Understanding Abnormal Uterine Bleeding
Unusual Uterine Bleeding, also known as anovulatory bleeding, refers to menstrual bleeding that occurs outside the regular monthly cycle. Let’s delve into the intricacies of this condition, its impact on daily life, and the need for timely medical attention.

Symptoms
Identifying abnormal uterine bleeding involves recognizing a spectrum of symptoms. Here’s a breakdown:
- Heavy Periods: Experiencing unusually heavy menstrual flow.
- Bleeding Between Periods: Noticing bleeding episodes between regular cycles.
- Prolonged Periods: Menstrual periods lasting more than seven days.
- Irregular Menstrual Cycles: Variations in the regularity of menstrual cycles.
These signs, if persistent, may indicate an underlying medical condition that warrants investigation.
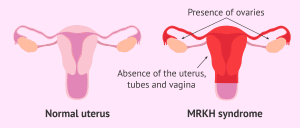
Common Causes
Understanding the root causes is crucial for effective management. Key contributors include:
- Hormone Changes: Imbalances affecting the release and regulation of hormones.
- Issues with Uterus: Fibroids, polyps, adenomyosis, and endometriosis.
- Other Health Conditions: Cervical, endometrial, or uterine cancer; kidney, liver, thyroid, or adrenal gland disorders; infections; and sexually transmitted diseases.
Exploring these causes sheds light on the diverse factors contributing to abnormal uterine bleeding.
Diagnosing Abnormal Uterine Bleeding
A systematic approach to diagnosis involves:
- Detailed Symptom Tracking: Maintaining a record of symptoms over several cycles.
- Physical Examination: A thorough assessment of overall health and pelvic examination.
- Blood Work: Checking for iron deficiency, hormonal imbalances, blood disorders, or chronic diseases.
- Imaging Techniques: Utilizing ultrasound, hysteroscopy, biopsy, and magnetic resonance imaging for a comprehensive evaluation.
These diagnostic tools help healthcare professionals pinpoint the underlying cause.

Treatment Options for Abnormal Uterine Bleeding
Tailored treatments depend on the identified cause and individual circumstances. Explore the diverse options:
Hormonal Treatments
- Birth Control Pills: Regulating menstrual cycles and reducing bleeding.
- Hormone Therapy: Balancing hormonal levels for improved menstrual regularity.
Surgical Interventions
- Endometrial Ablation: Employing heat, cold, electricity, or laser to eliminate the uterine lining.
- Myomectomy or Uterine Artery Embolization: Removing fibroids or cutting off blood supply.
- Hysterectomy: Removal of the uterus, considered a last resort in severe cases.
Each treatment has considerations regarding fertility, post-treatment care, and overall effectiveness.
Complications Associated
Understanding potential complications emphasizes the importance of timely intervention:
- Trouble Getting Pregnant: Impacts fertility in some cases.
- Anemia or Blood Loss: Excessive bleeding leading to health concerns.
Being aware of these complications underscores the urgency of addressing abnormal uterine bleeding promptly.
Conclusion:
Empower yourself with knowledge about abnormal uterine bleeding. Consultation with a healthcare professional is essential for personalized guidance and determining the most suitable treatment strategy tailored to individual needs.