Introduction
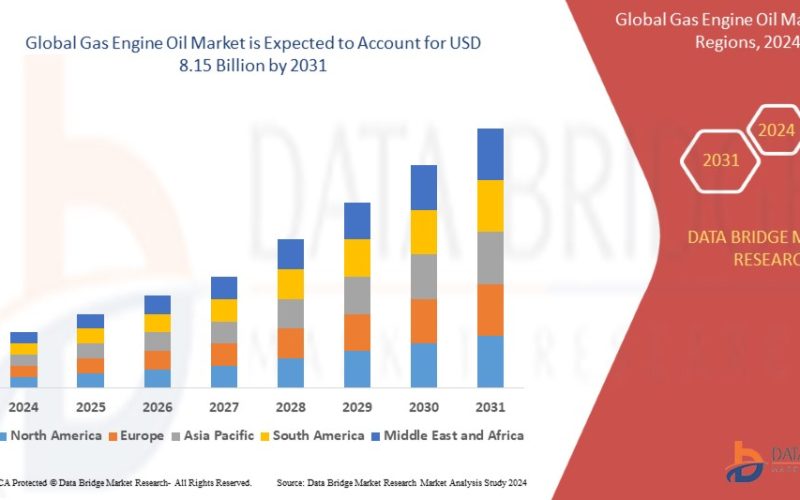
The gas engine oil market is growing because more people are using natural gas and other gaseous fuels in power plants, vehicles, and factories. In 2023, this market was worth USD 5.60 billion. By 2031, it could reach USD 8.15 billion if it keeps growing at about 4.8% each year.
A special part of this market natural gas engine oils was USD 50 million in 2023. It is expected to grow to USD 72.2 million by 2030, which means it’s growing about 11.2% per year.
According to Data Bridge Market Research, from 2024 to 2031 the global gas engine oil market will grow from USD 5.60 billion to USD 8.15 billion at a 4.8% annual rate. Their reports cover things like market size, growth rate, product types, regions, and top companies. They also offer expert insights, production and capacity details by region, distributor and partner networks, price trends, and supply-and-demand analysis.
What is Gas Engine Oil?
1. Definition & Purpose
Gas engine oil, also called natural gas engine lubricant, is a special oil made for engines that run on gas like methane. This oil coats engine parts so they move smoothly, keeps the engine from getting too hot, and stops rust and damage caused by gas burn-off.
2. Why Gas Engines Need Special Oil
Gas engines run hotter than regular engines and make acidic leftovers when they burn fuel. Because of this, the oil must:
- Stay strong at high temperatures
- Clean up and neutralize acids
- Keep engine parts safe from wear and tear
- Help the engine keep running smoothly and efficiently
Market Overview & Forecast
1. Market Size and CAGR
-
Global gas engine oil market: USD 5.60 billion in 2023 → USD 8.15 billion by 2031 (4.8% CAGR)
-
Natural gas engine oils: USD 50 million in 2023 → USD 72.2 million by 2030 (11.2% CAGR)
-
Stationary gas engine oils: USD 3.5 billion in 2022 → USD 5.1 billion by 2030 (5.6% CAGR)
These figures reflect rising usage of gas-fueled vehicles, onsite power generators, and industrial machinery.
2. Regional Insights
-
Asia-Pacific leads adoption, due to increased industrialization and cleaner fuel mandates
-
North America remains a key market, bolstered by robust natural gas infrastructure
-
Europe is growing steadily, supported by environmental regulations
Segmentation Analysis
1. By Product Type
-
Conventional vs. Synthetic vs. Semi-Synthetic: Synthetic oils dominate due to superior heat resistance and longer life.
-
Mineral and semi-synthetic: Oils continue to serve cost-sensitive segments
2. By End-Use Industry
-
Power Generation (Utilities, CHP): Largest segment for stationary gas engines.
-
Industrial: Gas engines in manufacturing, irrigation, and mining.
-
Automotive/Mobility: Natural gas vehicles (CNG, LNG trucks) are expanding in transport and logistics.
-
Marine & Others: Emerging use in LNG-powered ships
Key Market Drivers
-
Shift to cleaner fuels: Natural gas engines help reduce CO₂ and particulate emissions versus diesel .
-
Industrial and utility demand: Decentralized power and backup generation boost oil usage.
-
Environmental regulations: Policies that lower emissions drive gas-engine adoption.
-
Technological advances: Better additives and synthetic blends improve engine performance and oil longevity.
Challenges & Barriers
-
Technical demands: Gas engines create acid byproducts and high exhaust temperature, requiring specialty oil formulations.
-
Higher costs: Synthetic gas engine oils are more expensive than conventional options.
-
Infrastructure gaps: Distribution networks for specialty oils lag in emerging regions.
-
Methane slip: Emissions from LNG engines pose environmental challenges
Competitive Landscape
Leading players include ExxonMobil, Shell, Chevron, Total Energies, BP, Fuchs, Valvoline, PetroChina, Lukoil, Idemitsu, Castrol India, and Sinopec These firms emphasize product R&D, partnerships with engine OEMs, and global distribution expansion.
SWOT Analysis
1. Strengths
-
Tailored solutions for high-performing gas engines
-
Increasing adoption in power and transport sectors
-
Superior engine protection and efficiency benefits
2. Weaknesses
-
Premium pricing limits broader penetration
-
Complex oil requirements due to combustion byproducts
-
Reliant on synthetic formulation innovation
3. Opportunities
-
Growth in natural gas vehicle fleets and microgrid deployment
-
Rising demand for high-efficiency lubricants in LNG marine engines
-
Expansion into emerging markets with new power installations
4. Threats
-
Competition from electric systems and hydrogen engines
-
Methane emission regulation for LNG-fueled engines
-
Volatile supply of additives and base oils
Future Trends & Opportunities
- Synthetic high-performance oils are now the industry standard because they fight acid better.
- Marine LNG engine oils are made to work with very cold fuels and to meet environmental rules.
- Eco-friendly bio-lubricants are gaining interest, but only a small amount is made so far.
- Data-driven oil management uses IoT sensors and predictive analytics to tell you the best time to change oil and cut down waste.
- India, Southeast Asia, and Latin America are growing fast as they build new power plants and add more gas engines.
Conclusion
The gas engine oil market is positioned for sustained growth amid a global shift toward cleaner, efficient power solutions. Valued at approximately USD 5.6 billion in 2023, with strong projections through 2031, the market thrives on its tailored formulations, technological advances, and expanding industrial applications.
To lead, companies must balance innovation in synthetic and eco-friendly formulations, strategic market expansion, and service offerings that include advanced lubrication management systems.
As gas engines grow in power generation, transport, and marine sectors, their lubricants will play a pivotal role in ensuring durability, performance, and sustainability—shaping the future of cleaner combustion management.