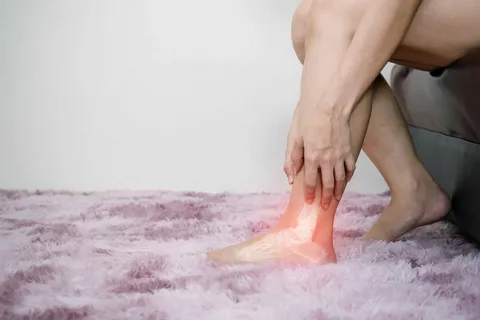
Understanding Ankle Inflammation
Ankle inflammation, medically termed “ankle swelling” or “edema,” is a common issue that many individuals encounter. It often arises due to various factors such as injury, medical conditions, or lifestyle choices. While occasional swelling might not be alarming, chronic or severe inflammation can signify underlying health issues. It’s crucial to delve deeper into the triggers of ankle inflammation to effectively manage and prevent its occurrence. Explore More About Health Problems And Their Solutions (Which Disease Usually Begins First)
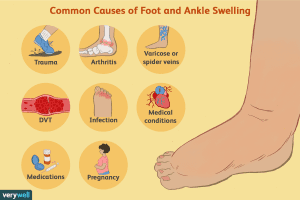
Common Causes of Ankle Inflammation
Several factors can contribute to ankle inflammation. Understanding these triggers is essential for effectively addressing the root cause:
- Injury and Trauma: Ankle sprains, fractures, or other traumatic injuries can lead to immediate swelling. The body’s natural response to injury is inflammation, which aids in the healing process. However, prolonged or severe trauma may result in chronic inflammation.
- Overuse and Strain: Engaging in activities that exert excessive pressure on the ankles, such as running or standing for prolonged periods, can strain the muscles and ligaments, leading to inflammation.
- Medical Conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as arthritis, gout, or tendonitis, can cause chronic inflammation in the ankles. These conditions often result from autoimmune responses or metabolic imbalances within the body.
- Poor Circulation: Reduced blood flow to the lower extremities can contribute to fluid retention and swelling in the ankles. Conditions like peripheral artery disease or venous insufficiency can impair circulation, exacerbating inflammation.
- Diet and Lifestyle Factors: High sodium intake, dehydration, obesity, and sedentary lifestyle choices can all influence fluid retention and inflammation in the ankles. Making dietary and lifestyle modifications can play a significant role in managing swelling.
Identifying Trigger Factors
To effectively manage ankle inflammation, it’s crucial to identify the specific triggers that contribute to swelling in each individual case. This often requires a comprehensive assessment by a healthcare professional to determine underlying causes and develop a personalized treatment plan.
Strategies for Managing Ankle Inflammation
Once the triggers of ankle inflammation are identified, implementing targeted strategies can help alleviate symptoms and prevent recurrence. Here are some effective approaches:
R.I.C.E. Protocol
The R.I.C.E. protocol—rest, ice, compression, and elevation—is a standard method for managing acute ankle injuries and inflammation. Following these steps can help reduce pain and swelling:
- Rest: Avoid putting weight on the affected ankle and refrain from strenuous activities to allow the injured tissues to heal.
- Ice: Apply ice packs or cold therapy to the swollen area for 15-20 minutes several times a day to constrict blood vessels and reduce inflammation.
- Compression: Use compression bandages or wraps to apply gentle pressure to the ankle, which can help prevent fluid buildup and provide support.
- Elevation: Keep the affected ankle elevated above heart level whenever possible to promote drainage of excess fluid and reduce swelling.
Physical Therapy
For chronic or recurring ankle inflammation, physical therapy can be highly beneficial. A skilled therapist can design a customized exercise program to strengthen the muscles around the ankle, improve flexibility, and enhance stability. Additionally, techniques such as ultrasound or electrical stimulation may be used to promote healing and reduce inflammation.
Medications
In some cases, medications may be prescribed to alleviate pain and inflammation. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen or naproxen can help reduce swelling and discomfort. However, it’s essential to use these medications as directed and consult with a healthcare professional, especially if there are underlying medical conditions or concerns about potential side effects.
Lifestyle Modifications
Making changes to diet and lifestyle habits can have a significant impact on ankle inflammation. Key modifications include:
- Reducing Sodium Intake: Excessive salt consumption can lead to fluid retention and aggravate swelling. Limiting sodium intake by avoiding processed foods and opting for fresh, whole foods can help alleviate inflammation.
- Staying Hydrated: Adequate hydration is essential for maintaining fluid balance in the body. Drinking plenty of water throughout the day can prevent dehydration and reduce the risk of ankle swelling.
- Maintaining a Healthy Weight: Obesity puts added stress on the ankles and can contribute to inflammation. Adopting a balanced diet and engaging in regular exercise can help achieve and maintain a healthy weight, reducing strain on the joints.
Alternative Therapies
Several alternative therapies may complement traditional treatments for ankle inflammation:
- Acupuncture: This ancient practice involves the insertion of thin needles into specific points on the body to alleviate pain and promote healing. Acupuncture has been shown to be effective in reducing inflammation and improving mobility in some individuals with ankle issues.
- Herbal Remedies: Certain herbs and supplements, such as turmeric, bromelain, or ginger, possess anti-inflammatory properties and may help reduce swelling. However, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare provider before incorporating these remedies, as they may interact with medications or have contraindications.
Management Strategies for Ankle Inflammation
| Strategy | Description |
|---|---|
| R.I.C.E. Protocol | Standard method for managing acute ankle injuries, involving rest, ice, compression, and elevation. |
| Physical Therapy | Customized exercise programs to strengthen muscles, improve flexibility, and enhance stability. |
| Medications | Prescription or over-the-counter drugs to alleviate pain and inflammation, such as NSAIDs. |
| Lifestyle Modifications | Dietary and lifestyle changes to reduce sodium intake, stay hydrated, and maintain a healthy weight. |
| Alternative Therapies | Complementary approaches like acupuncture or herbal remedies to reduce inflammation and improve mobility. |
Implementing a combination of these strategies can effectively address ankle inflammation and promote overall musculoskeletal health.
Conclusion
Ankle inflammation can significantly impact daily functioning and quality of life, but with proper understanding and management, individuals can effectively alleviate symptoms and prevent recurrence. By identifying the underlying triggers, implementing targeted strategies such as the R.I.C.E. protocol, physical therapy, medications, and lifestyle modifications, individuals can regain mobility and comfort in their ankles. It’s essential to work closely with healthcare professionals to develop a personalized treatment plan that addresses specific needs and promotes long-term healing.