Understanding Leukemia
Leukemia is a form of cancer impacting the blood and bone marrow, crucial for blood cell production. In this article, we delve into the causes, risk factors, types, treatment options, symptoms, diagnosis, frequently asked questions, and outlook related to Navigating Leukemia.
Causes of Leukemia
- Genetic Damage: Leukemia occurs when there is damage to the DNA of developing blood cells, particularly white cells.
- Uncontrolled Growth: Damaged blood cells grow and divide uncontrollably, hindering the normal life cycle of blood cells.
- Overcrowding in Blood: Cancer cells multiply, overcrowding the blood, affecting white blood cells, platelets, and red blood cells.
- Disruption in Bone Marrow: As cancer cells increase, they disrupt the bone marrow’s ability to produce healthy blood cells.
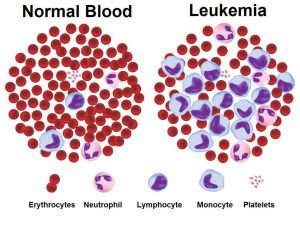
Risk Factors
- Infections: Certain infections, such as the Epstein-Barr virus, may increase the risk of leukemia.
- Ionizing Radiation: Exposure to radiation from sources like radiation therapy, nuclear weapons testing, or background radiation can be a risk factor.
- Birth Weight: Both high and low birth weights have been linked to an increased risk of leukemia.
- Gender: Leukemia rates are higher among males compared to females.
- Chemical Exposure: Contact with pesticides, benzene, and air pollution is associated with an elevated risk.
- Genetic Conditions: Conditions like Down syndrome or Klinefelter syndrome may contribute to leukemia risk.
- Previous Cancer Treatment: A history of chemotherapy or exposure to certain toxins increases the likelihood.

For more details on risk factors, refer to the table below:
| Risk Factor | Associated with Leukemia? |
|---|---|
| Infections | Yes |
| Ionizing radiation | Yes |
| Birth weight | Yes |
| Gender | Yes (higher in males) |
| Chemical exposure | Yes |
| Genetic conditions | Yes |
Types of Leukemia
Doctors classify leukemia based on the type of blood cell affected, whether it’s acute or chronic, and if it occurs in a child or an adult. Acute leukemia progresses rapidly, while chronic leukemia develops more slowly. The two main categories are lymphocytic and myelogenous leukemias.
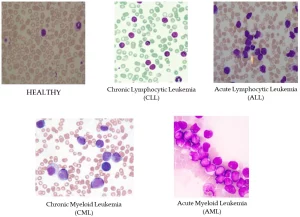
Common Types of Leukemia:
- Acute Lymphocytic Leukemia (ALL): More common in children under 5 years but can affect adults.
- Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL): Primarily seen in individuals over 70 years, more common in males.
- Acute Myelogenous Leukemia (AML): More common in adults, rare in children.
- Chronic Myeloid Leukemia (CML): Accounts for about 15% of all leukemia cases in the U.S.
- Hairy Cell Leukemia (HCL): A rare type that mostly affects adults in middle age and older.
Treatment Options
- Watchful Waiting: Applicable for slow-growing leukemias, like CLL and HCL, involves monitoring without immediate intervention.
- Chemotherapy: Administering drugs to kill or control cancer cells.
- Radiation Therapy: Using high-energy rays to target and destroy cancer cells.
- Targeted Therapy: Employing drugs that specifically target cancer cells with minimal damage to normal cells.
- Immunotherapy: Enhancing the body’s immune system to combat leukemia.
- Bone Marrow Transplant: Replacing damaged bone marrow with healthy stem cells.
- Surgery: Removal of the spleen may be recommended in some cases.
- Stem Cell Transplant with Chemotherapy: Replacing diseased bone marrow with healthy stem cells after chemotherapy.
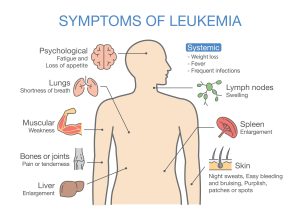
Leukemia Symptoms
- Easy Bruising or Bleeding: Platelet dysfunction makes it difficult for blood to clot, resulting in easy bruising, slow-healing wounds, nosebleeds, and bleeding from gums.
- Frequent Infections: White blood cell abnormalities lead to an increased susceptibility to infections.
- Anemia: Insufficient red blood cells may cause symptoms like faintness, weakness, tiredness, shortness of breath, rapid heartbeat, body aches, and pallor.
- Other Symptoms: Nausea, fever, bone pain, and weight loss may also be observed.
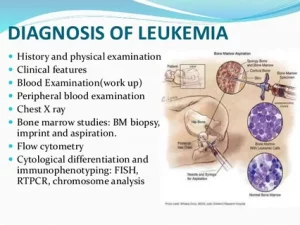
Diagnosis
- Physical Examination: A doctor conducts a thorough physical examination.
- Medical History: Inquires about personal and family medical history.
- Anemia Check: Checks for signs of anemia.
- Blood Testing: Takes blood samples for laboratory testing.
- Bone Marrow Biopsy: A potential recommendation for confirming leukemia type, involving the extraction of bone marrow.
- Diagnostic Tests: Various tests aid in identifying the presence and type of leukemia.
Frequently Asked Questions
- How do you get leukemia?
- Genetic and environmental factors may play a role, and exposure to radiation and toxins can increase the risk.
- Is leukemia a serious cancer?
- Yes, all types of leukemia are serious, but with treatment, survival rates have improved.
- What is the survival rate for leukemia?
- Overall, the 5-year survival rate is 65.7%, varying by leukemia type. Children with ALL have a 90% chance of surviving at least 5 years.
Outlook
The outlook for individuals with leukemia depends on the type, age, and overall health. Treatment can lead to remission, requiring ongoing monitoring to prevent recurrence.
Summary
Leukemia, a cancer affecting blood and bone marrow, has various types with different impacts. While exact causes are unclear, genetic factors and toxin exposure may contribute. Treatment options, including chemotherapy, exist, offering hope for improved survival rates. Regular monitoring is crucial for long-term management.
For more detailed information on leukemia, consult with a healthcare professional.