Introduction
Ringworm, despite its name, isn’t caused by worms at all. Rather, it’s a fungal infection that affects the skin, scalp, and nails. This article aims to provide comprehensive insights into, including its identification, causes, treatment, and prevention strategies.
- Ringworm, scientifically known as dermatophytosis, is a contagious fungal infection affecting the skin, scalp, and nails.
- No Worms Involved: Despite its common name, there are no actual worms involved in this condition.
Understanding ringworm is crucial due to its contagious nature and the discomfort it can cause. Contrary to popular belief, is not limited to humans; it can also affect animals, including dogs, cats, and livestock.
- Contagious Nature: Ringworm spreads easily through direct contact or contaminated surfaces.
- Affects Animals Too: It’s not exclusive to humans; pets can also contract and transmit ringworm.
Types of Ringworm
Ringworm presents itself in different forms depending on the affected area of the body. The most common types include:
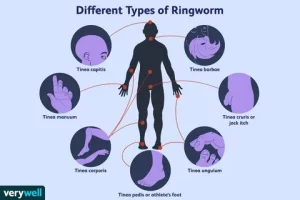
- Tinea Corporis (Ringworm of the Body): Circular, red, itchy patches on the skin, resembling rings.
- Tinea Capitis (Ringworm of the Scalp): Primarily affecting children, leading to hair loss and scalp inflammation.
- Tinea Pedis (Athlete’s Foot): Itching, burning, and cracking of the skin on the feet, especially between the toes.
Causes of Ringworm
Ringworm is caused by fungi known as dermatophytes. These fungi thrive in warm, moist environments and can be transmitted through direct contact with infected individuals or animals, contaminated surfaces, or shared items such as towels, clothing, and combs.
- Fungal Origin: Dermatophytes, not worms, are responsible for ringworm infections.
- Modes of Transmission: Direct contact, contaminated objects, and shared items facilitate the spread of ringworm.
Symptoms and Signs
The symptoms of ringworm vary depending on the location of the infection. Common signs include red, scaly patches on the skin, itching, and in severe cases, blistering or oozing lesions.
- Varied Symptoms: Symptoms range from red, scaly patches to itching and blistering.
- Location Matters: The type and severity of symptoms depend on the affected area of the body.
Diagnosis Methods
Healthcare professionals diagnose ringworm through physical examination, skin scrapings, or fungal cultures. Accurate diagnosis is essential to initiate appropriate treatment and prevent the spread of the infection.
- Medical Evaluation: Diagnosis involves physical examination and laboratory tests.
- Accuracy Matters: Proper diagnosis ensures effective treatment and prevents further transmission.
Treatment Options
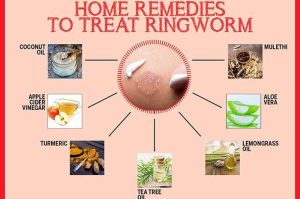
Treatment for ringworm typically involves antifungal medications, either topical or oral, depending on the severity and location of the infection. Over-the-counter antifungal creams are often effective for mild cases, while oral medications may be necessary for more severe or widespread infections.
- Medication Choices: Topical or oral antifungal medications are prescribed based on the severity of the infection.
- Effective Options: Over-the-counter creams and prescription medications offer effective treatment solutions.
Preventive Measures
Preventing ringworm involves practicing good hygiene, avoiding sharing personal items, keeping the skin clean and dry, and minimizing contact with infected individuals or animals.
- Hygiene Practices: Regular handwashing and keeping the skin dry are crucial preventive measures.
- Avoidance Strategies: Minimize contact with infected individuals and animals to prevent transmission.
Ringworm in Specific Populations
Certain populations, such as children, the elderly, and individuals with weakened immune systems, may be more susceptible to ringworm infections. Special precautions and treatment considerations may be necessary for these groups.
- Vulnerable Groups: Children, elderly, and immunocompromised individuals require special attention.
- Tailored Approaches: Customized treatment plans address the unique needs of specific populations. Explore more About (enhancing memory)
Debunking Common Myths
There are several myths and misconceptions surrounding, including beliefs about its causes, transmission, and treatment. It’s essential to distinguish fact from fiction to effectively manage and prevent infections.
- Myth Clarification: Dispelling common misconceptions about aids in better understanding and management.
- Educational Efforts: Promoting accurate information helps combat misinformation and stigma.
Impact on Daily Life
Ringworm can have a significant impact on daily life, causing discomfort, embarrassment, and disruption of daily activities. Coping strategies and support from healthcare providers and loved ones are crucial for managing the physical and emotional effects of the infection.
- Emotional Toll: Beyond physical discomfort, can affect self-esteem and social interactions.
- Support Systems: Counseling and support from healthcare providers and peers alleviate emotional distress.
Conclusion
In conclusion, ringworm is a common fungal infection that can affect various parts of the body. By understanding its causes, symptoms, and treatment options, individuals can take proactive steps to identify, treat, and prevent infections.