Introduction
Laryngeal tumors, encompassing a subset of head and neck cancers impacting the throat, demand a nuanced understanding of their symptoms. This comprehensive guide aims to provide an in-depth exploration of early and late-stage indicators, comparisons with benign tumors, frequently asked questions, and the critical junctures necessitating consultation with medical professionals.
General Symptoms Overview
- Location Influence: The manifestation of laryngeal tumor symptoms is intricately tied to the tumor’s location within the larynx.
- Three Sections: Understanding the larynx’s anatomy is crucial—glottis (vocal cords), supraglottis (above vocal cords), and subglottis (below vocal cords).
- Early Detection: Early symptoms often correlate with vocal cord involvement, allowing for swifter identification.

Early Symptoms
- Stage 0 and 1: Subtle or absent symptoms in the earliest stages, with vocal cord cancer possibly exhibiting no obvious signs.
- Vocal Quality Changes: Changes in vocal quality or hoarseness may be early indicators.
- Progression Awareness: Understanding the evolving nature of symptoms as the disease advances.
Late Symptoms
- Progressive Signs: As laryngeal cancer advances, a spectrum of symptoms emerges.
- Common Indicators: Persistent sore throat, difficulty swallowing, ear pain, and unintentional weight loss are prevalent late-stage signs.
- Timely Intervention: Recognizing late symptoms is crucial for timely medical intervention and improved prognosis.
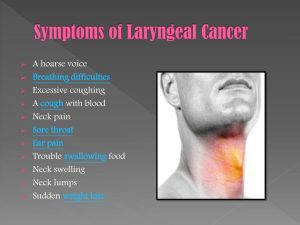
Vs. Symptoms of a Benign Laryngeal Tumor
- Benign Lesions Overview: Laryngeal papilloma, vocal cord nodules, vocal cord granuloma, and polypoid corditis are benign conditions.
- Positive Outlook: Benign tumors often have a positive prognosis but may require treatment in certain cases.
- Shared Symptoms: Symptoms such as trouble breathing, voice hoarseness, and difficulty swallowing are common between benign and cancerous conditions.
Frequently Asked Questions
- Self-Check Limitations: Throat cancer cannot be self-checked at home; symptoms should be discussed with a healthcare professional.
- Sex-Specific Differences: Research on sex-specific differences in laryngeal cancer symptoms is ongoing.
- Prevalence Disparity: Laryngeal cancer occurs more frequently in males than females, with distinct lifetime risk figures.
When to Contact a Doctor
- Urgency Recognition: Hoarseness persisting for over three weeks or other symptoms enduring beyond two weeks necessitate prompt medical consultation.
- Differentiating Conditions: Early-stage symptoms may mimic less severe conditions, emphasizing the need for vigilant attention.
Summary
In summary, early laryngeal cancer symptoms may mirror common cold symptoms, emphasizing the importance of prolonged symptoms like throat pain, voice hoarseness, and cough. The later stages unveil more severe signs, underscoring the need for timely medical attention. While benign laryngeal tumors share some symptoms, accurate diagnosis through proper testing remains imperative for informed decision-making regarding treatment.