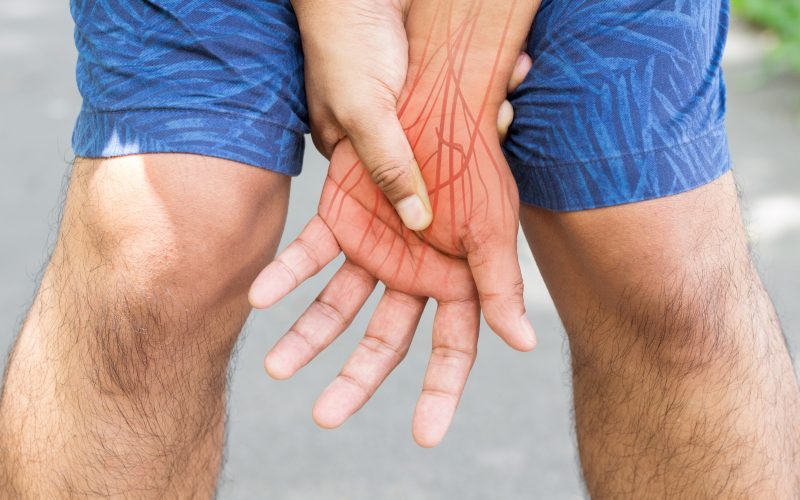
Introduction
Small Fiber Neuropathy (SFN) may sound like a minor issue, but its impact on individuals’ lives can be profound. Despite its name, SFN is not a small matter when it comes to the quality of life for those affected. In this article, we delve into the significance of SFN pain, its causes, symptoms, and treatment options. Understanding the intricacies of SFN is crucial in offering effective support and management for those living with this condition. You Need To Know About Other Health Problems Or Solutions (Allergies or Snoring)
Understanding Small Fiber Neuropathy
Small Fiber Neuropathy affects the small nerve fibers responsible for transmitting sensory information, such as pain and temperature, from the skin to the brain. While it may not manifest as visibly as other forms of neuropathy, its impact can be debilitating. The small nerves involved in SFN are abundant throughout the body, explaining why symptoms can vary widely among individuals.
Causes of Small Fiber Neuropathy
Several underlying conditions and factors can contribute to the development of SFN. These include:
- Diabetes Mellitus: One of the most common causes of SFN is diabetes mellitus, particularly in those with poorly controlled blood sugar levels.
- Autoimmune Disorders: Conditions such as Sjögren’s syndrome, lupus, and rheumatoid arthritis can lead to autoimmune-related SFN.
- Genetic Predisposition: In some cases, SFN may have a genetic component, making certain individuals more susceptible to developing the condition.
- Toxic Exposures: Exposure to certain toxins, such as chemotherapy drugs, heavy metals, or environmental pollutants, can damage small nerve fibers and trigger SFN.
- Infections: Viral or bacterial infections, such as HIV, Lyme disease, or hepatitis C, have been associated with the development of SFN.
Symptoms of Small Fiber Neuropathy
The symptoms of SFN can vary widely from person to person and may include:
- Pain: Burning, stabbing, or shooting pain, often in the feet or hands, is a hallmark symptom of SFN. This pain can be constant or intermittent and may worsen at night.
- Sensory Disturbances: Individuals with SFN may experience heightened sensitivity to touch, temperature changes, or even the slightest pressure on the skin.
- Autonomic Dysfunction: SFN can also affect the autonomic nervous system, leading to symptoms such as changes in sweating, heart rate, blood pressure, and digestion.
- Skin Changes: Some individuals may notice changes in the appearance or texture of their skin in affected areas, such as thinning or hair loss.

Diagnosis and Treatment Options
Diagnosing SFN can be challenging due to its varied presentation and the need for specialized testing. However, a thorough medical history, physical examination, and nerve conduction studies can aid in diagnosis. Additionally, skin biopsy and specialized tests, such as quantitative sensory testing, may be necessary to confirm SFN.
Once diagnosed, treatment aims to manage symptoms and address any underlying causes. This may include:
- Medications: Pain-relieving medications, such as antidepressants, anticonvulsants, or topical creams, can help alleviate neuropathic pain.
- Physical Therapy: Exercises to improve balance, strength, and mobility can be beneficial for individuals with SFN.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Maintaining optimal blood sugar control, avoiding toxins, and managing underlying conditions can help slow the progression of SFN.
- Alternative Therapies: Some individuals find relief from SFN symptoms through acupuncture, massage therapy, or biofeedback techniques.
Treatment Options for Small Fiber Neuropathy
| Treatment Option | Description |
|---|---|
| Medications | Various medications can be prescribed to manage neuropathic pain, including antidepressants, anticonvulsants, and topical creams. |
| Physical Therapy | Exercises and techniques aimed at improving balance, strength, and mobility can help individuals cope with SFN-related symptoms. |
| Lifestyle Modifications | Optimal blood sugar control, toxin avoidance, and managing underlying conditions are crucial in slowing the progression of SFN. |
| Alternative Therapies | Some individuals find relief through alternative therapies such as acupuncture, massage therapy, or biofeedback techniques. |
Conclusion
Small Fiber Neuropathy may be small in name, but its impact on individuals’ lives is far from insignificant. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for SFN, healthcare professionals can offer effective support and management strategies for those affected. Through a multidisciplinary approach that addresses both symptom management and underlying causes, individuals with SFN can experience improved quality of life and symptom relief.
Understanding and addressing the significance of SFN pain is essential in providing comprehensive care and support for those living with this challenging condition.