The Gut Microbiome Explained
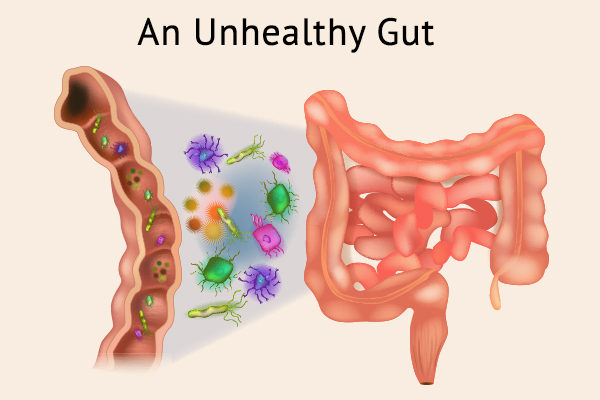
Your gut is a bustling ecosystem, home to trillions of microorganisms that play a crucial role in various bodily functions. This community of bacteria, fungi, parasites, and viruses, collectively known as the gut microbiome, resides mainly in the large and small intestines but is also found throughout the body. Led by experts like Rouenne Seeley, D.O., a board-certified gastroenterologist, it’s understood that this microbiome regulates digestion, supports the immune system, and contributes to overall health Unhealthy Gut.
Signs of an Unhealthy Gut
Recognizing the signs of an unhealthy gut is vital for maintaining overall well-being. Symptoms such as gas, bloating, stomach pain, and irregular bowel movements could indicate an imbalance in the gut microbiome. Additionally, unintentional weight fluctuations, skin issues like acne or eczema, mood swings, and fatigue may also be linked to poor gut health. By being aware of these signs, individuals can take proactive steps to address gut imbalances and improve their health.
- Gas and Bloating: Poor digestion and stomach discomfort are common indicators of an unhealthy gut. When the bacteria in the gut struggle to break down certain foods, it can lead to excess gas production and bloating.
- Weight Fluctuations: Unintentional weight gain or loss, not attributed to changes in diet or exercise, may signal an imbalance in the gut microbiome. Certain bacteria can affect how calories are absorbed from food, potentially influencing weight regulation.
- Skin Issues: The connection between gut health and skin conditions like acne, rosacea, and eczema is increasingly recognized. Imbalances in the gut microbiome can trigger inflammation, contributing to skin problems.
- Moodiness and Irritability: The gut-brain axis links gut health to mental well-being. Disruptions in the gut microbiome can impact neurotransmitter production, influencing mood, and cognitive function.
- Fatigue or Insomnia: Poor gut health can disrupt sleep patterns, leading to fatigue or insomnia. Serotonin, a neurotransmitter crucial for mood and sleep regulation, is primarily produced in the gut.
- Sugar Cravings: Imbalances in the gut microbiome can influence food cravings, particularly for sugary foods. Certain bacteria thrive on sugar, perpetuating a cycle of unhealthy eating habits.
How Gut Health Impacts Weight and Skin
Maintaining a healthy gut microbiome is essential for weight management and skin health. Studies suggest that the diversity and balance of gut bacteria play a significant role in metabolism, nutrient absorption, and inflammation regulation. Individuals with a balanced gut microbiome may find it easier to maintain a healthy weight and have clearer, healthier skin.
- Weight Regulation: The gut microbiome influences energy extraction from food and the storage of fat. Imbalances in gut bacteria have been linked to obesity and metabolic disorders.
- Skin Health: Research indicates that gut health directly affects skin conditions like acne, eczema, and psoriasis. By supporting a diverse and balanced gut microbiome, individuals can improve skin clarity and reduce inflammation.

Mental Health and Gut Connection
The gut-brain axis facilitates communication between the gut and the brain, impacting mental health and cognitive function. Studies have demonstrated a bidirectional relationship, with gut health influencing mood and stress levels, and vice versa. Disruptions in the gut microbiome have been associated with mood disorders such as anxiety and depression.
- Anxiety and Depression: Imbalances in gut bacteria can trigger inflammatory responses and affect neurotransmitter production, contributing to mood disorders. Anxiety and depression are commonly observed in individuals with gut dysbiosis.
- Cognitive Function: The gut microbiome influences neurotransmitter levels and neuroinflammation, which can impact cognitive function and behavior. Maintaining a healthy gut may support optimal brain health and cognitive performance. Explore More About Different Health Issues Like (How Much Sleep Do You Need)

Improving Gut Health: Practical Tips
Enhancing gut health involves adopting lifestyle changes and dietary habits that promote a diverse and balanced gut microbiome. Simple yet effective strategies include increasing fiber intake, staying hydrated, exercising regularly, managing stress levels, and prioritizing sleep. Additionally, certain diets, such as the Mediterranean diet and low-FODMAP diet, have been shown to support gut health and overall well-being.
Do’s and Don’ts for a Healthy Gut
Promoting gut health requires mindful choices in diet and lifestyle. Incorporating fiber-rich foods, hydrating adequately, and engaging in regular physical activity are essential for maintaining a healthy gut microbiome. Conversely, habits like smoking and consuming a diet high in processed foods, sugar, and saturated fats can disrupt gut balance and contribute to inflammation.
- Do increase fiber intake and hydration: Fiber-rich foods and adequate hydration support digestive health and promote a diverse gut microbiome.
- Don’t smoke or consume excessive meat, sugar, fat, and salt: Smoking and a diet high in processed foods can negatively impact gut health and increase the risk of gut-related disorders.

- Do consider low-FODMAP and Mediterranean diets: These diets focus on nutrient-rich foods and have been shown to support gut health and overall well-being.
- Do prioritize regular exercise: Physical activity can enhance gut microbial diversity and promote optimal digestive function.

| Sign of Unhealthy Gut | Symptoms |
|---|---|
| Gas and Bloating | Poor digestion, stomach pain |
| Weight Fluctuations | Unintentional weight gain/loss |
| Skin Issues | Acne, rosacea, eczema |
| Moodiness and Irritability | Anxiety, depression |
| Fatigue or Insomnia | Disrupted sleep patterns |
| Sugar Cravings | Increased desire for sugary foods |
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the complex interplay between gut health and overall well-being is essential for maintaining a healthy lifestyle. By recognizing the signs of an unhealthy gut and implementing practical strategies to support gut health, individuals can take proactive steps towards optimizing their health and well-being. Consultation with healthcare professionals can provide personalized guidance and support on the journey to better gut health.