical treatments and therapies. They are crucial for clinical trials in the pharmaceutical industry, allowing researchers to better understand diseases, track responses to treatments, and identify potential drug targets. But how do human biospecimens influence the process of clinical trials, and why are they so essential in the pharmaceutical industry?
In this article, we will explore the significant role human biospecimens play in clinical trials, how they are used to advance drug development, and the ethical considerations that come with their use. Understanding their impact can help patients, researchers, and the general public appreciate how biospecimens contribute to the future of healthcare.
What Are Human Biospecimens?
Human biospecimens are biological materials derived from human bodies. These include a wide range of samples like:
- Blood: Used to test for diseases, monitor treatment responses, and study biomarkers.
- Tissue: Sourced from biopsies, helping researchers understand the genetic and molecular basis of diseases.
- Saliva and Urine: Non-invasive samples that can provide important information on disease markers.
- Cell Lines: Cells that can be cultured in a lab and used for drug testing.
These biospecimens are critical tools in medical research, especially when it comes to clinical trials. By examining these samples, researchers can observe how different individuals or groups respond to certain treatments, allowing them to refine drugs and therapies for better effectiveness.
The Role of Biospecimens in Clinical Trials
Clinical trials are designed to test new treatments in a controlled, scientific manner. Human biospecimens play a vital role in many aspects of clinical trials, particularly in the early phases of drug development. Here’s how they help:
1. Understanding Disease Mechanisms
Biospecimens provide insight into the molecular and genetic foundations of diseases. For example, by analyzing blood samples from cancer patients, researchers can identify the genetic mutations that drive tumor growth. This information helps scientists develop targeted therapies that specifically attack those mutations. As a result, the treatment is more effective and causes fewer side effects.
2. Personalized Medicine
One of the most significant trends in modern medicine is personalized medicine, which tailors treatment to individual patients based on their unique genetic makeup. Human biospecimens are central to this approach. For example, analyzing a patient’s blood sample can reveal how their body metabolizes certain drugs, helping doctors select the most effective treatment for that individual.
In clinical trials, this approach helps identify which treatments work best for specific subgroups of patients, making trials more accurate and efficient. By using biospecimens to assess how different populations respond to treatments, researchers can develop drugs that are safer and more effective for everyone.
3. Monitoring Treatment Responses
Biospecimens are used throughout clinical trials to monitor how participants are responding to the drug being tested. For example, blood tests can show how a drug is affecting various biomarkers, while tissue samples can track any changes in disease progression. By collecting regular biospecimen samples, researchers can determine if the drug is working as expected or if adjustments are needed to improve its effectiveness.
4. Identifying Adverse Reactions
Not all drugs work the same way for every person. Some may cause adverse reactions or side effects. Through biospecimens, researchers can identify potential risks early in the clinical trial process. Blood tests, for example, can measure liver function, kidney function, or immune system responses, allowing researchers to spot any negative side effects that could harm the patient. This early detection is crucial to ensure that drugs are safe before they are widely distributed.
The Advantages of Using Human Biospecimens in Clinical Trials
There are several benefits to using human biospecimens in clinical trials:
1. Improved Accuracy in Research
Human biospecimens provide real-world data that is much more accurate than lab-grown cells or animal models. Since they come directly from people, they better represent how the drug will perform in human bodies. This leads to more reliable trial results and better predictions for how the drug will behave once it reaches the market.
2. Faster Drug Development
By leveraging biospecimens, researchers can speed up the process of identifying the most promising drugs. For example, they can analyze tissue samples from trial participants to identify genetic markers that predict how a person will respond to treatment. This allows researchers to narrow down the most effective treatment options more quickly, which ultimately reduces the time it takes to bring a new drug to market.
3. Increased Focus on Specific Diseases
Biospecimens also allow researchers to focus on specific diseases, particularly those that are rare or difficult to treat. For example, analyzing tumor biopsies in cancer clinical trials helps scientists better understand the behavior of different types of cancer and how they respond to various drugs. This leads to better-targeted therapies and greater advancements in treatments for specific conditions.
Ethical Considerations in Using Human Biospecimens
While human biospecimens offer immense value in clinical trials, their use also raises important ethical questions. Researchers must handle biospecimens with the utmost respect for individuals’ privacy and autonomy. Here are some key ethical considerations:
1. Informed Consent
Before any biospecimen is collected, the individual providing it must give informed consent. This means they fully understand how their sample will be used, including potential risks and benefits. Participants must also have the option to withdraw their consent at any time during the trial.
2. Privacy and Confidentiality
Biospecimens often contain sensitive information about a person’s health and genetic makeup. Researchers must ensure that all data is kept confidential and that participants’ identities are protected. Strict guidelines govern the sharing and storage of biospecimens to maintain privacy.
3. Equitable Access to Benefits
Another consideration is ensuring that the benefits of research are shared fairly. Individuals providing biospecimens must be assured that the results from the research will be used to benefit public health, rather than solely the interests of pharmaceutical companies. It’s also important to ensure that underrepresented populations are included in research, so that the benefits of clinical trials are accessible to everyone.
Conclusion
Human biospecimens play an essential role in the success of clinical trials and the pharmaceutical industry. They provide critical insights into disease mechanisms, treatment responses, and potential drug safety. The ability to personalize treatments, speed up drug development, and focus on specific diseases has revolutionized modern medicine. However, it is vital that researchers handle biospecimens ethically, ensuring informed consent, privacy, and equitable access to the benefits of research.
As we continue to rely on biospecimens for clinical trials, their importance will only grow, enabling the development of safer, more effective therapies. For the pharmaceutical industry, the thoughtful use of human biospecimens represents not just a scientific advancement, but also an opportunity to improve healthcare outcomes on a global scale.