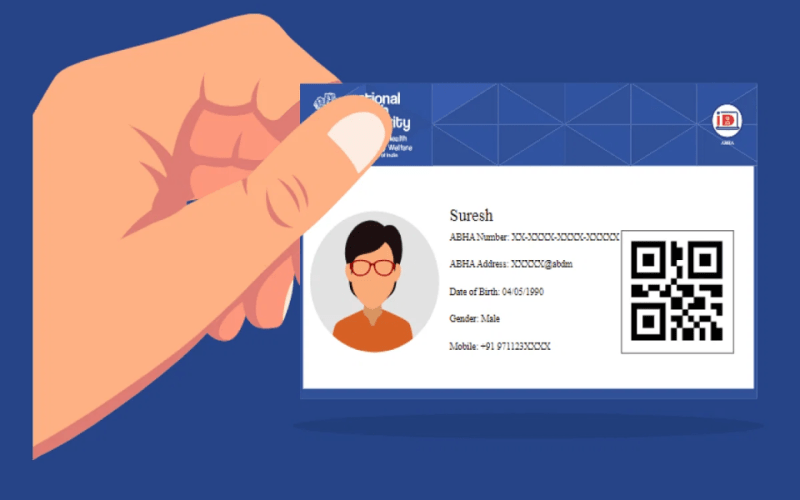
The government of India has initiated a landmark step in digital healthcare with the mandatory rollout of the ABHA card (Ayushman Bharat Digital Health Account) across the country. The ABHA card aims to streamline access to medical records by creating a unique digital health ID for every citizen.
With rapid adoption, citizens can easily link their medical information across healthcare providers, clinics, and hospitals, simplifying diagnosis and treatment. However, while the benefits of seamless health data access are promising, the move has also raised significant concerns about data privacy and security. This article delves into the complexities of the ABHA card, its implications for healthcare, and the ongoing debate surrounding data protection in India’s health sector.
Understanding the ABHA card
The ABHA card is a digital health identification system introduced under the Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission (ABDM), launched by the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare. It provides individuals with a unique 14-digit health ID that securely stores their health records, lab reports, prescriptions, and other medical information digitally.

How to get the ABHA card download
Citizens can easily obtain their ABHA card by registering through the official ABHA portal or authorized
health applications available on smartphones. The ABHA card download involves a straightforward registration process using an Aadhaar card, mobile number or other identity proofs followed by the creation of a secure health ID. Once registered, users can access their digital health records anytime, anywhere. This process increases transparency and enables patients to control their data shared with hospitals or health professionals.
Benefits of the ABHA card in the healthcare ecosystem
The digital health ID promises several advantages that align with the government’s goal of making healthcare more accessible and efficient:
- Simplified medical history access: Patients and doctors can effortlessly retrieve complete medical records, improving diagnosis accuracy
- Reduced paperwork: Diminishes the need for physical report submissions, cutting down administrative delays
- Data interoperability: Health data can be shared between various providers seamlessly, facilitating an integrated healthcare experience
- Cost efficiency: Minimizes duplication of tests and saves on unnecessary expenditure
- Remote healthcare facilitation: Enables telemedicine and remote consultations with authentic patient records
These benefits collectively aim to improve health outcomes while reducing the patient’s burden in managing their medical information manually.
Data privacy concerns associated with the ABHA card
Despite the clear potential advantages, mandatory adoption of the ABHA card has sparked a nationwide debate on data privacy. India’s healthcare data ecosystem is highly sensitive, and digitising such information poses challenges around identity theft, data breaches, and misuse.
Concerns expressed by privacy experts and citizens
- Data security risks: Experts warn that the digital health IDs might become attractive targets for cybercriminals looking to exploit personal health data
- Lack of clear regulation: While the government has laid out a privacy framework under ABDM, many feel the laws are insufficient to tackle sophisticated cyber threats
- Data ownership ambiguity: Patients may not fully understand who owns their health data or how it could be used by insurance companies or other stakeholders
- Potential misuse: There is apprehension about data being used beyond healthcare—for commercial exploitation or discriminatory purposes
Several civil society groups have urged for stronger legal protections and stricter enforcement mechanisms before making the ABHA card compulsory.
The government’s efforts to safeguard data privacy
The Ministry of Health and Family Welfare continues to reassure citizens by highlighting several measures incorporated in the ABHA platform:
- Consent-driven data sharing: Patient information is shared only with explicit consent and permission-based access is enforced
- Anonymization of data: Where possible, data is anonymized to prevent identification in large-scale health analytics
- Use of encryption: Sophisticated encryption technologies protect data both in transit and at rest
- Data localization: Health data collected in India is stored on domestic servers compliant with India’s data protection policies
- Audit trails and accountability: Every access to health records leaves a trace to hold entities accountable for misuse
- The government’s intention is to build trust and make individuals active participants in managing their personal health data
Legal framework landscape for healthcare data protection in India
India does not yet have a specialized law solely dedicated to healthcare data protection, but several regulations apply in conjunction:
- Information Technology Act, 2000 (IT Act): Provides provisions for protecting sensitive personal data, including health data
- Personal Data Protection Bill: Still under parliamentary consideration, this bill proposes comprehensive safeguards for personal data covering healthcare and beyond
- The Digital Information Security in Healthcare Act (DISHA): A proposed law focusing exclusively on electronic health data protection. Its implementation is eagerly anticipated by industry and advocacy groups
Effective legal backing is essential to complement the technology infrastructure underpinning the ABHA card, ensuring patient rights and privacy are firmly protected.
Implications for the insurance and banking sectors
The ABHA card’s extensive digital health data repository can revolutionise health insurance underwriting and loan assessments. Insurers may leverage medical histories for customised risk profiling, while banks could incorporate health data in creditworthiness evaluations.
Opportunities and caution in finance
- Faster claims processing: Insurance companies can verify data swiftly, reducing fraud and delays.
- Personalized insurance products: Data-driven insights enable tailored policies to suit individual health profiles.
- Credit evaluation enhancement: Better health data can contribute to comprehensive financial assessments for personal loans or health financing
However, without stringent safeguards, there is a risk that discrimination or privacy violations could occur. The finance industry must collaborate closely with healthcare and regulatory bodies to uphold data ethics.
How individuals can protect their health data while using the abha card
Citizens using the ABHA card should adopt best practices to guard their health information:
- Regularly update passwords and avoid sharing OTPs.
- Monitor all apps and portals linked to the health ID.
- Exercise caution in providing consent for data sharing, only permitting trusted healthcare providers.
- Stay informed about government policies and changes in the digital health ecosystem.
Proactive awareness and responsible usage will empower users to benefit from the ABHA card without compromising privacy.
The future of digital health in India
The integration of the ABHA card into the Indian healthcare system is a pivotal step towards a comprehensive digital health infrastructure. With advancement in AI, big data, and telemedicine, digital health IDs are likely to become indispensable tools.
However, the future success hinges on balancing technological innovation with strong data protection frameworks. Public trust will be the cornerstone of digital health transformation in India.
Conclusion
The introduction of the ABHA card as a mandatory digital health ID represents a significant evolution in India’s healthcare delivery, promising efficiency and improved patient care. The process of ABHA card download and usage offers unprecedented convenience and control over personal health data.
However, the accompanying challenges around data privacy cannot be overlooked. Ensuring robust security, clear regulatory guidelines, and transparent data usage policies will be essential to sustain public confidence. Stakeholders including government, healthcare providers, and citizens must collaborate to navigate this digital transition responsibly. With the right safeguards in place, the ABHA card can truly revolutionise healthcare in India while upholding individual privacy rights.