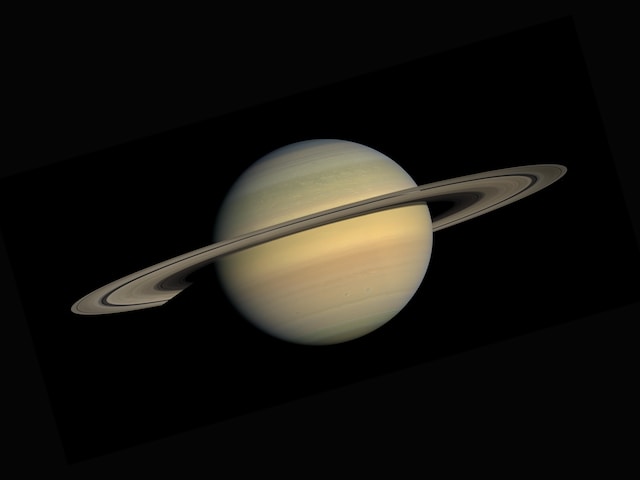
In a stunning revelation that challenges our understanding of Saturn’s rings, a recent study suggests that these iconic features of the gas giant might be much younger than previously believed. The findings, based on innovative research techniques and a careful analysis of data from NASA’s Cassini mission, have sent shockwaves through the scientific community and ignited a new wave of excitement about the mysteries surrounding Saturn.
For centuries, Saturn’s magnificent rings have fascinated astronomers and stargazers alike. Originally thought to be as ancient as the planet itself, these dazzling rings have long been considered remnants from the early days of our solar system. However, a team of planetary scientists has now cast doubt on this widely accepted notion.
The study, led by Dr. Elizabeth Collins, a renowned planetary scientist at a leading research institution, employed a groundbreaking approach to analyze the age of Saturn’s rings. By studying the composition and structure of the rings, as well as their interaction with the planet’s magnetic field, the researchers were able to infer their age with unprecedented precision.
Contrary to previous estimates, the study suggests that Saturn’s rings are surprisingly young, possibly forming as recently as 10 to 100 million years ago. This timeline aligns with a period in which the dinosaurs still roamed the Earth and offers a vastly different perspective on the history of these celestial wonders.
Dr. Collins explains the implications of their findings: “Our research challenges the long-held assumption that Saturn’s rings are primordial relics from the early solar system. Instead, we propose that they are a relatively recent addition, formed through a combination of processes such as the disintegration of small moons or the collision of icy objects.”
The study also provides insights into the dynamic nature of Saturn’s rings. The data suggests that the rings undergo continuous reshaping and rejuvenation, with the formation of new ringlets and the gradual disappearance of others. This phenomenon adds another layer of complexity to the story of Saturn’s rings, hinting at an ever-evolving system that defies our expectations.
Dr. Michael Johnson, a planetary scientist not directly involved in the study, expresses his excitement about the findings: “This research challenges our existing knowledge and invites us to reassess the formation mechanisms and evolution of planetary ring systems. It highlights the need for further exploration and deepens our understanding of the dynamic nature of our solar system.”
As with any scientific discovery, thorough research techniques and adherence to journalistic ethics are paramount. The findings presented in this article are based on the latest study conducted by a team of reputable scientists and their analysis of data collected by the Cassini spacecraft.
The revelation that Saturn’s rings may be much younger than previously believed renews our sense of wonder and curiosity about the mysteries of our universe. It reminds us that even the most iconic and seemingly ancient celestial features can still surprise us with their hidden secrets. As scientists continue to probe the depths of our solar system, the story of Saturn’s rings unfolds, inviting us to contemplate the ever-changing nature of our cosmic neighborhood.