In an era where digital innovation drives industries forward, health information technology (Health IT) has emerged as a vital force in modern healthcare. Health IT refers to the use of information technology in managing patient data, enhancing medical services, and supporting healthcare providers in delivering efficient and patient-centered care. With foundations rooted in the early 2000s, Health IT gained a significant boost through government initiatives like those introduced by Presidents George W. Bush and Barack Obama, which incentivized hospitals to adopt electronic health records (EHRs). Today, Health IT encompasses a range of digital tools and systems that streamline operations, reduce errors, improve patient care quality, and reduce healthcare costs.
Key Components of Health IT
The Health IT infrastructure is composed of various elements that serve specific roles in supporting patient data management, facilitating communication, and enhancing care delivery.
Electronic Health Records (EHRs)

EHRs are central to Health IT, providing a comprehensive digital record of a patient’s health history that can be accessed across multiple healthcare facilities. Unlike traditional paper records, EHRs are accessible to authorized providers, making it easier to coordinate patient care.
Personal Health Records (PHRs)
PHRs empower patients to manage their health information, promoting patient engagement and giving individuals more control over their healthcare journey. While not as detailed as EHRs, PHRs provide a valuable bridge between patients and healthcare providers.
Health Information Exchange (HIE)
HIEs facilitate the sharing of healthcare data among organizations that have committed to interoperability. Through HIEs, healthcare providers access patient data from different systems, ensuring continuity and comprehensive care across various healthcare providers.
Benefits of Health IT
Health IT provides tangible benefits that improve the quality and efficiency of healthcare delivery.
Enhanced Data Sharing and Communication
Health IT systems facilitate easy data sharing between healthcare providers, ensuring patient data is accessible wherever needed. This reduces the chance of duplicate tests or conflicting treatments, leading to faster, more accurate diagnostics.
Cost Savings and Efficiency
The digitization of healthcare records and automated processes reduce administrative tasks, allowing healthcare professionals to focus on patient care rather than paperwork. With EHRs, providers can quickly retrieve information, reducing wait times and improving patient satisfaction.
Improved Patient Safety and Quality of Care

With accessible patient history and streamlined communication, Health IT reduces the chance of medical errors and enhances treatment outcomes. For instance, automated alerts within EHRs notify providers of potential drug interactions or allergies, leading to safer treatment plans.
Patient Empowerment and Engagement
Patient portals and PHRs allow patients to access their health data, book appointments, communicate with providers, and even receive test results online. This transparency promotes patient involvement in healthcare decisions and improves satisfaction.
The Role of Data Analytics in Health IT
Data analytics has transformed healthcare by enabling providers to leverage big data to improve patient outcomes and streamline operations. In population health management (PHM), for instance, data analytics helps identify trends in chronic diseases, enabling proactive intervention and reducing healthcare costs.
Example: Data Analytics in Chronic Disease Management
Through predictive analytics, healthcare providers can track patients at high risk of diseases like diabetes or hypertension. By targeting interventions toward these patients, healthcare providers can prevent costly emergency room visits and hospitalizations. Analytics also assist in identifying the effectiveness of treatments, helping providers to tailor medical approaches based on data rather than assumptions.
Real-Life Case Studies and Success Stories
Health IT’s impact is evident in real-world cases where digital transformation has positively changed healthcare delivery and patient outcomes.
Telemedicine in Rural Areas
In rural and remote areas, patients often face limited access to healthcare. Telemedicine, enabled by Health IT, bridges this gap by allowing patients to consult doctors via video calls. For instance, the Veterans Health Administration (VHA) has successfully used telemedicine to provide remote mental health support to veterans. This approach has led to improved mental health outcomes for veterans who would otherwise struggle to access care.
Reducing Medical Errors with EHRs
The University of Pittsburgh Medical Center (UPMC) implemented a comprehensive EHR system that integrated clinical alerts and decision support tools. The system reduced medication errors by automatically checking for allergies and drug interactions before issuing prescriptions. This reduced adverse drug reactions, underscoring how EHRs can significantly improve patient safety.
PACS and VNAs in Radiology
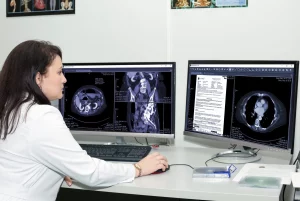
Radiology departments traditionally managed medical images in isolation. With Picture Archiving and Communication Systems (PACS) and Vendor-Neutral Archives (VNAs), radiology images are now accessible to various healthcare departments. A large-scale hospital in Texas implemented a VNA system to centralize imaging across cardiology, neurology, and radiology, improving diagnostic accuracy and reducing imaging redundancy.
Challenges and Obstacles in Health IT
Despite its benefits, Health IT faces notable challenges.
Interoperability Issues
A lack of standardized data-sharing practices hinders seamless communication across Health IT systems. Although Health Level Seven (HL7) has introduced the Fast Health Interoperability Resources (FHIR) standard, full interoperability remains a work in progress.
Cybersecurity and Data Privacy Concerns
With sensitive patient information stored digitally, healthcare organizations are prime targets for cyberattacks. Ensuring data security is challenging, especially given recent ransomware attacks in the healthcare sector. In 2017, the WannaCry ransomware attack highlighted vulnerabilities in hospital IT systems worldwide, emphasizing the need for robust cybersecurity measures.
Information Blocking by Vendors
Some vendors or providers deliberately restrict access to patient information to maintain control over data within their systems. Known as information blocking, this practice disrupts continuity of care and patient data access. Health regulators have expressed a firm stance against information blocking, introducing penalties for organizations that engage in this behavior.
Future Trends and Emerging Technologies in Health IT
The future of Health IT is marked by innovation, with new technologies driving better patient outcomes and transforming healthcare delivery.
Blockchain for Enhanced Data Security
Blockchain technology promises to improve data security in Health IT by creating an immutable record of patient data. This innovation allows patients to control who accesses their data, ensuring transparency and security. For example, Estonia has implemented blockchain in its national EHR system, securing citizens’ health data and providing a model for other nations.
Telemedicine and Mobile Health Integration
As mobile health (mHealth) apps become mainstream, telemedicine’s role continues to expand. Patients now have access to mobile platforms that connect them with providers, track their health data, and receive reminders about medications or appointments. These apps cater to patients who prefer managing their healthcare digitally, enhancing accessibility and convenience.
AI and Predictive Analytics
AI is expected to enhance Health IT through predictive analytics, particularly in diagnostics and treatment planning. AI algorithms analyze vast amounts of health data to predict disease risks and recommend tailored treatment plans. Although still evolving, AI is already being tested in diagnostic imaging, where it assists radiologists in detecting anomalies more quickly and accurately.
Final Thought
Health IT represents a transformative force in healthcare, offering substantial benefits in data accessibility, patient safety, and healthcare efficiency. By incorporating digital records, patient portals, data analytics, and emerging technologies, Health IT has reshaped how providers deliver care and how patients interact with healthcare services. While challenges such as interoperability and cybersecurity persist, ongoing advancements promise a future where Health IT is even more integrated, secure, and beneficial.
The future of Health IT lies in embracing patient-centric approaches, where individuals can actively manage and monitor their health data, engage in informed decision-making, and receive personalized care. As Health IT evolves, so does the healthcare landscape, with digital tools bridging gaps in accessibility and improving patient outcomes on a global scale.