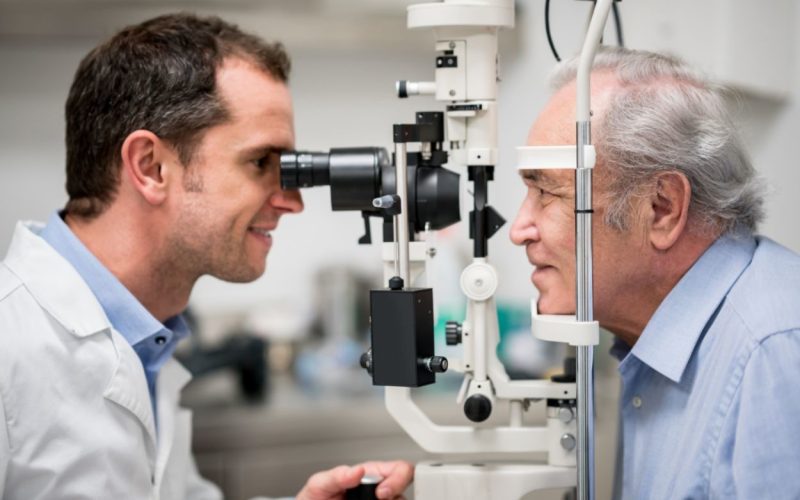
Vision is one of the most vital senses, enabling us to navigate and understand the world around us. Over the years, the field of ophthalmology has made significant strides, revolutionizing vision care and improving quality of life for millions. This article delves into the latest advances in ophthalmology and how they are transforming vision care.
The Evolution of Ophthalmology
Ophthalmology, the branch of medicine that deals with the diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of eye diseases, has a rich history dating back to ancient civilizations. From rudimentary techniques in ancient Egypt to the sophisticated procedures of today, the field has undergone tremendous evolution. Modern ophthalmology leverages cutting-edge technology and innovative research to address various eye conditions more effectively.
Key Advances in Ophthalmology
1. Laser-Assisted Procedures
Laser technology has revolutionized ophthalmology, offering precision and reduced recovery times. Procedures such as LASIK (Laser-Assisted In Situ Keratomileusis) have become commonplace, providing a permanent solution to refractive errors like myopia, hyperopia, and astigmatism. LASIK reshapes the cornea, allowing light to be properly focused on the retina, thereby improving vision.
Another significant laser-assisted procedure is Photorefractive Keratectomy (PRK). Unlike LASIK, PRK does not involve creating a corneal flap, making it suitable for patients with thinner corneas. Both LASIK and PRK have high success rates and have dramatically reduced the need for corrective eyewear.
2. Cataract Surgery Innovations
Cataract surgery is one of the most common and successful procedures in ophthalmology. Traditional cataract surgery involves removing the clouded lens and replacing it with an artificial intraocular lens (IOL). Recent advances have introduced femtosecond laser-assisted cataract surgery (FLACS), which enhances precision and safety.
Additionally, the development of premium IOLs, such as multifocal and accommodating lenses, has improved postoperative outcomes. These lenses allow patients to see at multiple distances, reducing dependence on glasses after surgery.
3. Advanced Diagnostic Tools
Accurate diagnosis is crucial for effective treatment. Advances in diagnostic tools have significantly improved the early detection and management of eye diseases. Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) is a non-invasive imaging technique that provides detailed cross-sectional images of the retina. OCT is instrumental in diagnosing and monitoring conditions like macular degeneration, diabetic retinopathy, and glaucoma.
Fundus photography, which captures detailed images of the retina, has also seen improvements. Modern fundus cameras offer high-resolution images, aiding in the early detection of retinal diseases.
4. Gene Therapy
Gene therapy is an emerging field with promising applications in ophthalmology. It involves introducing genetic material into cells to treat or prevent disease. One of the notable successes in this area is the treatment of Leber’s Congenital Amaurosis (LCA), a rare genetic disorder that causes severe vision loss at an early age. The FDA-approved gene therapy, Luxturna, delivers a functional copy of the RPE65 gene directly to retinal cells, restoring vision in affected individuals.
Gene therapy holds potential for treating other genetic eye disorders, offering hope for patients with previously untreatable conditions.
5. Stem Cell Therapy
Stem cell therapy is another groundbreaking advancement in ophthalmology. It involves using stem cells to regenerate damaged tissues and restore function. Research in this area has shown promise for conditions like age-related macular degeneration (AMD) and retinitis pigmentosa.
Clinical trials are underway to evaluate the safety and efficacy of stem cell-based treatments. While still in the experimental stage, stem cell therapy could potentially provide a cure for degenerative eye diseases.
6. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning are transforming vision care by enhancing diagnostic accuracy and predicting disease progression. AI algorithms can analyze vast amounts of data from retinal images, identifying patterns and abnormalities that may be missed by human observers.
For instance, AI-powered platforms can detect diabetic retinopathy with high accuracy, facilitating early intervention. Machine learning models are also being developed to predict the progression of glaucoma, enabling timely treatment to prevent vision loss.
7. Teleophthalmology
The COVID-19 pandemic accelerated the adoption of telemedicine, including teleophthalmology. Teleophthalmology allows patients to consult with eye care professionals remotely, reducing the need for in-person visits. This approach is particularly beneficial for individuals in remote or underserved areas, ensuring they receive timely vision care.
Teleophthalmology platforms offer various services, including virtual consultations, remote monitoring, and digital imaging. While it cannot replace all aspects of in-person care, it provides a valuable supplement to traditional ophthalmology services.
The Impact on Vision Care
The advances in ophthalmology have significantly impacted vision care, improving patient outcomes and quality of life. Here are some key benefits:
1. Enhanced Precision and Safety
Modern surgical techniques, such as laser-assisted procedures and advanced cataract surgery, offer greater precision and safety. These innovations reduce the risk of complications and improve surgical outcomes, allowing patients to recover faster and achieve better vision.
2. Early Detection and Intervention
Advanced diagnostic tools, like OCT and AI-powered platforms, enable early detection of eye diseases. Early intervention is crucial for preventing vision loss and managing chronic conditions effectively. By identifying issues at an early stage, ophthalmologists can implement appropriate treatments and monitor progress more accurately.
3. Personalized Treatment
Advances in gene therapy and stem cell therapy pave the way for personalized treatment approaches. These therapies target the underlying causes of genetic and degenerative eye diseases, offering tailored solutions for individual patients. Personalized treatment enhances the effectiveness of interventions and improves patient satisfaction.
4. Increased Accessibility
Teleophthalmology has increased accessibility to vision care, particularly for individuals in remote or underserved areas. Remote consultations and monitoring ensure that patients receive timely care without the need for extensive travel. This approach also reduces the burden on healthcare facilities and optimizes resource utilization.
Conclusion
The field of ophthalmology continues to evolve, driven by technological advancements and innovative research. From laser-assisted procedures and advanced diagnostic tools to gene therapy and teleophthalmology, these developments are transforming vision care and improving patient outcomes. As we look to the future, ongoing research and collaboration will further enhance our ability to diagnose, treat, and prevent eye diseases, ensuring better vision and quality of life for all.
Advances in ophthalmology are not just about improving vision; they are about empowering individuals to live fuller, more independent lives. By embracing these innovations, we can continue to make significant strides in vision care and provide hope for those affected by eye conditions.