Meet Dr. Stella Jones: Unveiling the Universe’s Secrets
Dr. Stella Jones, a renowned astrophysicist with a keen eye for the cosmos, has dedicated her career to unraveling the mysteries of our solar system. Particularly enthralled by the giant planet Jupiter, Dr. Jones utilizes data captured by telescopes like Hubble to unveil the wonders of this celestial giant for astronomy enthusiasts and the general public.
A Colossal Guardian Revealed: Unveiling Jupiter’s Majesty
Jupiter, the undisputed king of our solar system, reigns supreme with its awe-inspiring size and dynamic atmosphere. Boasting a mass 318 times that of Earth, Jupiter’s presence has captivated astronomers for centuries. Its swirling storms, vibrant bands of color, and captivating dance of moons paint a spectacle unlike any other in our cosmic neighborhood.
For centuries, astronomers relied on Earth-based telescopes for glimpses of Jupiter. However, these observations were limited by our atmosphere, blurring details and hindering a deeper understanding of the gas giant.
Hubble’s Unwavering Gaze: Piercing the Veil of Distance
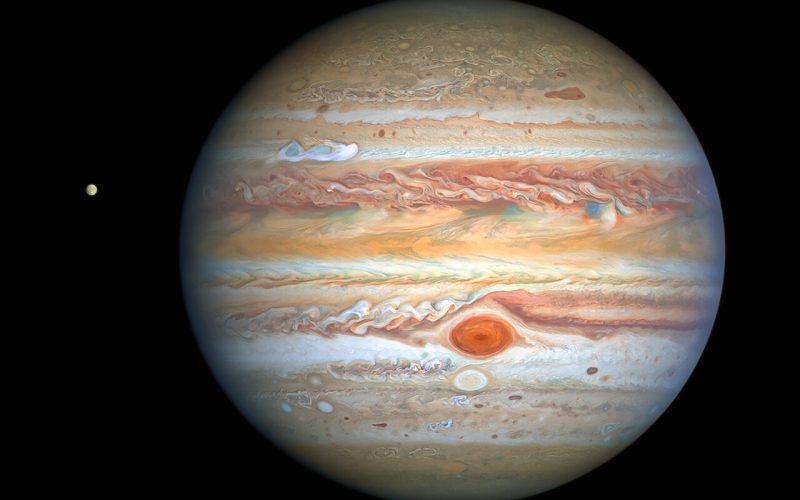
The launch of the Hubble Space Telescope in 1990 marked a turning point in our exploration of Jupiter. Positioned above the Earth’s atmosphere, Hubble boasts a clear, unobstructed view of the cosmos. This marvel of modern astronomy has revolutionized our understanding of the giant planet, providing unparalleled close-up views that reveal details invisible from ground-based telescopes.
Hubble’s sharp gaze allows us to appreciate the intricate details of Jupiter’s atmosphere. The iconic Great Red Spot, a colossal anticyclonic storm raging for centuries, is just one of the many captivating features brought to light by Hubble. With its swirling vortex spanning twice the diameter of Earth, the Great Red Spot is a testament to the dynamic nature of Jupiter’s atmosphere.

A Symphony of Color: Unveiling Jupiter’s Vibrant Bands
One of the most striking features of Jupiter, visible even through small telescopes, is its colorful atmosphere. Hubble observations have revealed this mesmerizing tapestry in unprecedented detail. The planet’s vibrant bands, swirling with ammonia, hydrogen, and other atmospheric elements, offer a glimpse into Jupiter’s dynamic composition.
These colorful bands are not merely aesthetic features; they represent zones of rising and descending atmospheric currents. The lighter-colored zones are regions where warm, less dense air rises, while the darker bands represent areas of cooler, denser air sinking. This continuous circulation creates a mesmerizing interplay of color and movement across Jupiter’s atmosphere.
The Stormy Ballet: Witnessing Jupiter’s Dynamic Atmosphere
Jupiter’s atmosphere is a place of constant change, a celestial stage where a dynamic ballet of storms unfolds. Hubble observations have played a crucial role in revealing the emergence of new storms, the dissipation of old ones, and the ever-shifting patterns of the planet’s swirling bands. This continuous dance of atmospheric phenomena paints a picture of a restless and ever-evolving world.
One of the most captivating aspects of Jupiter’s atmosphere is the formation of the Great Red Spot’s junior counterparts. These smaller anticyclonic storms, often oval-shaped and white in color, can erupt and persist for months or even years before fading away. Hubble observations have documented the birth, growth, and eventual disappearance of these fascinating temporary storms, providing valuable insights into Jupiter’s atmospheric dynamics.

A Captivating Court: Exploring Jupiter’s Moon System
Jupiter is not a solitary giant in its celestial realm. The planet is orbited by a captivating court of moons, each with its own unique characteristics. The four largest moons, known as the Galilean moons – Io, Europa, Ganymede, and Callisto – were discovered by Galileo Galilei in 1610. These moons offer a glimpse into the diversity of celestial bodies within our solar system.
Io, the innermost Galilean moon, is the most volcanically active body in our solar system. Hubble observations have revealed towering plumes of volcanic sulfur spewing from Io’s surface, painting a picture of a world in constant flux. Europa, on the other hand, harbors a vast subsurface ocean, raising intriguing questions about the potential for extraterrestrial life. Ganymede, the largest moon in our solar system, even boasts a tenuous atmosphere of oxygen.
Hubble observations have provided valuable insights into the geology and potential habitability of these moons. Studies of Europa’s icy surface, for instance, have revealed evidence of cracks and fissures that may allow plumes of water to erupt from its subsurface ocean. These findings have fueled speculation about the possibility of a liquid water environment existing beneath Europa’s icy crust, a potential habitat for microbial life as we know it.
A Celestial Dance: Comparing Jupiter and Earth
While Jupiter reigns supreme in size and grandeur, comparing it to our own planet Earth reveals fascinating insights into the diversity of worlds within our solar system.
| Feature | Jupiter | Earth |
|---|---|---|
| Size | 318 times Earth’s mass | 1 Earth mass |
| Atmosphere | Primarily hydrogen and helium | Nitrogen and oxygen |
| Temperature | Average -145°C (-233°F) | Average 15°C (59°F) |
| Rings | Faint rings of dust particles | No rings |
As the table highlights, Jupiter is a gas giant composed primarily of hydrogen and helium, with an average temperature far colder than Earth’s. Earth, on the other hand, boasts a rocky surface and an atmosphere rich in nitrogen and oxygen, crucial for life as we know it. Despite these vast differences, studying Jupiter offers valuable insights into the formation and evolution of our solar system. By understanding the composition and processes at play within Jupiter, we gain a deeper appreciation for the unique conditions that fostered life on Earth.

Jupiter’s Legacy: A Beacon of Discovery and Inspiration
The study of Jupiter is not merely an exercise in celestial observation; it is a gateway to unlocking the secrets of our solar system’s formation and evolution. By studying Jupiter’s atmosphere and composition, we gain a deeper understanding of the processes that shaped our own planet Earth. The swirling storms and vibrant bands of Jupiter offer clues about the early stages of our solar system, providing insights into the conditions that led to the birth of planets like Earth.
Furthermore, Jupiter’s captivating moons, particularly Europa with its potential subsurface ocean, raise intriguing questions about the possibility of extraterrestrial life. The exploration of Jupiter, fueled by observations from Hubble and other space telescopes, inspires us to push the boundaries of our knowledge and search for life beyond our planet.
Conclusion: Unveiling the Universe, One Observation at a Time
Jupiter’s ever-changing beauty, captured by the unwavering gaze of Hubble, serves as a constant reminder of the universe’s boundless wonders. Each observation unveils new details about the giant planet, its dynamic atmosphere, and its captivating moon system. These discoveries fuel our curiosity and inspire further exploration, propelling us forward in our quest to understand the cosmos.
As Dr. Stella Jones emphasizes, “Jupiter is a celestial teacher, offering valuable lessons about planetary formation, atmospheric dynamics, and the potential for life beyond Earth. Hubble’s observations have been instrumental in unlocking these secrets, and future space missions promise to reveal even more about this captivating giant.”
The exploration of Jupiter is a testament to the enduring human spirit of curiosity and discovery. As we continue to unravel the mysteries of this celestial giant, one observation at a time, we gain a deeper appreciation for our place in the vast and awe-inspiring universe.