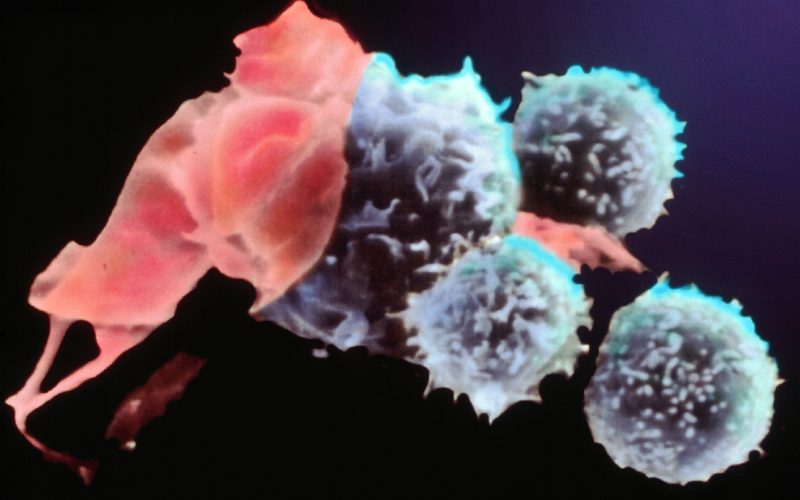
Cancer remains one of the most formidable challenges in modern medicine, but recent breakthroughs in cancer research are offering new hope. This article delves into the latest developments, highlighting how innovative approaches and cutting-edge technologies are revolutionizing the way we understand, diagnose, and treat this complex disease.
Precision Medicine: Tailoring Treatment to the Individual
One of the most significant breakthroughs in cancer research is the advent of precision medicine. This approach involves tailoring treatment based on the genetic profile of both the patient and the tumor. By understanding the unique mutations and characteristics of a patient’s cancer, doctors can prescribe therapies that are more likely to be effective.
Genetic Profiling and Targeted Therapy
Genetic profiling allows researchers to identify specific mutations that drive cancer growth. Targeted therapies are then developed to inhibit these mutations. For example, drugs like Trastuzumab (Herceptin) have been designed to target HER2-positive breast cancer, significantly improving outcomes for patients with this subtype. Similarly, BRAF inhibitors have shown promise in treating melanoma with specific genetic mutations.
Immunotherapy: Harnessing the Body’s Immune System
Immunotherapy has emerged as a game-changer in cancer treatment. This approach involves stimulating the patient’s immune system to recognize and destroy cancer cells. There are several types of immunotherapy, including checkpoint inhibitors, CAR-T cell therapy, and cancer vaccines.
Checkpoint Inhibitors
Checkpoint inhibitors, such as Pembrolizumab (Keytruda) and Nivolumab (Opdivo), work by blocking proteins that prevent the immune system from attacking cancer cells. These drugs have shown remarkable success in treating various cancers, including melanoma, lung cancer, and Hodgkin lymphoma.
CAR-T Cell Therapy
Chimeric Antigen Receptor T-cell (CAR-T) therapy involves genetically modifying a patient’s T cells to recognize and attack cancer cells. This personalized treatment has shown promising results in treating certain types of leukemia and lymphoma.
Cancer Vaccines
Cancer vaccines are designed to stimulate the immune system to target cancer cells. Unlike traditional vaccines that prevent disease, cancer vaccines aim to treat existing cancers. Provenge, for example, is an FDA-approved vaccine for prostate cancer that has shown to extend survival in patients.
Liquid Biopsies: A Non-Invasive Diagnostic Tool
Traditional biopsies, which involve surgically removing tissue samples, can be invasive and uncomfortable. Liquid biopsies offer a non-invasive alternative by analyzing cancer-related biomarkers in bodily fluids, such as blood. This technique allows for earlier detection, monitoring of treatment response, and identification of resistance mutations.
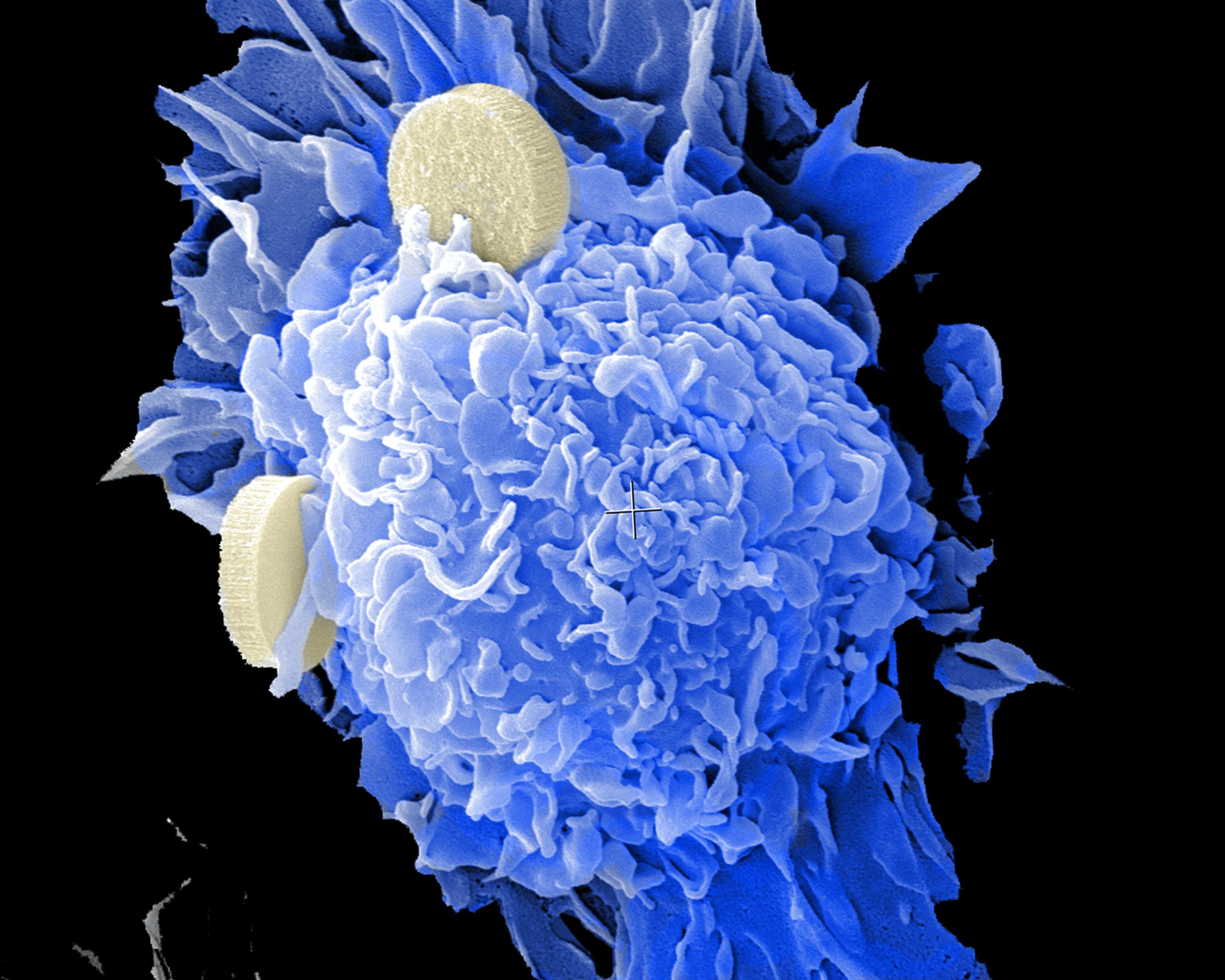
Circulating Tumor DNA (ctDNA)
One of the most promising aspects of liquid biopsies is the analysis of circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA). This approach enables the detection of genetic mutations associated with cancer, providing valuable information for personalized treatment plans. Liquid biopsies are particularly useful for monitoring metastatic cancers, where traditional biopsies may be challenging.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning are transforming cancer research by improving diagnostic accuracy and accelerating drug discovery. These technologies analyze vast amounts of data to identify patterns and make predictions that would be impossible for humans to achieve alone.
Diagnostic Imaging
AI algorithms are being used to enhance diagnostic imaging techniques, such as MRI and CT scans. These algorithms can detect subtle changes in imaging data that may be indicative of cancer, leading to earlier and more accurate diagnoses.
Drug Discovery
Machine learning models are also being employed to identify potential drug candidates. By analyzing chemical structures and biological data, these models can predict which compounds are likely to be effective against specific cancer types. This accelerates the drug discovery process and increases the likelihood of finding successful treatments.
Epigenetics: Understanding Gene Expression
Epigenetics is the study of changes in gene expression that do not involve alterations to the DNA sequence. These changes can be influenced by various factors, including environmental exposures and lifestyle choices. Understanding epigenetic modifications is crucial for developing new cancer therapies.

Epigenetic Therapies
Epigenetic therapies aim to reverse abnormal gene expression patterns associated with cancer. For example, DNA methyltransferase inhibitors and histone deacetylase inhibitors are being explored as potential treatments for various cancers. These drugs work by modifying the epigenetic landscape, restoring normal gene function and inhibiting cancer growth.
Microbiome Research: The Gut-Cancer Connection
Emerging research suggests that the microbiome – the community of microorganisms living in our bodies – may play a role in cancer development and treatment response. Studies have shown that certain gut bacteria can influence the effectiveness of immunotherapy and chemotherapy.
Probiotics and Cancer Treatment
Researchers are investigating the potential of probiotics to enhance cancer treatment. By modifying the gut microbiome, it may be possible to improve the body’s response to therapy and reduce side effects. This area of research is still in its early stages, but it holds promise for future cancer treatments.
Conclusion
The landscape of cancer research is rapidly evolving, with breakthroughs offering new hope for patients and their families. Precision medicine, immunotherapy, liquid biopsies, artificial intelligence, epigenetics, and microbiome research are just a few of the innovative approaches that are transforming cancer care. As we continue to unravel the complexities of this disease, these advancements bring us closer to a future where cancer is not only treatable but potentially curable. The progress made so far underscores the importance of continued investment in cancer research, as each discovery brings us one step closer to overcoming this formidable challenge.