Introduction:
As concerns about climate change continue to grow, individuals around the world are seeking ways to reduce their environmental impact. One emerging dietary trend that has gained attention is the climatarian diet. In this article, we explore what the climatarian diet entails and why it is considered beneficial for the planet.
1. Defining the Climatarian Diet:
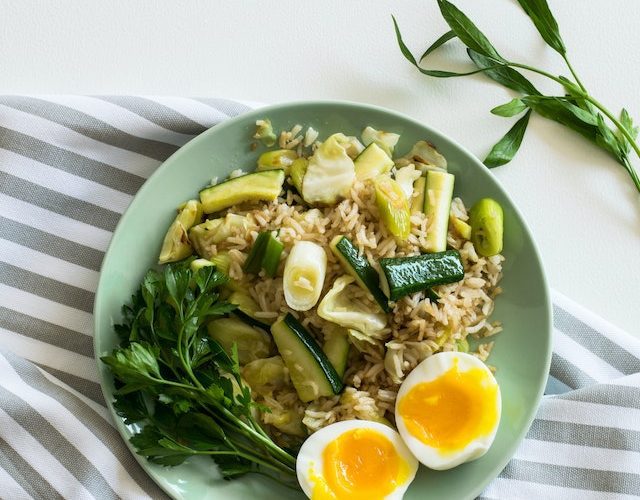
The climatarian diet is a conscious eating approach that prioritizes the environmental impact of food choices. It involves selecting foods that have a lower carbon footprint and minimizing the consumption of high-emission foods, such as meat and dairy products. The goal is to reduce greenhouse gas emissions associated with food production and promote sustainable farming practices.
2. Emphasizing Plant-Based Foods:
A key aspect of the climatarian diet is the emphasis on plant-based foods. Fruits, vegetables, legumes, whole grains, and nuts form the foundation of this eating pattern. These foods generally have lower carbon footprints compared to animal-based products and contribute to a more sustainable food system.
3. Minimizing Meat and Dairy Consumption:
While the climatarian diet does not require complete elimination of meat and dairy, it encourages reducing their consumption. Livestock production, particularly beef and lamb, is associated with significant greenhouse gas emissions, deforestation, and water usage. By reducing meat and dairy intake, individuals can help mitigate these environmental impacts.
4. Choosing Sustainable Protein Sources:
In place of animal-based proteins, climatarians opt for sustainable alternatives such as plant-based proteins, including tofu, tempeh, legumes, and quinoa. These options have lower environmental footprints and often provide comparable nutritional value.
5. Prioritizing Local and Seasonal Foods:
Another important aspect of the climatarian diet is the emphasis on local and seasonal foods. Choosing locally sourced produce reduces the carbon emissions associated with long-distance transportation, supports local farmers, and promotes regional food resilience. Seasonal foods also tend to have a smaller environmental footprint as they require less energy-intensive cultivation practices.
6. Reducing Food Waste:
The climatarian diet encourages mindful consumption and aims to minimize food waste. Food waste contributes to greenhouse gas emissions when it decomposes in landfills. By planning meals, utilizing leftovers, and composting organic waste, climatarians can significantly reduce their ecological impact.
7. Supporting Sustainable Agriculture:
Adopting a climatarian diet involves supporting sustainable agricultural practices. This includes favoring organic and regenerative farming methods that prioritize soil health, biodiversity, and natural resource conservation. By choosing foods produced through sustainable practices, individuals contribute to the preservation of ecosystems and the reduction of chemical inputs.
Conclusion:
The climatarian diet offers a practical and accessible way for individuals to make a positive impact on the planet through their food choices. By emphasizing plant-based foods, reducing meat and dairy consumption, choosing sustainable protein sources, favoring local and seasonal produce, and reducing food waste, climatarians can significantly reduce their carbon footprint. Embracing a climatarian diet not only benefits the environment but also promotes healthier eating patterns and supports a more sustainable and resilient food system. As more people recognize the urgent need to address climate change, the climatarian diet serves as a valuable tool for individuals to contribute to a more sustainable future.