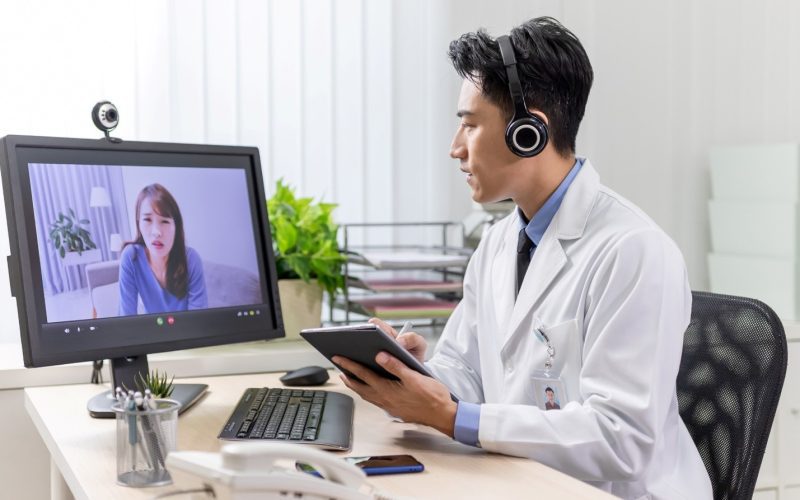
In recent years, the healthcare landscape has been undergoing a seismic shift, driven by technological advancements and changing patient expectations. Among the most transformative developments is the rise of telemedicine, which has redefined how healthcare is delivered and accessed. Telemedicine is not merely a fleeting trend but a significant evolution in the healthcare industry. This article delves into the current telemedicine trends and explores how virtual care is reshaping the future of healthcare.
The Emergence of Telemedicine
Telemedicine, the practice of delivering medical care remotely using telecommunications technology, has been around for decades. However, it was the global COVID-19 pandemic that catalyzed its widespread adoption. With social distancing measures in place and healthcare facilities overwhelmed, telemedicine emerged as a vital tool for ensuring continuity of care. As a result, both patients and providers quickly adapted to this new mode of healthcare delivery.
Telemedicine Trends: A Closer Look
Several key trends are driving the growth of telemedicine and shaping its future. Understanding these trends is crucial for appreciating the transformative potential of virtual care.
1. Increased Patient Adoption
One of the most significant telemedicine trends is the surge in patient adoption. According to a report by McKinsey & Company, telehealth utilization has stabilized at levels 38 times higher than before the pandemic. Patients have become more comfortable with virtual consultations, appreciating the convenience and accessibility they offer. This trend is expected to continue as more people experience the benefits of telemedicine.
2. Integration with Wearable Technology
The integration of telemedicine with wearable technology is another trend gaining momentum. Wearable devices, such as smartwatches and fitness trackers, can monitor vital signs and health metrics in real-time. This data can be shared with healthcare providers during virtual consultations, enabling more accurate diagnoses and personalized treatment plans. The synergy between telemedicine and wearable technology is poised to revolutionize preventive care and chronic disease management.
3. Expansion of Telemedicine Services
Initially, telemedicine was primarily used for primary care consultations. However, its scope has expanded significantly. Today, telemedicine encompasses a wide range of specialties, including mental health, dermatology, cardiology, and even physical therapy. This expansion allows patients to access specialized care without the need for travel, making healthcare more inclusive and equitable.
4. Advancements in Telemedicine Technology
Technological advancements are at the heart of telemedicine’s growth. High-definition video conferencing, secure messaging platforms, and AI-powered diagnostic tools have enhanced the quality and reliability of virtual care. Additionally, the development of user-friendly telemedicine apps has made it easier for both patients and providers to navigate virtual consultations. These technological innovations are continually improving the telemedicine experience.
5. Regulatory Support and Reimbursement Policies
Regulatory changes and updated reimbursement policies have played a crucial role in the rise of telemedicine. Governments and healthcare authorities have recognized the value of virtual care and have implemented measures to support its growth. For instance, the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) in the United States expanded telehealth coverage, allowing more patients to access virtual care services. Such regulatory support is essential for sustaining the momentum of telemedicine.
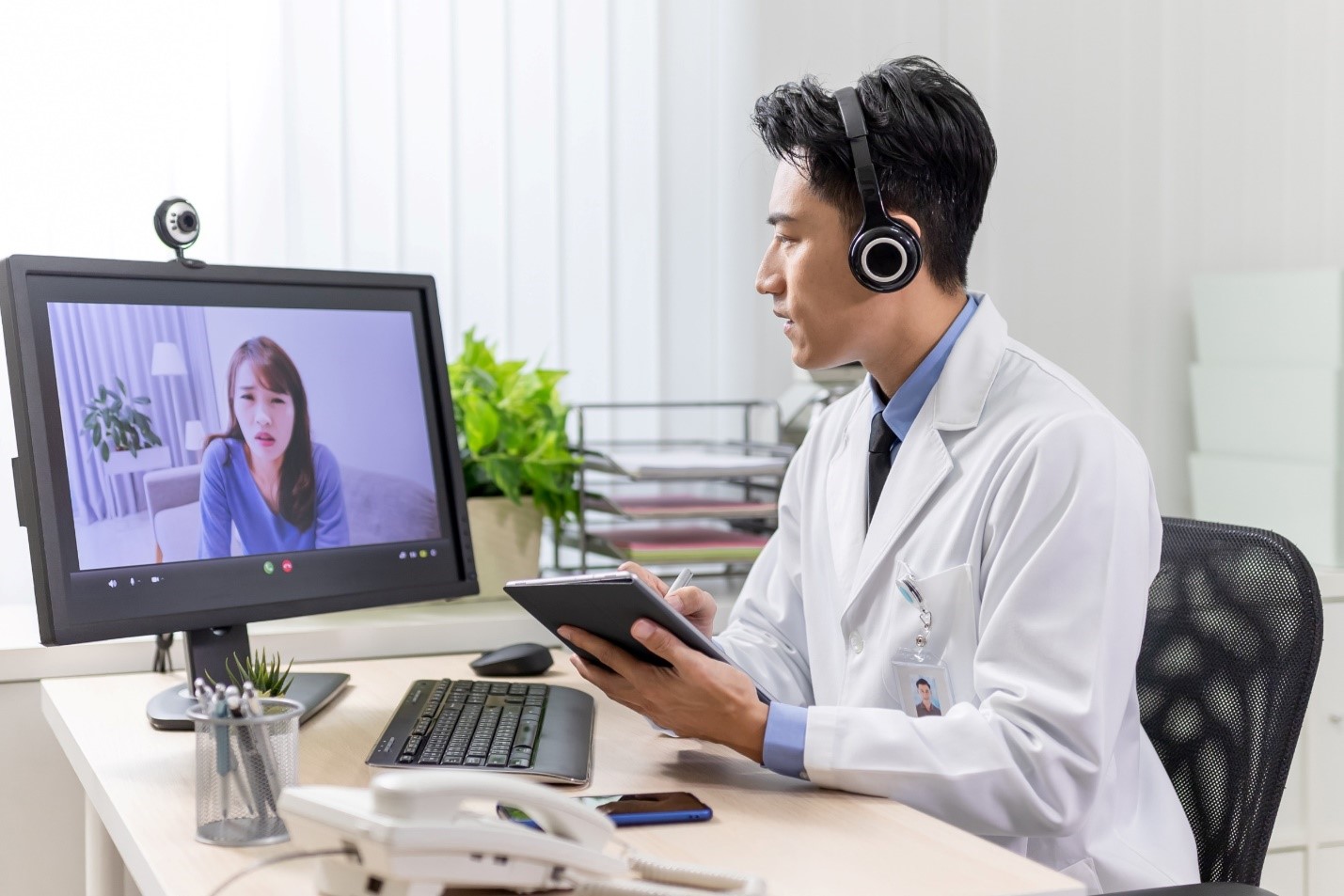

The Benefits of Telemedicine
The rise of telemedicine is not just a matter of convenience; it brings several tangible benefits to both patients and healthcare providers.
1. Improved Access to Care
Telemedicine breaks down geographical barriers, enabling patients in remote or underserved areas to access healthcare services. This is particularly important for individuals with limited mobility or those living in rural communities where healthcare facilities may be scarce. By bridging the gap between patients and providers, telemedicine ensures that more people receive timely and appropriate care.
2. Enhanced Patient Engagement
Virtual care fosters greater patient engagement and participation in their own healthcare. Patients can easily schedule appointments, access their medical records, and communicate with their healthcare providers through telemedicine platforms. This level of engagement empowers patients to take an active role in managing their health, leading to better outcomes.
3. Cost Savings
Telemedicine can significantly reduce healthcare costs for both patients and providers. Patients save on travel expenses and time off work, while providers can optimize their resources and reduce overhead costs associated with maintaining physical facilities. Additionally, telemedicine can help prevent costly hospital readmissions by enabling proactive monitoring and early intervention.
4. Continuity of Care
Telemedicine ensures continuity of care, even in challenging circumstances. During the COVID-19 pandemic, telemedicine allowed patients to continue receiving essential healthcare services without risking exposure to the virus. This continuity is vital for managing chronic conditions, monitoring treatment progress, and providing follow-up care.

Challenges and Future Directions
While telemedicine holds immense promise, it is not without challenges. Addressing these challenges is crucial for realizing the full potential of virtual care.
1. Digital Divide
The digital divide remains a significant barrier to telemedicine adoption. Not all patients have access to the necessary technology or reliable internet connections. Bridging this gap requires concerted efforts from governments, healthcare providers, and technology companies to ensure that telemedicine is accessible to all.
2. Privacy and Security Concerns
The use of digital platforms for healthcare delivery raises concerns about data privacy and security. Ensuring that telemedicine platforms comply with stringent security standards and regulations is essential to protect patient information and maintain trust in virtual care services.
3. Provider Training and Adaptation
Healthcare providers need adequate training and support to effectively integrate telemedicine into their practice. This includes familiarizing themselves with telemedicine technology, understanding virtual care protocols, and adapting their communication skills for remote consultations. Ongoing education and support are vital for successful telemedicine implementation.
4. Sustainable Reimbursement Models
While regulatory changes have facilitated telemedicine growth, sustainable reimbursement models are needed to ensure its long-term viability. Policymakers and healthcare payers must continue to evaluate and refine reimbursement policies to support the widespread adoption of telemedicine.
Conclusion
The rise of telemedicine marks a transformative shift in the healthcare industry. Driven by telemedicine trends such as increased patient adoption, integration with wearable technology, and advancements in telemedicine technology, virtual care is reshaping how healthcare is delivered and accessed. The benefits of telemedicine, including improved access to care, enhanced patient engagement, cost savings, and continuity of care, underscore its potential to revolutionize healthcare.
However, realizing the full potential of telemedicine requires addressing challenges such as the digital divide, privacy and security concerns, provider training, and sustainable reimbursement models. As stakeholders work together to overcome these challenges, telemedicine is poised to become an integral part of the healthcare ecosystem, offering a more accessible, efficient, and patient-centered approach to care.