Introduction
Gallstones, though small, can have a significant impact on one’s health, leading to discomfort and complications. This comprehensive guide aims to shed light on the causes, symptoms, and preventive measures associated with gallstones, offering valuable insights for better digestive well-being.
Understanding Gallstones
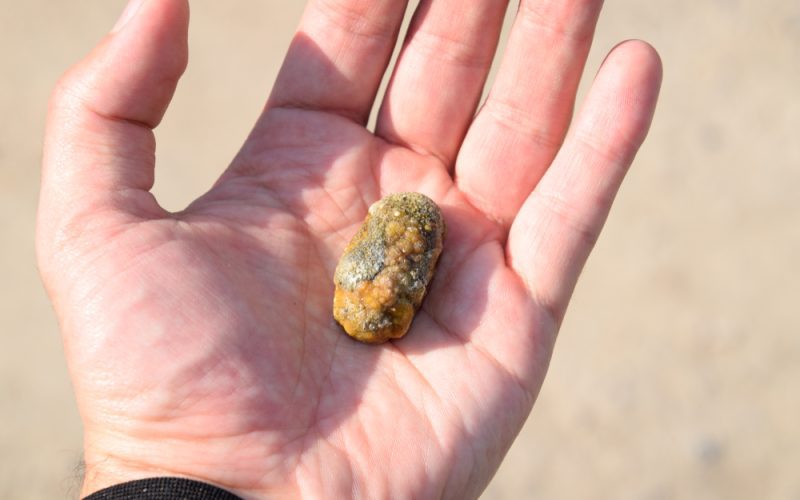
Gallstones are crystalline formations that develop in the gallbladder, a pear-shaped organ beneath the liver. These stones, primarily composed of bile components, vary in size, from as small as a grain of sand to as large as a golf ball. The gallbladder plays a crucial role in digestion, releasing bile into the small intestine to aid in the breakdown of fats.
Gallbladder and Gallstones
Gallstones form when there is an imbalance in the composition of bile. Bile, a digestive fluid produced by the liver and stored in the gallbladder, can lead to stone formation when it becomes too concentrated. The stones can range in number – from an individual stone to multiple stones occurring simultaneously.
Symptoms – A Quick Overview
Recognizing the symptoms of gallstones is vital for early detection and intervention. The symptoms may include:
- Sudden and Intense Abdominal Pain: Typically in the upper right portion or center of the abdomen.
- Back Pain Between Shoulder Blades: Pain may radiate to the back.
- Nausea and Vomiting: Particularly after meals.
- Pain in the Right Shoulder: Discomfort may extend to the shoulder.
Symptoms in Detail
Sudden and Intense Abdominal Pain
One of the hallmark symptoms of gallstones is a sudden and intense pain in the upper right portion of the abdomen. This pain may radiate to the center of the abdomen, just below the breastbone, lasting from several minutes to a few hours.
Back Pain Between Shoulder Blades
Gallstone-induced pain can extend to the back between the shoulder blades, causing additional discomfort.
Nausea and Vomiting
Gallstones can trigger feelings of nausea, often accompanied by vomiting, especially after consuming meals.
Pain in the Right Shoulder
Pain may manifest in the right shoulder, indicating potential gallbladder issues.
Causes of Gallstones
The precise cause of gallstones remains elusive, but certain factors contribute to their formation:
- Excessive Cholesterol: When the liver produces more cholesterol than bile can dissolve, crystals and stones may develop.
- High Bilirubin Levels: Conditions like cirrhosis, biliary tract infections, or certain blood disorders can lead to elevated bilirubin, contributing to gallstone formation.
- Inefficient Gallbladder Emptying: If the gallbladder doesn’t empty properly, bile becomes concentrated, fostering gallstone development.
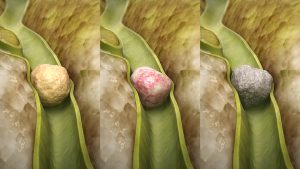
Types of Gallstones
Understanding the types of gallstones provides insight into their composition and characteristics:
Cholesterol Gallstones
- Composition: Mainly cholesterol.
- Appearance: Often yellow.
- Formation: Imbalance in cholesterol levels.
- Prevalence: Most common type.
Pigment Gallstones
- Composition: Excess bilirubin.
- Appearance: Dark brown or black.
- Formation: Elevated bilirubin levels.
- Prevalence: Less common.
Risk Factors
Certain factors increase the likelihood of gallstone formation:
- Gender: Being female.
- Age: 40 or older.
- Ethnicity: Native American or Hispanic of Mexican origin.
- Weight: Overweight or obese.
- Lifestyle: Sedentary.
- Pregnancy: Especially in women.
- Diet: High in fat or cholesterol, low in fiber.
- Genetics: Family history of gallstones.
- Medical Conditions: Diabetes, certain blood disorders, or liver disease.
- Rapid Weight Loss: Losing weight too quickly.
- Medications: Those containing estrogen.
Complications
Gallstones can lead to various complications, including:
Inflammation of the Gallbladder (Cholecystitis)
A lodged gallstone in the gallbladder’s neck can cause inflammation, resulting in severe pain and fever.
Blockage of the Common Bile Duct
Gallstones obstructing the ducts can lead to pain, jaundice, and bile duct infections.
Blockage of the Pancreatic Duct
Pancreatic duct blockage due to gallstones can lead to pancreatitis, causing intense abdominal pain and requiring hospitalization.
Gallbladder Cancer
While rare, individuals with a history of gallstones face an increased risk of gallbladder cancer.
When to See a Doctor
While mild symptoms may be manageable, any signs or symptoms causing concern should prompt a visit to the doctor. Immediate medical attention is crucial if experiencing:
- Intense Abdominal Pain: So severe that finding a comfortable position is impossible.
- Yellowing of Skin and Eyes (Jaundice): Indicates a potential blockage.
- High Fever with Chills: Suggesting a severe complication.

Prevention
Taking proactive measures can significantly reduce the risk of developing gallstones:
- Regular Meals: Avoid skipping meals to maintain consistent digestion.
- Gradual Weight Loss: Aim for a steady weight loss of 1-2 pounds per week to prevent gallstone formation.
- High-Fiber Diet: Include fruits, vegetables, and whole grains in your diet for better digestion.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Obesity increases gallstone risk, making weight management crucial.
- Exercise: Regular physical activity contributes to overall well-being. explore other health issues
Conclusion
Understanding gallstones empowers individuals to take charge of their digestive health. Recognizing symptoms, addressing risk factors, and adopting preventive measures are crucial steps toward maintaining a healthy gallbladder. Regular medical check-ups, coupled with lifestyle adjustments, play a pivotal role in preventing complications and ensuring overall well-being. By embracing a proactive approach, individuals can navigate the challenges posed by gallstones and lead healthier lives.