Understanding Blood Pressure: Importance and Implications
Blood pressure, often referred to as the “silent killer,” plays a crucial role in overall health and well-being. Monitoring blood pressure levels regularly is essential for detecting and managing hypertension, a major risk factor for cardiovascular disease and other serious health conditions.
The Significance of Blood Pressure Monitoring
Maintaining optimal blood pressure levels is vital for:
- Cardiovascular Health: High blood pressure can strain the heart and blood vessels, increasing the risk of heart disease, stroke, and other cardiovascular complications.
- Overall Well-being: Uncontrolled hypertension can lead to damage to vital organs such as the kidneys, eyes, and brain, impacting overall health and quality of life.
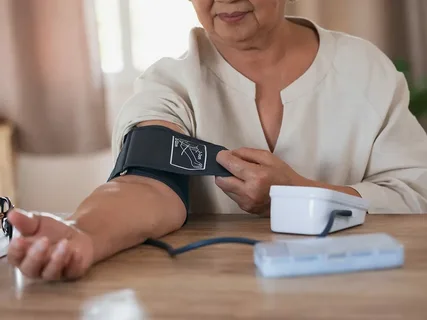
The Need for Home Blood Pressure Monitoring
While blood pressure measurements taken in clinical settings provide valuable insights, home monitoring offers several advantages:
- Convenience: Home monitoring allows individuals to track their blood pressure regularly without the need for frequent visits to healthcare facilities.
- Accuracy: Some individuals experience “white coat hypertension,” where blood pressure readings are elevated in clinical settings due to anxiety. Home monitoring provides more accurate readings in familiar environments.
- Early Detection: Regular monitoring at home enables early detection of fluctuations or trends in blood pressure, facilitating timely intervention and management.
Guidelines for Effective Home Blood Pressure Monitoring
1. Choosing a Blood Pressure Monitor
Selecting the right blood pressure monitor is crucial for accurate measurements. Consider the following factors:
- Type of Monitor: Choose between automatic or manual monitors based on personal preference and ease of use.
- Cuff Size: Ensure the monitor’s cuff size fits your arm circumference accurately to obtain precise readings.
- Validation: Opt for monitors validated by reputable medical organizations to ensure accuracy and reliability.
2. Preparation for Measurement
To obtain accurate blood pressure readings at home, follow these preparation steps:
- Rest: Sit quietly for at least 5 minutes before taking measurements to allow your body to relax.
- Empty Bladder: Ensure your bladder is empty, as a full bladder can affect blood pressure readings.
- Avoid Stimulants: Refrain from consuming caffeine, tobacco, or engaging in strenuous activities for at least 30 minutes before measurement.
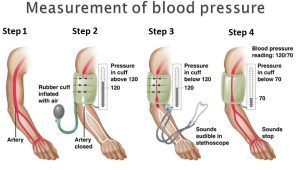
3. Taking Measurements
Follow these steps for proper blood pressure measurement:
- Positioning: Sit comfortably with your back supported, feet flat on the floor, and arm supported at heart level.
- Placement: Position the cuff on your bare upper arm, aligning it with the brachial artery.
- Multiple Readings: Take two to three consecutive measurements, with a one-minute interval between readings, and record the average value. Explore About (Toenail Health)
4. Interpretation and Action
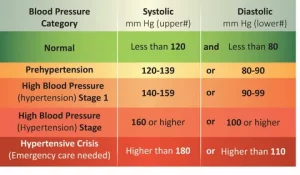
Understanding blood pressure readings is essential for effective management:
- Normal: A systolic pressure (top number) below 120 mmHg and diastolic pressure (bottom number) below 80 mmHg is considered normal.
- Elevated: Systolic pressure between 120-129 mmHg and diastolic pressure below 80 mmHg indicates elevated blood pressure.
- Hypertension: Consistently elevated readings above 130/80 mmHg may indicate hypertension, requiring consultation with healthcare providers for further evaluation and management.
Conclusion
Empowering individuals with the knowledge and tools for effective home blood pressure monitoring is paramount for maintaining cardiovascular health and overall well-being. By adhering to guidelines outlined in this article, individuals can take proactive steps towards early detection, management, and prevention of hypertension-related complications.