How Artificial Intelligence (AI) Is Shaping the Future of Retail
While artificial intelligence (AI) has been a game changer in many sectors, the retail industry has felt its effects the most acutely. Adapting to the ever-changing expectations of tech-savvy clients is crucial for organizations in the retail industry, and AI is assisting in this process.
Retailers may automate processes, improve consumer experiences, streamline operations, and acquire competitive advantages through the use of artificial intelligence. Let’s take a look at the ways artificial intelligence is changing retail by analyzing its uses, advantages, and some real-life instances.
Personalized Customer Experiences

AI in retail enables brands to understand and cater to individual customer preferences. By analyzing shopping habits and consumer data, AI algorithms generate personalized product recommendations, tailor marketing strategies, and even customize in-store experiences.
Example: Online retailers like Amazon use AI-powered recommendation engines to suggest products based on past purchases and browsing history, driving higher engagement and sales.
Frictionless Shopping and Checkout
The traditional shopping experience has been completely transformed by AI, with technologies like computer vision and machine learning making checkout faster and more efficient. Frictionless shopping solutions, such as self-checkout systems and cashier-free stores, are growing in popularity.
Example: Amazon Go stores use AI and computer vision to create a seamless shopping experience where customers can simply pick up items and walk out, with purchases automatically charged to their accounts.
Improved Demand Forecasting and Merchandising
Understanding customer demand is crucial for retailers, and AI tools can analyze vast amounts of data to predict trends and optimize inventory management. This helps retailers reduce waste, prevent stockouts, and ensure that popular products are always available.
Case Study: Zara, the global fashion retailer, leverages AI to analyze customer feedback and sales data, ensuring that its inventory aligns with current fashion trends and customer preferences.
Enhanced Operational Efficiency
AI is streamlining retail operations by optimizing the supply chain and automating inventory management. Retailers can track products in real-time, improve warehouse logistics, and make data-driven decisions to boost overall efficiency.
Example: Walmart uses AI to automate warehouse operations, employing robots to sort and manage inventory, significantly reducing manual labor and improving efficiency.
Loss Prevention and Security

Retail shrink, or losses from theft and mismanagement, is a growing problem. AI-powered systems use advanced analytics and computer vision to monitor store activities and prevent theft. These technologies can detect suspicious behavior in real-time, alerting store staff to potential risks.
Case Study: Walgreens implemented AI-driven cameras in its stores to monitor activities and prevent theft. These systems help identify high-risk scenarios and reduce losses effectively.
Improved Customer Insights
AI technologies can segment customer profiles and analyze buying patterns to provide granular insights into consumer behavior. This enables retailers to craft highly targeted marketing campaigns and optimize customer service strategies.
Example: Starbucks uses AI to power its rewards program, analyzing customer purchase history to offer personalized promotions and recommendations.
Efficient Inventory Management
Maintaining accurate inventory records is essential for retailers. AI can automate stock management, identify low-stock items, and optimize inventory placement based on data analysis.
Example: Lowe’s uses inventory robots to scan shelves and identify items that need restocking, allowing employees to focus on customer service instead of routine tasks.
AI Use Cases in Retail
Frictionless Shopping and Checkout
AI-driven technologies like facial recognition, smart self-checkout systems, and integrated video analytics make shopping faster and more convenient. These solutions eliminate the need for traditional checkout lines, creating a seamless experience.
Example: Kroger, a major grocery chain, uses smart checkout systems to identify products even when barcodes are missing or damaged, reducing delays and enhancing customer satisfaction.
Personalized Engagements
AI can deliver personalized advertising and promotional content based on a customer’s location, preferences, and shopping history. Digital signage and touchless kiosks also enable more interactive and engaging in-store experiences.
Example: Nike uses AI-driven kiosks to offer personalized product recommendations, allowing shoppers to browse items that align with their preferences and style.
Heat Mapping and Store Optimization
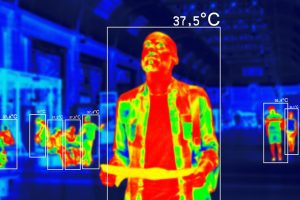
Computer vision and heat mapping technologies analyze customer behavior within stores to optimize product placement and layout. Retailers can track which areas attract the most traffic and adjust store arrangements to maximize sales opportunities.
Case Study: Macy’s used AI to create heat maps of customer movement within its stores. This data informed better product placements and helped increase sales by highlighting popular items.
Demand Forecasting
AI models can predict which products are likely to be in high demand, helping retailers optimize their supply chain and inventory management. By understanding consumer trends, retailers can make informed decisions about stock levels and avoid overstocking or understocking.
Example: H&M uses AI to predict fashion trends and optimize inventory distribution across its global network, ensuring that stores are stocked with the right products at the right time.
Conversational AI for Customer Service

AI-powered chatbots and voice assistants are transforming customer service in retail. These tools can handle routine inquiries, assist with product recommendations, and even process orders, freeing up human employees for more complex tasks.
Example: Sephora’s virtual assistant uses AI to provide personalized beauty advice, helping customers choose products that match their needs and preferences.
Challenges and Considerations
While AI offers numerous benefits, it also presents challenges that must be addressed:
Responsible AI and Data Privacy
Retailers must ensure that AI systems are transparent, accountable, and aligned with ethical guidelines. Additionally, data privacy is a significant concern, as AI tools often require access to large amounts of customer data. Retailers must implement robust security measures to prevent data breaches and maintain customer trust.
Example: The European Union’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) sets strict guidelines for data privacy, and retailers operating in the EU must comply with these regulations when using AI.
Organizational Investment and Integration
Implementing AI technologies can be costly and require significant changes to existing systems. Retailers must invest in staff training and work with technology partners to ensure seamless integration and minimal disruption.
Case Study: Target invested heavily in AI and data analytics to improve supply chain efficiency. The company worked with tech partners to integrate AI solutions and trained employees to use these tools effectively.
Customer Perceptions and Tolerance
Some customers may be uncomfortable with digital tracking and AI-driven personalization. Retailers must be mindful of how AI technologies align with their brand image and consider customer sensitivities when implementing new solutions.
Example: Nordstrom experimented with AI-powered recommendations but ensured that customers could opt out of tracking features to respect their privacy preferences.
The Future of AI in Retail

The future of retail will see AI becoming even more embedded in operations and customer experiences. Emerging technologies, such as generative AI, will further automate routine tasks and free up employees to focus on higher-value activities like relationship building and problem-solving.
Increased Automation
AI will continue to automate inventory management, warehouse logistics, and customer service, making retail operations more efficient. Automated systems will improve order accuracy, speed up deliveries, and enhance overall productivity.
Greater Personalization
As AI technologies advance, retailers will be able to offer even more personalized experiences. From tailored product recommendations to customized marketing campaigns, AI will help brands connect with customers on a deeper level.
Resilient Supply Chains
AI will enhance supply chain visibility, making it easier to adapt to disruptions. Technologies like edge AI and connected fleet logistics will provide real-time data on inventory and shipping, enabling faster, more efficient responses to changing circumstances.
Final Thought
The retail sector is being transformed by artificial intelligence, which is enabling the development of more secure, efficient, and personalized purchasing experiences. AI offers retailers a range of powerful tools to address contemporary challenges and consumer expectations, including automated checkouts, personalized marketing, advanced inventory management, and loss prevention.
The prospective advantages of AI in retail are undeniable, despite the fact that there are obstacles to overcome, including data privacy and integration costs. In the competitive landscape of the future, retailers that adopt innovation and responsibly utilize AI technologies will be well-positioned for success.












