Introduction
Chikungunya is a viral infection primarily transmitted to humans through the bites of infected mosquitoes, particularly Aedes mosquitoes. While the virus is not typically fatal, it can cause debilitating symptoms and prolonged joint pain. Understanding the intricacies of chikungunya, from its symptoms to diagnosis and treatment, is crucial for effective management.
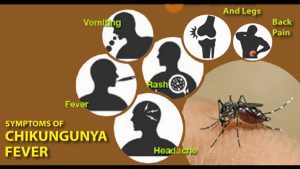
Symptoms of Chikungunya Virus
Chikungunya symptoms usually manifest 3–7 days after being bitten by an infected mosquito. The primary indicators include:
- Fever: One of the hallmark symptoms of chikungunya is a sudden onset of fever. The temperature may spike rapidly, causing discomfort and fatigue.
- Joint Pain: Joint pain, often severe and debilitating, is a characteristic feature of chikungunya. It commonly affects the wrists, ankles, and small joints of the hands and feet. The pain can persist for an extended period, sometimes lasting for months.
- Headache: Many individuals with chikungunya experience persistent headaches, adding to the overall discomfort and malaise associated with the infection.
- Muscle Pain: Muscular pain is another common symptom. The muscles may ache and feel tender, contributing to the overall sense of unease.
- Joint Swelling: Swelling of the joints, particularly in the affected areas, can occur. This can further limit mobility and contribute to the overall impact on daily activities.
- Rash: Some individuals may develop a rash, characterized by red spots or bumps on the skin. While not universal, the rash adds to the diverse range of symptoms associated with chikungunya.
- At-Risk Populations: Certain groups are more vulnerable to severe manifestations of the disease. Newborns infected around the time of birth, older adults (≥65 years), and individuals with underlying medical conditions like high blood pressure, diabetes, or heart disease are at an increased risk of experiencing more severe symptoms.
- Recovery: While most patients begin to feel better within a week, the lingering joint pain can pose challenges. For some individuals, this symptom may persist for an extended period, affecting their quality of life.
- Rare Fatalities: It’s important to note that death from chikungunya is rare. However, the impact on daily life can be substantial, especially for those who experience prolonged joint pain.
Diagnosing
If you find yourself in an area where chikungunya is prevalent and experience the described symptoms, it’s crucial to seek medical attention promptly. Diagnosis involves several key steps:
- Healthcare Provider Consultation: Schedule a visit to your healthcare provider and provide detailed information about when and where you traveled. This information is crucial for assessing potential exposure to the chikungunya virus.
- Blood Tests: To confirm the presence of the chikungunya virus or rule out similar infections like dengue and Zika, your healthcare provider may order blood tests. These tests help in identifying the specific virus causing the symptoms, guiding appropriate treatment measures.
- Healthcare Provider Resources: For healthcare providers, there are resources available to aid in testing and diagnosing chikungunya. These resources contribute to a more accurate and timely diagnosis.
Treatment Approaches for Chikungunya
As of now, there is no specific antiviral medication available for treating chikungunya. However, there are supportive measures that can help manage symptoms and promote recovery:
- Rest and Fluids: Adequate rest and hydration are essential components of chikungunya management. They help the body combat the infection and cope with the associated symptoms.
- Pain Medications: Over-the-counter pain medications, such as acetaminophen (Tylenol®) or paracetamol, can be used to reduce fever and alleviate joint and muscle pain. It’s crucial to avoid aspirin and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) until dengue can be ruled out to prevent the risk of bleeding.
- Preventing Mosquito Bites: During the initial week of illness, chikungunya virus can be present in the blood, allowing mosquitoes to become carriers. Treatment for other health problems Preventing mosquito bites during this period is vital to curbing the spread of the virus. This involves using mosquito repellents, wearing long sleeves and pants, and staying indoors during peak mosquito activity times.

Chikungunya, Dengue, and Zika
To provide a clearer understanding, here’s a comparative table highlighting key differences between chikungunya, dengue, and Zika:
| Criteria | Chikungunya | Dengue | Zika |
|---|---|---|---|
| Onset of Symptoms | 3–7 days after mosquito bite | 4–10 days after infection | 3–14 days after infection |
| Common Symptoms | Fever, joint pain, headache | High fever, severe headache, | Mild fever, rash, joint pain |
| pain behind the eyes | |||
| Treatment | Supportive care, pain meds | Supportive care, fluid | Supportive care, rest |
| replacement, pain relief | |||
| Prevention | Avoid mosquito bites during | Avoid mosquito bites during | Avoid mosquito bites during |
| the first week of illness | illness | illness |
Conclusion
In conclusion, chikungunya is a viral infection with distinct symptoms that can significantly impact an individual’s well-being. Understanding the symptoms, seeking timely medical attention, and adopting preventive measures are crucial aspects of managing the disease. The comparative table further aids in distinguishing chikungunya from related viruses, contributing to better awareness and preparedness. By staying informed and taking appropriate precautions, individuals can navigate the complexities of chikungunya more effectively.












