Introduction
In the realm of wireless communication systems, the integration of simultaneous wireless information and power transfer (SWIPT) with non-orthogonal multiple access (NOMA) has emerged as a promising technique. This fusion aims not only to enhance spectral efficiency but also to enable energy harvesting, thereby revolutionizing the efficiency paradigm of wireless networks.
Understanding SWIPT-NOMA
Merging Data and Power Transmission
Simultaneous Wireless Information and Power Transfer (SWIPT) is a pioneering technology that allows wireless devices to receive both data and energy simultaneously over the same radio frequency signals. By leveraging this technology, devices can harvest energy from the radio signals they receive, in addition to decoding the information being transmitted.
Non-Orthogonal Multiple Access
Non-Orthogonal Multiple Access (NOMA) is a multiple access technique where multiple users share the same time-frequency resource, but with different power levels or codebooks. This enables users to be served simultaneously, enhancing spectral efficiency compared to traditional orthogonal multiple access schemes.

The Synergy of SWIPT and NOMA
Benefits of Integration
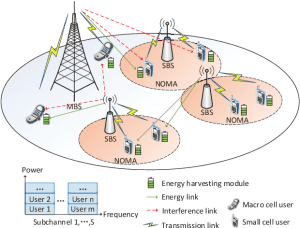
The amalgamation of SWIPT with NOMA results in a symbiotic relationship, where the power-domain multiplexing capabilities of NOMA complement the energy harvesting capabilities of SWIPT. This integration unlocks higher spectral efficiency, extended coverage, and increased energy sustainability, promising a paradigm shift in wireless communication systems.
Dynamic Power Control Mechanisms
Adaptive Power Allocation Algorithms
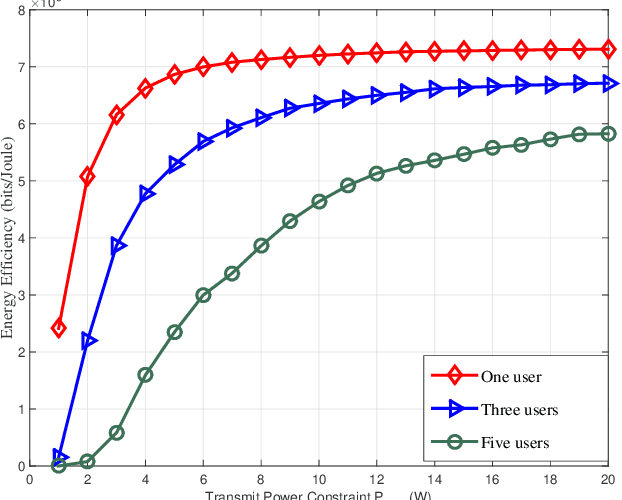
Dynamic power control mechanisms play a pivotal role in optimizing the performance of SWIPT-NOMA systems. Adaptive power allocation algorithms dynamically allocate power among users to maximize the sum-rate or energy efficiency while considering the varying channel conditions and energy harvesting capabilities.
Reinforcement Learning-based Power Control
Integrating machine learning techniques, particularly reinforcement learning, offers a novel approach to power control in SWIPT-NOMA systems. By continuously learning from the environment, these algorithms adaptively adjust transmission parameters, optimizing the system’s performance over time.
Joint Resource Allocation and Beamforming
Efficient resource allocation, including subcarrier assignment and beamforming, further enhances the performance of SWIPT-NOMA systems. By jointly optimizing these parameters, the system maximizes the overall throughput and harvested energy while mitigating interference among users.
Challenges and Future Directions
Interference Management and Mitigation
One of the primary challenges in SWIPT-NOMA systems is mitigating interference among users sharing the same resources. Future research focuses on advanced interference management techniques, such as advanced signal processing and interference alignment, to improve system performance.
Security and Reliability
Ensuring the security and reliability of SWIPT-NOMA systems remains a crucial aspect. Developing robust authentication, encryption, and error correction mechanisms is imperative to safeguard the integrity of both data transmission and energy harvesting processes.
Integration with Emerging Technologies
The integration of SWIPT-NOMA with emerging technologies like IoT (Internet of Things) and 6G networks holds promise for diverse applications. Future research explores synergies and adaptations to accommodate the requirements of these evolving technologies.
Conclusion
The integration of SWIPT with NOMA presents a groundbreaking approach that revolutionizes wireless communication by enabling simultaneous data transmission and energy harvesting. Dynamic power control mechanisms play a pivotal role in optimizing the performance of SWIPT-NOMA systems, offering enhanced efficiency, extended coverage, and increased energy sustainability. As research continues to evolve, addressing challenges and exploring synergies with emerging technologies will further propel the capabilities and applications of SWIPT-NOMA systems in the future wireless communication landscape.