Understanding Age-Related Eye Problems
As we age, our bodies undergo numerous changes, and our eyes are no exception. With each passing year, the risk of developing various eye problems increases. From cataracts to glaucoma, aging brings forth a host of challenges that can impact our vision and overall quality of life. In this comprehensive guide, Eye Problems with Aging we’ll delve into four key eye problems commonly associated with aging and explore their causes, symptoms, and treatment options.
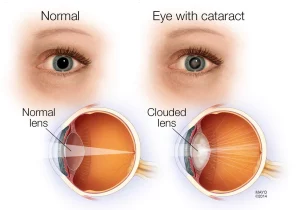
Cataracts: The Clouding of Vision
What Are Cataracts?
Cataracts refer to the clouding of the lens in the eye, which leads to a gradual loss of vision. This condition often develops slowly and can affect one or both eyes.
Causes and Risk Factors
While aging is the primary risk factor for cataracts, other factors such as prolonged exposure to sunlight, smoking, diabetes, and certain medications can also contribute to their development.
Symptoms
Common symptoms of cataracts include blurred vision, increased sensitivity to glare, difficulty seeing at night, and a yellowing of colors.
Treatment Options
Surgical removal of the cloudy lens is the most effective treatment for cataracts. During the procedure, the natural lens is replaced with an artificial one, restoring clear vision. Explore More About (Dizziness After Meal)
Glaucoma: The Silent Thief of Sight
Understanding Glaucoma
Glaucoma is a group of eye conditions that damage the optic nerve, often due to increased pressure within the eye. It is one of the leading causes of blindness worldwide.
Types of Glaucoma
There are several types of glaucoma, including open-angle glaucoma, angle-closure glaucoma, and normal-tension glaucoma. Each type has its own set of characteristics and risk factors.
Risk Factors
Advanced age, family history, ethnicity, and certain medical conditions such as diabetes and hypertension increase the risk of developing glaucoma.
Symptoms
In its early stages, glaucoma may not present any noticeable symptoms. However, as the condition progresses, individuals may experience peripheral vision loss, blurred vision, eye pain, and nausea.
Treatment Strategies
Treatment for glaucoma aims to lower intraocular pressure and prevent further damage to the optic nerve. This may involve the use of eye drops, oral medications, laser therapy, or surgical interventions.
Age-Related Macular Degeneration (AMD)
Understanding AMD
Age-related macular degeneration is a progressive eye condition that affects the macula, the central portion of the retina responsible for sharp, central vision.
Types of AMD
There are two types of AMD: dry AMD and wet AMD. Dry AMD is characterized by the presence of drusen, yellow deposits beneath the retina, while wet AMD involves the growth of abnormal blood vessels beneath the macula.
Risk Factors
Advanced age, genetics, smoking, obesity, and a diet high in saturated fats are all risk factors for developing AMD.
Symptoms
Symptoms of AMD include blurry or distorted central vision, difficulty reading or recognizing faces, and the appearance of dark spots in the central visual field.
Treatment Options
While there is no cure for AMD, treatment options such as anti-VEGF injections, photodynamic therapy, and laser surgery can help slow disease progression and preserve remaining vision.
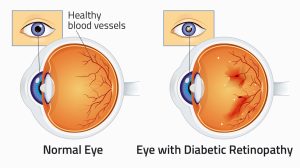
Diabetic Retinopathy: A Complication of Diabetes
Understanding Diabetic Retinopathy
Diabetic retinopathy is a diabetes complication that affects the blood vessels in the retina. High levels of blood sugar can damage the tiny blood vessels, leading to leakage, swelling, and the growth of abnormal blood vessels.
Risk Factors
Individuals with diabetes, particularly those with poorly controlled blood sugar levels, are at an increased risk of developing diabetic retinopathy.
Stages of Diabetic Retinopathy
Diabetic retinopathy progresses through several stages, including mild nonproliferative retinopathy, moderate nonproliferative retinopathy, severe nonproliferative retinopathy, and proliferative diabetic retinopathy.
Symptoms
In its early stages, diabetic retinopathy may not cause any noticeable symptoms. However, as the condition progresses, individuals may experience blurred vision, fluctuating vision, floaters, and dark spots in their visual field.
Treatment Approaches
Treatment for diabetic retinopathy may include laser photocoagulation, intravitreal injections of anti-VEGF medications, vitrectomy surgery, and strict control of blood sugar levels.
Age-Related Eye Problems
| Eye Problem | Description | Causes and Risk Factors | Symptoms | Treatment Options |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cataracts | Clouding of the lens in the eye, leading to vision loss | Aging, sunlight exposure, smoking, diabetes, medications | Blurred vision, glare sensitivity, color changes | Surgical removal of the cloudy lens |
| Glaucoma | Optic nerve damage due to increased eye pressure | Advanced age, family history, ethnicity, diabetes, hypertension | Peripheral vision loss, blurred vision, eye pain | Eye drops, medications, laser therapy, surgery |
| Age-Related Macular Degeneration (AMD) | Progressive degeneration of the macula | Aging, genetics, smoking, obesity, diet high in saturated fats | Blurry central vision, difficulty reading | Anti-VEGF injections, photodynamic therapy, surgery |
| Diabetic Retinopathy | Damage to retinal blood vessels due to diabetes | Poorly controlled blood sugar levels, duration of diabetes | Blurred vision, floaters, dark spots | Laser photocoagulation, anti-VEGF injections |
Conclusion
As we age, our eyes become more susceptible to a variety of conditions that can impact our vision and overall well-being. From cataracts to glaucoma, age-related eye problems require prompt diagnosis and appropriate treatment to preserve vision and maintain quality of life. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for these conditions, individuals can take proactive steps to protect their eye health as they age.












