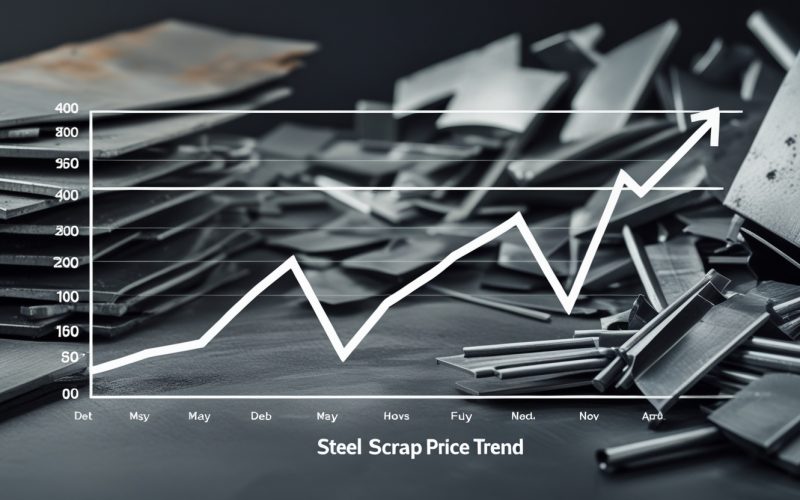
The global steel scrap market is a complex and ever-evolving sector influenced by a range of economic, political, and environmental factors. While steel scrap is traded worldwide, the price trends vary significantly from one region to another due to local market conditions, regulatory environments, and supply chain dynamics. Understanding these regional differences is essential for buyers, sellers, and stakeholders who want to optimize their strategies in 2025 and beyond.
This article explores the key factors behind the regional differences in steel scrap price trends and provides a comprehensive overview of what is driving prices in major markets globally.
Why Do Steel Scrap Prices Vary Regionally?
Steel scrap pricing is shaped by both global and regional forces. Although the overall demand for steel and the cost of production materials set a baseline, localized conditions often lead to divergent pricing trends. Several critical factors explain these regional variations:
- Supply and demand balance within the region
- Government policies, including export restrictions and tariffs
- Currency fluctuations impacting import/export competitiveness
- Infrastructure for collection, sorting, and processing scrap
- Energy costs and labor market conditions
- Environmental regulations and sustainability targets
By analyzing these variables across different regions, market participants can better understand price behavior and forecast future trends.
Asia-Pacific: Strong Demand Meets Supply Constraints
The Asia-Pacific region remains the largest consumer of steel scrap globally, driven by rapid industrialization and urbanization. Countries like India, China, and Southeast Asian nations are major players shaping the regional scrap price landscape.
Key Market Dynamics in 2025:
- India is emerging as a significant importer of steel scrap due to ongoing infrastructure expansion and increasing adoption of electric arc furnace (EAF) technology. India’s domestic scrap generation is insufficient to meet its steel production needs, so it relies heavily on imports.
- China, historically the world’s largest scrap importer, has tightened its import policies to promote domestic recycling industries and meet stringent environmental goals. This has led to reduced scrap inflows and increased demand for locally sourced scrap.
- Southeast Asian countries, including Vietnam, Thailand, and Indonesia, are experiencing increased steel production capacity, pushing scrap demand higher. However, scrap collection infrastructure remains underdeveloped, contributing to tight supply.
Impact on Prices:
These factors combined have led to generally higher scrap prices in Asia-Pacific compared to other regions. Import dependency, logistical challenges, and rising energy costs contribute to price volatility. Furthermore, currency fluctuations, especially against the U.S. dollar, affect import costs and pricing strategies.
Europe: Green Policies and Premium Prices
Europe’s steel scrap market is distinct due to stringent environmental regulations and an aggressive transition toward sustainable steel production.
Key Market Dynamics in 2025:
- The European Union (EU) has implemented carbon pricing and emissions reduction targets that incentivize the use of recycled steel scrap over virgin iron ore. This policy framework boosts demand for high-quality scrap.
- Several countries have imposed export restrictions on steel scrap to retain material for domestic consumption and ensure supply for green steelmakers.
- Europe boasts sophisticated scrap collection and recycling networks, producing high-quality grades that command premium prices.
Impact on Prices:
Due to limited scrap availability and strong domestic demand, steel scrap prices in Europe are among the highest globally. Premium grades, such as shredded scrap, especially command a price premium. High energy and labor costs also contribute to the overall elevated pricing environment.
North America: Stable Supply with Export Opportunities
North America’s steel scrap market is characterized by a mature recycling ecosystem and relatively stable demand.
Key Market Dynamics in 2025:
- The U.S. and Canada have well-established scrap collection and processing systems, supplying a steady flow of quality scrap to domestic steel mills, particularly electric arc furnace (EAF) producers.
- North America benefits from geographic proximity to both export markets and scrap-consuming regions like Mexico.
- The strength of the U.S. dollar influences export competitiveness, sometimes making North American scrap more expensive for foreign buyers.
Impact on Prices:
Steel scrap prices in North America tend to be more stable than in Asia or Europe, but export demand from Asia and Mexico has put upward pressure on prices. Efficient logistics and processing infrastructure help maintain supply consistency.
Middle East and North Africa (MENA): Import Reliance and Volatility
The MENA region is a significant steel producer but relies heavily on imported steel scrap to meet its production demands.
Key Market Dynamics in 2025:
- Countries such as Turkey, Egypt, and the United Arab Emirates (UAE) have robust steel manufacturing sectors that depend on scrap imports.
- Political instability, currency volatility, and logistical challenges often disrupt supply chains and affect pricing.
- The region’s growing infrastructure projects continue to boost steel demand, intensifying competition for scrap.
Impact on Prices:
Prices in the MENA region are generally high and volatile, influenced by global price benchmarks but adjusted for local risk factors, such as port delays, currency depreciation, and political uncertainty.
Latin America: Growing Demand Amid Economic Challenges
Latin America’s steel scrap market is marked by a mixture of growing demand and economic uncertainty.
Key Market Dynamics in 2025:
- Infrastructure investment in countries like Brazil, Mexico, and Argentina is driving demand for steel products, which in turn fuels scrap consumption.
- Domestic scrap availability varies widely across countries, with some relying on imports to fill gaps.
- Exchange rate fluctuations and political factors introduce uncertainty into the market.
Impact on Prices:
Steel scrap prices in Latin America can be highly variable. Brazil’s well-developed recycling industry provides some stability, while other countries experience more pronounced price swings depending on import dependency and economic conditions.
How Buyers and Sellers Can Navigate Regional Differences
For Buyers:
- Monitor regional price indexes and market reports regularly to stay informed on supply-demand balances and price movements.
- Diversify sourcing by considering multiple regions to hedge against supply disruptions and price spikes.
- Negotiate flexible contracts that account for currency fluctuations and regulatory changes.
For Sellers:
- Stay abreast of local regulations, including export controls and environmental standards that can impact trade flows.
- Invest in quality processing and sorting technologies to produce premium scrap grades attractive to global buyers.
- Implement currency risk management strategies when engaging in international transactions.
Conclusion
The steel scrap price trend in 2025 reflects a complex interplay between global demand drivers and deeply rooted regional market factors. Asia-Pacific’s booming industrial growth, Europe’s green policies, North America’s stable supply, MENA’s import reliance, and Latin America’s mixed economic backdrop all create distinct price environments.
For stakeholders in the steel scrap market, recognizing and adapting to these regional differences is critical for strategic decision-making. By leveraging localized insights and staying informed on global trends, both buyers and sellers can optimize their operations and navigate the evolving steel scrap landscape with confidence.
Read Our : finance blog