Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease
Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (CJD), often referred to as “classic” CJD, is a rare neurological disorder marked by the rapid breakdown of brain tissue. Unlike its bovine counterpart, “mad cow disease,” and the variant CJD associated with contaminated cattle products, classic CJD primarily affects humans, leading to severe cognitive and physical impairments. In this comprehensive exploration, we delve into the causes, symptoms, diagnostic challenges, and treatment landscape of this enigmatic disease.

Causes of Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease
- Sporadic Type: The most prevalent form of CJD, sporadic cases account for the majority. It is caused by the presence of misfolded proteins known as prions. These abnormal proteins, a natural part of the body, can fold incorrectly, leading to an infectious “misfolded” prion that infiltrates the brain, causing the destruction of vital brain cells. The perplexing aspect of sporadic CJD lies in the uncertainty surrounding why these proteins misfold in the first place.
- Familial Type: In a distinctive minority of cases (10%-15%), CJD is familial, meaning it occurs in individuals who inherit a faulty gene from a parent. This genetic predisposition contributes to the manifestation of the disease, adding a layer of complexity to its already intricate nature.
- Acquired Type: The rarest form of classic CJD is the acquired type, comprising less than 1% of cases. It occurs when an individual comes into contact with contaminated medical instruments, organs (via transplantation), or growth hormone. This highlights the disease’s potential transmission through medical procedures, further intensifying the challenges in its understanding and prevention.
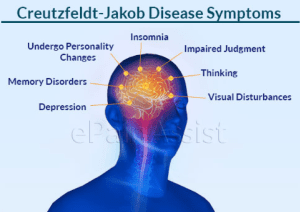
Symptoms
Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease is notorious for its rapid onset and swift progression. The symptoms mirror those of dementia, with individuals experiencing confusion, difficulty walking, jerky muscle movements, personality changes, and vision problems. As the disease advances, patients may encounter sleep disturbances, depression, and eventually lose the ability to speak or move. In the later stages, susceptibility to infections, including pneumonia, escalates, often leading to a comatose state.
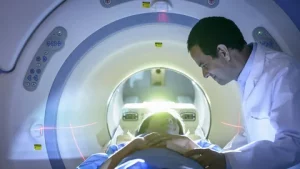
Navigating the Diagnostic Maze
- No Definitive Test: Diagnosing CJD remains a significant challenge due to the absence of a single definitive test. Physicians rely on the observation of symptoms, and the speed at which they escalate serves as a crucial indicator.
- Diagnostic Tools: Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), electroencephalogram (EEG), and lumbar puncture (spinal tap) are employed to gather insights into the disease. These tests help visualize changes in the brain over time and assess electrical brain activity.
- Biopsy Risks: While a biopsy of brain tissue remains the only conclusive diagnostic method, it is seldom performed due to inherent risks. Targeting the specific infected tissue within the brain is challenging, making the procedure both risky for the patient and the healthcare provider.
Treatment Challenges
- No Cure in Sight: Unfortunately, there is no cure for Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease. Despite numerous drug trials, researchers have not identified any treatment capable of slowing or halting the disease’s progression.
- Symptomatic Relief: Management of CJD primarily revolves around addressing symptoms. Pain medication, muscle relaxers, and anti-seizure drugs may offer some relief, but they do not alter the course of the disease.
- Full-Time Care: As the disease advances to its late stages, individuals with CJD require constant care due to the progressive nature of the neurological decline. Full-time caregiving becomes imperative for maintaining the quality of life for patients.

Comparative Overview
Table: Comparative Overview of Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease Types
| Type | Cause | Prevalence |
|---|---|---|
| Sporadic | Misfolded prion proteins | Most common |
| Familial | Inherited defective gene | 10%-15% |
| Acquired | Exposure to contaminated sources | <1% |
This table offers a nuanced perspective on the different types of Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease, shedding light on their causes and relative prevalence within the affected population.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease stands as a formidable challenge in the realm of neurological disorders. Its rarity, aggressive progression, and the absence of effective treatments underscore the pressing need for continued research. The intricate interplay of genetic predisposition, protein misfolding, and potential iatrogenic transmission demands a multifaceted approach to understanding and eventually conquering this perplexing disease. As we navigate the uncharted waters of CJD, the resilience of those affected and the dedication of researchers fuel the ongoing quest for answers, offering hope for improved diagnostic tools and, ultimately, a cure.