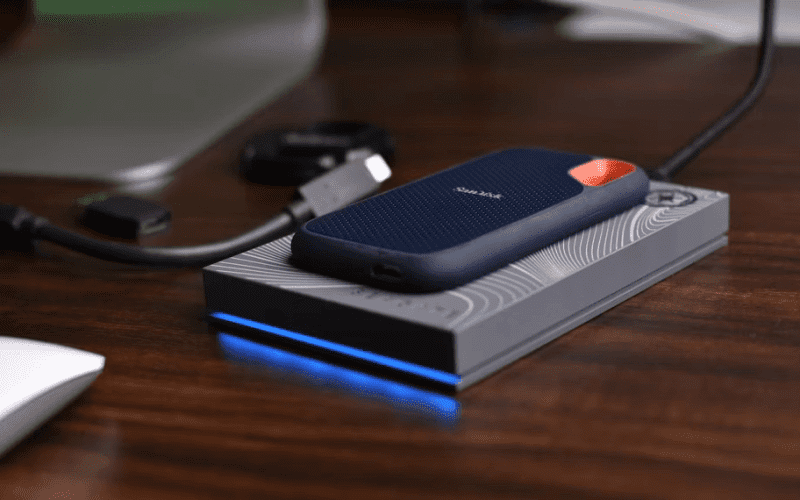
Introduction: eMMC vs. SSD
Digital storage solutions have evolved significantly, and the transition from HDDs to SSDs is the latest trend. However, with the market flooded with various types of SSDs, the decision-making process can be overwhelming. While SSDs are favored over HDDs, eMMC storage remains relevant and is often found alongside SSDs. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll help you navigate the choice between eMMC and SSDs for your PC or laptop.
Understanding eMMC Storage
Embedded MultMediaCard (eMMC): Unveiling the Basics
eMMC stands as an embedded iteration of MMC storage, a precursor to the widely used Secure Digital (SD) storage. Unlike traditional SD or microSD cards, eMMC chips are soldered directly onto the motherboard. This embedded design translates into improved performance and affordability. Powering eMMC storage is NAND flash memory, the same technology found in USB drives, memory cards, and SSDs.
eMMC: Ideal for Budget-Friendly Devices
The allure of eMMC storage lies in its cost-effectiveness, making it a favored choice for budget devices. Manufacturers catering to the lower price bracket often opt for eMMC storage due to its economical nature. However, the trade-off is its limited capacity, which suits devices with lower storage demands.
The World of SSD Storage
Solid State Drives (SSDs): A Swift Overview
While we’ve delved into SSDs extensively, let’s recap briefly. SSDs utilize NAND flash memory to efficiently read, write, and store data. Equipped with a controller, SSDs manage data and seamlessly interact with computers during read and write operations. They come in various shapes and sizes, each with its own underlying technology. QLC and TLC SSDs, distinguished by speed differences, are popular variants. Understanding SSD types, such as NVMe, SATA, and M.2, can further simplify your decision-making process.

Why SSDs Shine
Modern computers widely embrace SSDs due to their superiority over HDDs in regular use cases. The advantages extend to data transfer speed, durability, and overall performance, providing a comprehensive solution for storage needs.
eMMC vs. SSD: A Deep Dive into Differences
Speed: SSDs Triumph
SSDs, boasting multiple NAND gates, outpace eMMC storage in speed. While eMMC drives achieve data transfer speeds of around 400MB/s, SSDs can reach up to 3,500MB/s (PCIe 3.0) or even double with PCIe 4.0. Notably, SSDs offer faster data write speeds compared to eMMC drives.
Capacity: SSDs Secure Victory
eMMC storage predominantly occupies the 32GB to 256GB range, with limited options beyond. In contrast, SSDs span from 128GB to multiple terabytes, catering to devices requiring substantial storage.
Price and Availability: Budget vs. Versatility
SSDs exhibit a broader price range, influenced by capacity, technology, and form factor. eMMC storage leans towards budget-friendliness, with modules costing as low as $6-$11. While SSDs demand a higher upfront investment, they ensure prolonged convenience and expandability.
Selecting the Perfect Fit
Use Cases: Tailoring Your Choice
SSDs excel in scenarios demanding permanent and substantial storage, encompassing computers and consoles. On the other hand, eMMC storage suits budget devices and temporary storage solutions, like USB drives. While eMMC modules are challenging to replace, investing in SSDs promises long-term reliability and scalability.
Making the Right Investment
Choosing the apt storage solution is pivotal for seamless usage. Opting for eMMC might save money initially but could lead to storage limitations. In contrast, investing in SSDs ensures a smoother experience, sparing you from frequent storage woes. The initial cost of SSDs pays off with extended storage options and enhanced performance.
Informed Decisions for Storage Bliss
By delving into the differences between eMMC and SSDs, you’re better equipped to make an informed decision tailored to your device and usage requirements. Whether you prioritize affordability or seek unparalleled performance, understanding the nuances empowers you to choose the perfect storage companion.
About the Author
Yadullah Abidi is a tech enthusiast and writer with a passion for demystifying complex topics. With years of experience in the tech industry, Yadullah brings a unique perspective to deciphering the intricacies of digital storage. His insights guide readers towards making informed decisions for their technological needs.
Informative Table: eMMC vs. SSD Comparison
| Aspect | eMMC Storage | SSD Storage |
|---|---|---|
| Performance | Moderate speed (up to 400MB/s) | High speed (up to 3,500MB/s or more) |
| Capacity | Up to 512GB | From 128GB to multiple terabytes |
| Price Range | Budget-friendly | Variable, influenced by capacity |
| Use Cases | Budget devices, temporary storage | Computers, consoles, permanent storage |
| Longevity | Limited lifespan | High durability and longevity |
Comparative Table: QLC, TLC, NVMe, SATA, and M.2 SSDs
| SSD Type | Speed | Use Cases |
|---|---|---|
| QLC SSDs | Slower | Budget-friendly, casual use |
| TLC SSDs | Faster | Everyday use, gaming, multimedia |
| NVMe SSDs | Fast | High-performance applications |
| SATA SSDs | Fast | General-purpose, cost-effective |
| M.2 SSDs | Variable | Compact form factor, high-speed |












