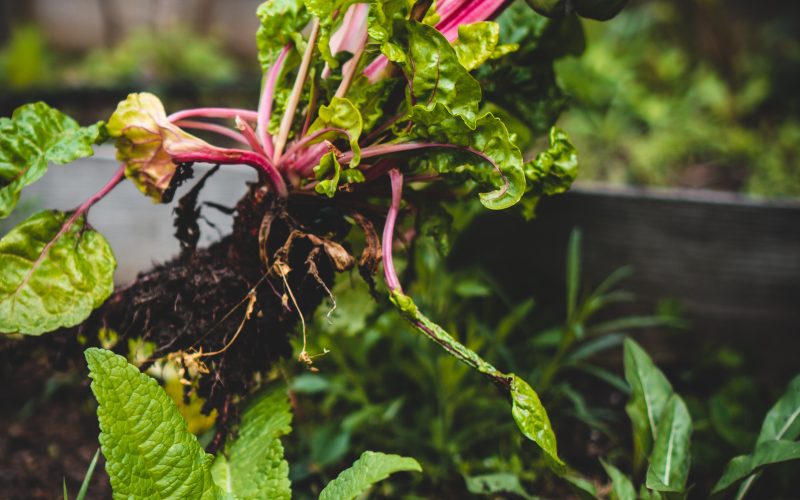
Microbes are tiny organisms that can be found almost everywhere, including the soil. Despite their small size, they play a crucial role in agriculture, affecting everything from soil health to crop yields. In recent years, there has been increasing interest in harnessing the power of these microscopic organisms to promote sustainable farming practices and boost food production.
One of the key ways that microbes benefit agriculture is by improving soil health. Soil microbes are responsible for decomposing organic matter, cycling nutrients, and breaking down contaminants. They also help to create soil structure and stability, which is essential for healthy plant growth. In fact, research has shown that healthy soils with high levels of microbial activity can lead to increased yields and higher quality crops.
Microbes also play an important role in reducing the need for harmful chemicals in agriculture. For example, certain microbes can protect crops from pests and diseases, reducing the need for synthetic pesticides and fungicides. This not only benefits the environment but can also save farmers money on expensive chemicals.
In addition to protecting crops, microbes can also be used to enhance their growth. Some types of microbes can produce plant growth hormones, which can stimulate root development and increase nutrient uptake. Others can fix atmospheric nitrogen, converting it into a form that plants can use to grow. By harnessing these natural processes, farmers can improve crop yields and reduce their reliance on synthetic fertilizers.
There are also innovative new ways that microbes are being used in agriculture. One example is the development of microbial-based fertilizers, which contain beneficial microbes that can be applied directly to the soil or to seeds. These fertilizers can help to boost soil health and plant growth while also reducing the need for synthetic fertilizers.
Despite the many benefits of microbes in agriculture, there are also potential risks to consider. Some microbes can be harmful to humans and animals, and there is always the risk of introducing invasive species into a new environment. Additionally, there is still much to learn about the complex interactions between microbes and plants, and more research is needed to fully understand the potential benefits and risks.
Overall, the role of microbes in agriculture is a fascinating and rapidly evolving field. As the world continues to grapple with food insecurity and environmental challenges, the potential of these tiny organisms to promote sustainable farming practices and boost food production is more important than ever. By continuing to explore the complexities of these microbial communities, we can unlock new insights and innovations to help build a healthier, more sustainable food system for generations to come.