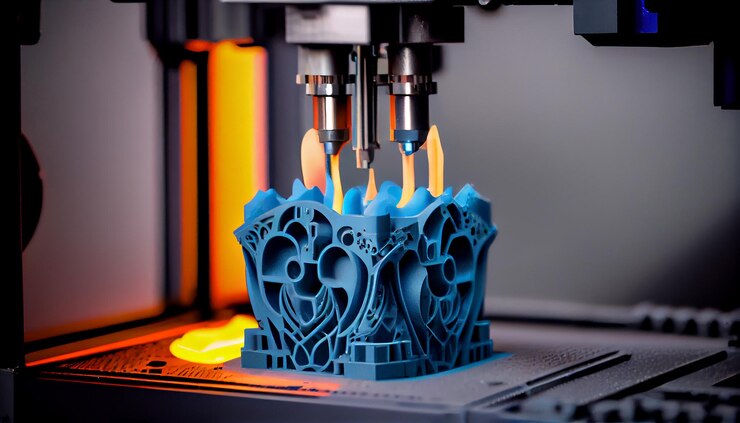
3D metal printing, also called metal additive manufacturing, is quickly changing the way things are made by making it possible to make complicated metal parts that are hard to make with traditional methods. This new and innovative technology makes metal parts one layer at a time, giving designers more freedom and better use of resources.
By 2024, metal 3D printing was easier to get and was used a lot in many fields, including fashion, healthcare, aircraft, and more. Metal 3D printing keeps getting better at what it can do, what it can do for you, and what it can be used for. This offers a bright future for new designs and more efficient production methods.
How Metal 3D Printing Works

Metal 3D printing involves a process where metal powders or filaments are fused using high-precision lasers or electron beams. The most common techniques include:
- Selective Laser Melting (SLM) and Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS): These involve laser fusion to produce strong, precise metal parts.
- Binder Jetting: A powder-based process where a binder is added to metal powders, followed by sintering in a furnace.
- Electron Beam Melting (EBM): Using an electron beam instead of a laser, EBM is particularly useful for high-density parts in aerospace and medical applications.
These processes offer significant design flexibility, allowing for intricate geometries, lightweight structures, and material efficiency previously unattainable with traditional subtractive manufacturing.
Benefits of Metal 3D Printing
The benefits of 3D metal printing extend across various aspects of manufacturing and product development:
A. Complex Design Capabilities
One of the most significant advantages of metal 3D printing is the ability to create intricate designs that would be impossible or too costly using traditional methods. Manufacturers can produce geometries with complex internal structures, reducing material waste and creating lighter, stronger parts.
B. Material Efficiency and Sustainability
Metal 3D printing is resource-efficient, using only the required material to create each layer, which minimizes waste. This approach aligns with the sustainability goals of many companies looking to reduce their environmental footprint.
C. Rapid Prototyping and Time Efficiency

With metal 3D printing, companies can produce prototypes and functional parts in days instead of weeks, accelerating product development timelines. This quick turnaround allows for faster testing, iteration, and production scaling.
D. Cost Reduction in Small Batch Manufacturing
For low-volume or custom part manufacturing, 3D metal printing is cost-effective compared to traditional methods that require expensive molds or tooling. This advantage is particularly valuable in industries like aerospace, where customized or low-volume parts are common.
E. On-Demand Production and Supply Chain Flexibility
3D metal printing enables on-demand manufacturing, eliminating the need for large inventories and reducing supply chain complexity. Parts can be printed on-site or closer to the point of use, reducing shipping costs and lead times.
Latest Trends in Metal 3D Printing
As metal 3D printing technology evolves, several key trends are shaping its development and application:
A. Multi-Material 3D Printing
Researchers are now exploring multi-material printing, which allows manufacturers to produce parts with varying material properties within a single piece. This trend is useful for creating components with enhanced durability, wear resistance, or conductive properties.
B. Larger Build Volumes and Faster Printing Speeds
Advancements in printer design have increased build volumes, making it possible to print larger parts in one go. Additionally, faster laser and electron beam systems are reducing print times, further enhancing productivity.
C. Enhanced Quality Control through AI and Machine Learning
AI and machine learning algorithms are being integrated into metal 3D printing systems to monitor the printing process and ensure consistency. These technologies help detect anomalies in real-time, improving quality and reducing post-processing work.
D. Improved Post-Processing Techniques
Post-processing has traditionally been time-consuming in metal 3D printing. However, advancements in automated support removal, surface finishing, and heat treatment processes have improved the quality of printed parts and reduced the time needed for finishing.
E. Expansion in Material Choices

Metal 3D printing materials are diversifying beyond stainless steel and titanium. New alloys like Inconel and copper blends have opened up more opportunities in industries such as electronics and medical devices, where specific material properties are required.
Applications and Examples of Metal 3D Printing
Metal 3D printing’s versatility makes it a perfect fit for various industries, from medical devices to automotive components. Here are some prominent applications:
Aerospace and Defense
The aerospace sector has embraced metal 3D printing for its ability to produce lightweight, strong, and heat-resistant components. For example, GE Aviation has used metal 3D printing to produce fuel nozzles for jet engines. These printed nozzles are 25% lighter and five times more durable than traditionally manufactured parts.
Medical Implants and Prosthetics
Metal 3D printing is critical in creating custom prosthetics and implants tailored to individual patients. Stryker, a medical technology company, uses metal 3D printing to create titanium implants with complex lattice structures that promote bone growth and better integration with human tissue.
Automotive Prototyping and Custom Parts
Automotive manufacturers leverage metal 3D printing to produce custom parts for high-performance vehicles. Bugatti, for instance, used metal 3D printing to develop brake calipers made of titanium, reducing weight and increasing performance.
Tooling and Molds
Companies like Siemens use metal 3D printing to create custom tools and molds quickly, streamlining the manufacturing process and reducing downtime. This approach is particularly beneficial in industries that require frequent tool changes or custom molds.
Energy and Industrial Applications
Metal 3D printing is used to produce durable components for energy applications, such as turbines and heat exchangers. Siemens Energy developed a 3D-printed gas turbine blade that withstands high temperatures and pressure, enhancing efficiency and durability in power generation.
Case Studies: Success Stories in Metal 3D Printing
Real-world examples of metal 3D printing highlight its transformative impact on various industries:
GE Aviation’s Fuel Nozzle
GE Aviation adopted metal 3D printing to manufacture fuel nozzles for its LEAP jet engines. Traditional manufacturing required 20 separate pieces to be welded together, whereas 3D printing consolidated this into a single piece, reducing weight by 25% and enhancing durability. The new nozzle improved fuel efficiency and cut down on manufacturing time, proving the cost-effectiveness of metal 3D printing in high-stakes applications.
Stryker’s Titanium Implants
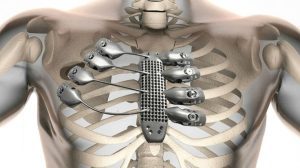
Stryker uses metal 3D printing to create patient-specific titanium implants. These implants feature complex lattice structures that encourage natural bone growth and improve the stability of the implant. Stryker’s use of metal 3D printing has improved patient outcomes and reduced time in surgery, demonstrating the technology’s value in healthcare.
NASA’s Rocket Engine Components
NASA has used metal 3D printing to produce rocket engine parts, reducing the manufacturing timeline from months to days. In one instance, a 3D-printed fuel injector performed well under high-stress testing, paving the way for further exploration of metal 3D printing in space exploration. The reduced production time and cost savings are substantial, allowing NASA to focus more resources on mission planning and development.
Challenges in Metal 3D Printing Manufacturing
While metal 3D printing has numerous advantages, it also faces several challenges that must be addressed as the technology advances.
A. High Initial Costs
The cost of metal 3D printing equipment and materials remains high, making it difficult for smaller companies to invest in this technology. However, as the technology becomes more mainstream, costs are expected to decrease.
B. Quality and Consistency Concerns
Ensuring quality and consistency in metal 3D printing is challenging, particularly for industries requiring high-precision parts. Variations in print quality can result from material inconsistencies or printer settings, necessitating stringent quality control.
C. Limited Material Options
While the range of materials is expanding, there are still limitations in the types of metals available for 3D printing. Specific applications may require properties that are not yet achievable with existing materials.
D. Post-Processing Requirements
Many 3D-printed metal parts require post-processing, such as heat treatment, to achieve desired properties. This additional step adds time and cost, reducing the overall efficiency of the printing process.
The Future of Metal 3D Printing
Metal 3D printing is poised for significant growth and innovation. As costs decrease and material choices expand, more industries will adopt the technology for various applications. Advancements in AI and machine learning will improve quality control, while blockchain may offer enhanced security for manufacturing data.
The future will likely see metal 3D printing play a central role in sustainable manufacturing, with greater emphasis on recycling and resource efficiency. Industries like aerospace, healthcare, and automotive will continue to leverage metal 3D printing for complex, lightweight, and high-performance components, driving the next generation of innovation.
Final Thought
3D metal printing manufacturing is revolutionizing how products are designed, produced, and delivered. With its advantages in flexibility, sustainability, and efficiency, metal 3D printing is increasingly adopted across industries and is pushing the boundaries of what’s possible in manufacturing. As technology progresses, metal 3D printing will bring us closer to a future where innovation is limited only by imagination, providing cost-effective solutions, reducing waste, and offering unparalleled design possibilities. The journey of metal 3D printing is just beginning, with exciting developments ahead for industries worldwide.