What is Astrophysics?
Astrophysics is the branch of astronomy that deals with the physical properties and processes of celestial bodies and the universe as a whole. It explores the mysteries of space, from the smallest subatomic particles to the largest galaxies.
Importance of Astrophysics
Astrophysics helps us understand the fundamental laws of nature and the origins of the universe. It contributes to advancements in technology, inspires curiosity and wonder, and expands our perspective of the cosmos.
The Birth of Stars
Nebulae: The Cosmic Nurseries
Nebulae are vast clouds of dust and gas scattered throughout space. Within these nebulae, gravitational forces cause the gas and dust to clump together, forming regions where new stars are born.
Protostars: The Early Stages
As the gas and dust continue to collapse under gravity, a protostar begins to form at the center of the nebula. Protostars are young stars in the early stages of formation, where nuclear fusion has not yet ignited.
Stellar Evolution
Over millions of years, protostars evolve into main sequence stars, where nuclear fusion ignites in their cores, producing energy and heat. The life cycle of a star is determined by its mass, with larger stars burning brighter and hotter, but also consuming their fuel more rapidly.
The Life and Death of Stars
Main Sequence Stars
Main sequence stars, like our sun, spend the majority of their lives fusing hydrogen into helium in their cores. This process creates the energy that sustains the star and keeps it shining for billions of years.
Supernovae: Explosive Endings
When massive stars exhaust their nuclear fuel, they undergo a catastrophic explosion known as a supernova. During a supernova, the star releases an immense amount of energy, producing elements essential for life and scattering them into space.
White Dwarfs and Black Holes
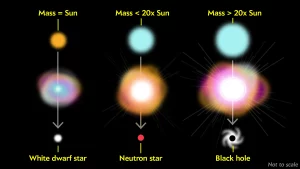
The remnants of supernovae vary depending on the mass of the original star. Smaller stars may collapse into dense white dwarfs, while the most massive stars may become black holes, regions of spacetime where gravity is so intense that nothing can escape, not even light.
Galaxies: Cosmic Cities
Types of Galaxies
Galaxies come in a variety of shapes and sizes, ranging from spiral and elliptical to irregular. Each galaxy contains billions to trillions of stars, as well as dust, gas, and dark matter.
The Milky Way: Our Home
The Milky Way is a barred spiral galaxy containing our solar system and billions of other stars. It is just one of billions of galaxies in the observable universe.
Andromeda: A Neighbor in Space
The Andromeda Galaxy is the closest spiral galaxy to the Milky Way and is on a collision course with our galaxy. In approximately 4 billion years, the two galaxies will merge, forming a new, larger galaxy.
Dark Matter and Dark Energy
Unseen Forces in the Universe
Dark matter and dark energy are two mysterious components that make up the majority of the universe’s mass-energy content. While their exact nature remains unknown, their presence is inferred through their gravitational effects on visible matter.
The Mystery of Dark Matter
Dark matter is believed to be a form of matter that does not emit, absorb, or reflect light, making it invisible and undetectable by traditional means. Its gravitational influence is essential for the formation and stability of galaxies and galaxy clusters.
Dark Energy: The Accelerating Universe
Dark energy is a mysterious force that is causing the expansion of the universe to accelerate. Its existence challenges our understanding of fundamental physics and cosmology, and its origins remain one of the greatest mysteries in astrophysics.
The Expanding Universe
The Big Bang Theory
The prevailing cosmological model suggests that the universe began as a hot, dense singularity approximately 13.8 billion years ago. From this initial state, the universe expanded and cooled, eventually giving rise to the vast cosmos we observe today.
Cosmic Microwave Background Radiation
Evidence for the Big Bang comes from the cosmic microwave background radiation, a faint glow that fills the universe and is a remnant of the early hot, dense state. This radiation provides valuable clues about the universe’s early history and evolution.
The Fate of the Universe
The ultimate fate of the universe depends on its density and the balance between gravitational attraction and dark energies’ repulsive force. Depending on these factors, the universe may continue to expand indefinitely or eventually collapse in a “Big Crunch.”
Exoplanets: Worlds Beyond Our Solar System

Hunting for Exoplanets
In recent years, astronomers have discovered thousands of exoplanets orbiting stars outside our solar system. These planets come in a variety of sizes, compositions, and orbital configurations, sparking interest in the search for habitable worlds.
Alien Worlds and Habitability
The study of exoplanets offers insights into the diversity of planetary systems and the conditions necessary for life to thrive. Scientists are particularly interested in identifying Earth-like planets within the habitable zones of their parent stars.
The Search for Extraterrestrial Life
While no definitive evidence of extraterrestrial life has been found, the discovery of exoplanets has renewed interest in the possibility of life beyond Earth. Future missions and telescopes may provide further clues about the prevalence of life in the universe.
The Role of Astrophysics in Advancing Technology
Space Exploration
Astrophysics drives technological advancements in space exploration, enabling missions to distant planets, moons, and celestial bodies. Technologies such as telescopes, satellites, and spacecraft continue to expand our understanding of the universe.
Astronomy and Communication
Astrophysical research has also contributed to advancements in communication technologies, including satellite communication, GPS systems, and internet connectivity. These technologies have revolutionized how we communicate and navigate the world.
Astrophysics and Medicine
Astrophysical techniques and technologies have applications in medical imaging, diagnostics, and treatment. For example, imaging techniques developed for studying distant galaxies are now used in medical imaging to detect and diagnose diseases.
Conclusion: Embracing the Marvels of Astrophysics
Astrophysics offers a window into the vastness and complexity of the cosmos, from the birth of stars to the mysteries of dark matter and dark energy. By studying the universe, we gain insights into our place in the cosmos and advance technology for the benefit of humanity.
FAQs
What is the difference between astronomy and astrophysics?
Astronomy focuses on observing and studying celestial objects, while astrophysics delves deeper into the physical processes and properties of those objects.
How do astronomers study distant galaxies?
Astronomers use telescopes equipped with various instruments to observe light from distant galaxies, allowing them to analyze their composition, structure, and motion.
What is the significance of the cosmic microwave background radiation?
The cosmic microwave background radiation provides valuable insights into the early universe, including its temperature, density fluctuations, and overall composition.
Why is the study of exoplanets important?
Studying exoplanets helps us understand the prevalence and diversity of planetary systems in the universe, as well as the potential for life beyond Earth.
How does astrophysics contribute to technological advancements?
Astrophysics drives innovations in space exploration, communication, and medical imaging, leading to technological breakthroughs that benefit society as a whole.












