Introduction
Diabetes is one of the most challenging chronic diseases to manage, requiring continuous monitoring, timely intervention, and strict adherence to treatment plans. Traditional diabetes care often depends on periodic blood sugar checks and occasional clinic visits — methods that provide only snapshots of a patient’s health rather than a complete, real-time picture.
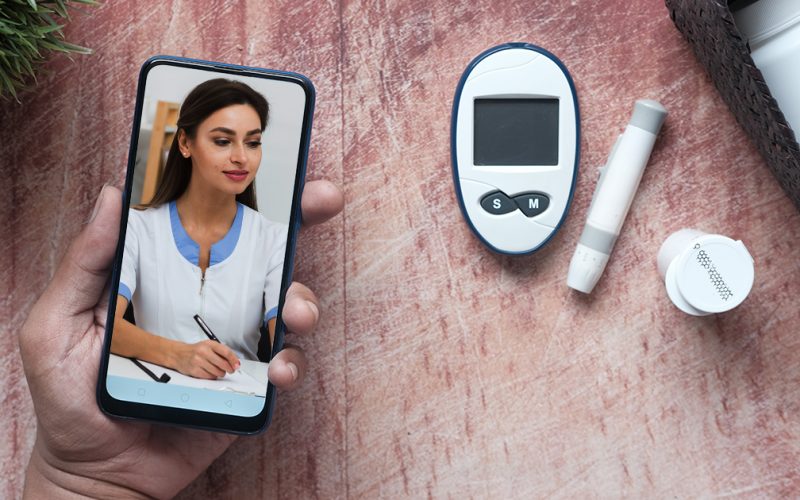
This gap between patient data and timely medical response has given rise to a transformative solution — Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM). By using connected devices and data-driven systems, RPM bridges the distance between patients and healthcare providers, enabling proactive, personalized, and continuous diabetes management.
What Is Remote Patient Monitoring in Diabetes Care?
Remote patient monitoring is a healthcare approach that uses digital devices to collect medical data from patients in their homes. These devices can include glucose meters, blood pressure monitors, wearable sensors, and mobile apps. The data collected is transmitted securely to healthcare providers, who can analyze it and provide timely feedback.
For diabetes patients, RPM offers a way to monitor blood glucose levels continuously or at regular intervals. Doctors can track patterns, detect early warning signs, and adjust treatment plans without requiring frequent in-person visits. Patients also receive reminders, alerts, and educational tips, which encourage better adherence to medications, diet, and lifestyle changes.
Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM) uses smart medical devices, cloud platforms, and mobile apps to collect and transmit real-time patient health data to healthcare professionals. In diabetes care, these devices include:
- Continuous Glucose Monitors (CGMs) that provide 24/7 glucose readings.
- Smart glucometers that sync automatically with mobile apps.
- Smart insulin pens and pumps that record dosage information.
- Wearable fitness trackers that capture physical activity, heart rate, and sleep data.
Together, these technologies create an ecosystem where data flows seamlessly from patients to clinicians, allowing for immediate feedback, better decision-making, and improved long-term outcomes.
Key Ways RPM Enhances Diabetes Management

1. Continuous and Real-Time Glucose Tracking
Unlike traditional finger-prick tests, RPM devices continuously monitor glucose levels, providing a dynamic and accurate view of fluctuations throughout the day. Real-time tracking allows both patients and healthcare providers to detect patterns such as post-meal spikes or night time lows and respond proactively.
With early alerts, patients can make quick adjustments to diet, exercise, or insulin intake — reducing the risk of severe hypoglycemia or hyper glycemia.
2. Personalized and Data-Driven Treatment Plans
Every diabetic patient’s condition is unique. Remote monitoring provides detailed insights into how specific lifestyle factors — such as meals, medication timing, and physical activity — influence blood glucose.
Healthcare providers use this data to tailor treatment plans for each individual, adjusting insulin doses and dietary recommendations based on real-world evidence rather than occasional readings. This personalized approach improves both treatment precision and patient engagement.
3. Early Detection of Complications
Continuous data collection enables physicians to spot warning signs of potential complications before they escalate. For instance, consistent glucose instability may indicate developing insulin resistance, while rising blood pressure readings could signal cardiovascular risk.
Early intervention helps prevent serious complications such as neuropathy, retinopathy, or kidney failure, leading to better long-term outcomes and reduced hospitalizations.
4. Enhanced Patient Engagement and Self-Management
RPM empowers patients to take an active role in managing their diabetes. Mobile health apps display glucose trends, meal logs, and activity reports, making it easier for users to understand how daily habits affect their blood sugar.
Patients receive automated alerts, reminders, and feedback — encouraging accountability and adherence to their care plan. This sense of empowerment boosts confidence and fosters healthier behavioral changes.
5. Improved Communication Between Patients and Providers
Remote monitoring bridges the communication gap between diabetic patients and their care teams. Providers can review patient data in real time, schedule virtual consultations, and send recommendations instantly — without waiting for the next appointment.
This constant connectivity strengthens the doctor-patient relationship, enhances trust, and ensures timely medical intervention when needed.
6. Reduced Emergency Visits and Hospital Readmissions
By providing continuous visibility into a patient’s condition, RPM allows healthcare providers to identify and address potential issues before they become emergencies.
Patients using RPM solutions have shown fewer hospitalizations, emergency room visits, and diabetes-related complications. This not only improves patient safety but also significantly reduces healthcare costs.
7. Data Integration with Electronic Health Records (EHRs)
Modern RPM systems integrate seamlessly with EHR platforms, allowing healthcare providers to access complete patient histories in one place. This integration enhances coordination among physicians, endocrinologists, and diabetes educators, ensuring holistic care management.
Such interoperability ensures that all stakeholders — from specialists to caregivers — have access to accurate, up-to-date patient data for better collaboration and decision-making.
The Role of Technology in Remote Diabetes Care
Technology has become the driving force behind modern diabetes management, enabling a shift from reactive care to proactive, data-driven treatment. Through Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM), patients with diabetes can now benefit from real-time tracking of their blood glucose levels, medication adherence, and lifestyle patterns using smart, connected devices.
Continuous Glucose Monitors (CGMs), smart glucometers, and wearable sensors automatically collect health data and transmit it to cloud-based platforms accessible to both patients and clinicians. This constant data flow allows healthcare providers to monitor trends, detect anomalies, and adjust treatment plans instantly — without requiring in-person visits.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and machine learning further enhance remote diabetes care by analyzing large data sets to predict glucose fluctuations, identify risk factors, and recommend preventive actions. Integration with mobile apps empowers patients with personalized insights, reminders, and feedback, fostering better self-management.
Moreover, secure data sharing and interoperability with Electronic Health Records (EHRs) ensure continuity of care across the healthcare ecosystem.
In essence, technology bridges the gap between patients and providers, ensuring continuous engagement, faster interventions, and improved clinical outcomes. By combining innovation and accessibility, digital health tools are redefining how diabetes is managed in the connected care era.
Benefits for Patients and Providers
For Patients:
- Improved quality of life through proactive management.
- Fewer complications and hospital visits.
- Greater convenience and control over daily health decisions.
For Healthcare Providers:
- Access to real-time, actionable data.
- Streamlined workflows through automation.
- Enhanced efficiency and better patient satisfaction rates.
Implementing an Effective RPM Program for Diabetes

To build a successful remote monitoring system, healthcare organizations should focus on:
- Selecting interoperable and user-friendly monitoring devices.
- Ensuring patient education and onboarding for effective device use.
- Integrating RPM data with clinical systems for unified visibility.
- Maintaining compliance with data privacy standards (HIPAA, GDPR).
- Partnering with experienced technology providers to ensure scalability and security.
Collaborating with a trusted patient monitoring software development partner helps organizations implement customized, compliant, and data-driven RPM solutions tailored to their patient population.
Challenges and Considerations
While RPM offers many benefits, there are challenges to consider:
- Technology Access and Literacy: Not all patients have access to smartphones, internet, or wearable devices. Additionally, some may struggle to use technology effectively. Providing user-friendly devices and training is essential.
- Data Security: Medical data is sensitive, so ensuring secure transmission and storage is critical. Healthcare providers must comply with privacy regulations to protect patient information.
- Cost and Insurance Coverage: The cost of RPM devices and services can vary. Insurance coverage may not always be available, so patients need to consider affordability. However, in the long term, reducing hospitalizations and complications can offset these costs.
- Integration with Traditional Care: RPM should complement, not replace, traditional diabetes care. Patients still need periodic in-person checkups, lab tests, and consultations to ensure comprehensive management.
The Future of Diabetes Care with RPM
As technology advances, remote patient monitoring is expected to play an even larger role in diabetes management. Emerging trends include:
- Artificial Intelligence: AI algorithms can predict blood sugar fluctuations and provide automated recommendations.
- Telehealth Integration: Seamless integration with telemedicine platforms allows for instant virtual consultations.
- Wearable Innovation: New wearable devices will offer more accurate, continuous monitoring of multiple health parameters.
- Personalized Digital Coaching: AI-driven coaching can provide personalized guidance on diet, exercise, and medication adherence.
The future points toward a more connected, data-driven, and patient-centered approach to diabetes management, where RPM plays a central role.
Conclusion
Remote Patient Monitoring is transforming diabetes management by making care continuous, connected, and data-driven. It shifts the focus from reactive treatment to proactive prevention — improving patient outcomes, reducing costs, and enhancing quality of life.
With real-time insights, seamless communication, and personalized care, RPM empowers both patients and clinicians to manage diabetes with greater precision and confidence. As healthcare moves toward a connected future, remote monitoring stands as one of the most powerful innovations shaping modern chronic disease management.