Demystifying Vegan Nutrition: Are Supplements Necessary?
What is a Vegan Diet?
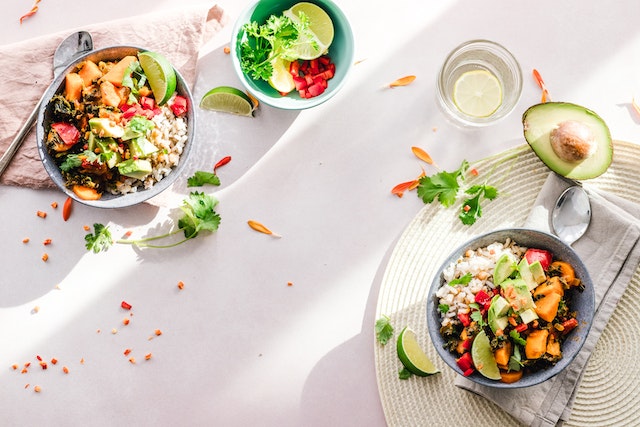
A Vegan Nutrition diet is centered around plant-derived foods, including soups, stews, stir-fries, salads, and various plant-based versions of traditional favorites like pizza, tacos, burgers, and desserts.
The Components of a Healthful Vegan Diet
A healthful vegan diet is comprised of four food groups: legumes, nuts, and seeds; grains; vegetables; and fruits. These groups provide essential nutrients and should be part of a balanced vegan meal plan.
- Legumes, Nuts, and Seeds: This group includes beans, lentils, nuts, seeds, and soy products, offering protein, fiber, minerals, B vitamins, and essential fatty acids.
- Grains: Whole grains like brown rice, oats, and quinoa provide B vitamins, fiber, minerals, and antioxidants. They are preferable to refined grains for optimal nutrition.
- Vegetables: Eating a variety of colorful vegetables ensures a diverse intake of protective nutrients, especially from calcium-rich leafy greens.
- Fruits: Fruits, particularly citrus fruits and berries, offer vitamin C and antioxidants. Whole fruits are preferred over juices for the added dietary fiber.

Photo by Ella Olsson: https://www.pexels.com/photo/photo-of-vegetable-salad-in-bowls-1640770/
Understanding Key Nutrients for Vegans
To maintain overall health, vegans need to be mindful of specific nutrients that may be lacking in their diet. These include vitamin B12, vitamin D, omega-3 fatty acids, and iodine, along with calcium, iron, and protein.
- Vitamin B12: Crucial for red blood cell formation and neurological function, B12 is primarily found in animal products. Vegans can meet their B12 needs through supplements or fortified foods.
- Vitamin D: Essential for bone health and immune function, vitamin D can be synthesized from sun exposure but is also found in few plant foods. Supplementation may be necessary, especially in areas with limited sunlight.
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Vital for brain function and heart health, vegans can obtain omega-3s from ALA sources like flaxseed, hemp, and walnuts, or through vegan DHA supplements.
- Iodine: Important for thyroid function and brain development, vegans should ensure adequate iodine intake through iodized salt, sea vegetables, and supplements if needed.
Ensuring a Well-Balanced Vegan Lifestyle
A healthful vegan lifestyle involves careful consideration of nutrient intake. Here are some tips to maintain a balanced vegan diet:
- Plant-Based Sources of Key Nutrients: Incorporate foods rich in essential nutrients, such as B12-fortified foods, fortified plant milks, and a variety of ALA sources.
- Choosing the Right Vegan Supplements: Consider vegan vitamin B12, vitamin D2 or D3 supplements, and DHA supplements if necessary. Always consult a healthcare provider for personalized recommendations.
- The Importance of Regular Health Checkups: Periodic blood tests can help monitor nutrient levels and ensure any deficiencies are addressed promptly.
In conclusion, a well-planned vegan diet can be healthful and nutritionally adequate for all stages of life. By understanding key nutrients and incorporating diverse plant-based foods and supplements when needed, vegans can thrive on their chosen dietary path.