Understanding POTS
Postural Orthostatic Tachycardia Syndrome, or POTS, is a condition characterized by the body’s inability to properly regulate blood flow, leading to symptoms such as dizziness, lightheadedness, fatigue, and a rapid increase in heart rate upon standing up. While the exact cause of POTS is not always clear, it often involves dysfunction in the autonomic nervous system, which controls involuntary bodily functions like heart rate and blood pressure. Explore More About (Link between Covid And diabetes)
Symptoms of POTS
Recognizing the symptoms of POTS is crucial for proper diagnosis and management. Common symptoms include:
- Dizziness and lightheadedness: Individuals with POTS often experience a sensation of spinning or feeling faint when transitioning from lying down to standing up.
- Tachycardia: A rapid increase in heart rate, typically more than 30 beats per minute within 10 minutes of standing up.
- Fatigue: Persistent tiredness or exhaustion, even after minimal physical or mental exertion.
- Brain fog: Difficulty concentrating, memory problems, and cognitive impairment.
- Nausea and abdominal discomfort: Some individuals may experience gastrointestinal symptoms such as nausea, bloating, or abdominal pain.

Diagnosing POTS
Diagnosing POTS can be challenging due to its overlapping symptoms with other conditions and the variability in individual experiences. However, healthcare providers typically use a combination of medical history, physical examination, and specialized tests to make an accurate diagnosis.
Medical History
A thorough medical history is essential for identifying potential risk factors and understanding the onset and progression of symptoms. Healthcare providers may inquire about:
- Symptom onset: When did the symptoms first begin, and have they been progressively worsening?
- Triggers: Are there specific activities or triggers that exacerbate symptoms, such as standing up or prolonged periods of sitting?
- Medical conditions: Do you have any underlying medical conditions or family history of autonomic dysfunction?
Physical Examination
During a physical examination, healthcare providers may assess vital signs, including heart rate and blood pressure, in various positions (lying down, sitting, and standing). Orthostatic vital signs, such as changes in heart rate and blood pressure upon standing, are indicative of autonomic dysfunction associated with POTS.
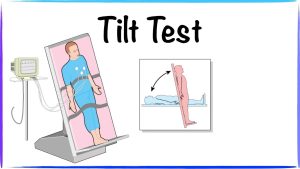
Tilt Table Test
The tilt table test is a diagnostic tool commonly used to assess autonomic function and diagnose POTS. During this test, the patient is securely strapped to a table that can be tilted upright. Vital signs are monitored continuously as the table is tilted to different angles, simulating changes in posture. A significant increase in heart rate without a corresponding drop in blood pressure upon standing is suggestive of POTS.
Autonomic Function Tests
Additional autonomic function tests may be performed to evaluate the integrity of the autonomic nervous system, including:
- Quantitative Sudomotor Axon Reflex Test (QSART): Assesses sweat gland function.
- Thermoregulatory Sweat Test (TST): Evaluates the body’s ability to regulate temperature.
- Heart Rate Variability (HRV) Analysis: Measures fluctuations in heart rate in response to various stimuli.
Managing POTS
While there is currently no cure for POTS, various treatment strategies aim to alleviate symptoms and improve quality of life. Treatment plans are tailored to individual needs based on symptom severity, underlying causes, and coexisting medical conditions.
Lifestyle Modifications
Making certain lifestyle modifications can help manage symptoms and reduce the impact of POTS on daily life:
- Hydration: Maintaining adequate hydration is essential to support blood volume and prevent orthostatic intolerance. Aim to drink plenty of fluids, especially water and electrolyte-rich beverages.
- Salt Intake: Increasing salt intake can help expand blood volume and improve orthostatic tolerance in some individuals with POTS. Consult with a healthcare provider or registered dietitian before making significant dietary changes.
- Physical Counterpressure Maneuvers: Performing maneuvers such as tensing leg muscles or crossing legs while standing can help mitigate symptoms of dizziness and lightheadedness.
- Compression Garments: Wearing compression stockings or abdominal binders can help improve venous return and prevent blood pooling in the lower extremities.
Medications
Medications may be prescribed to target specific symptoms associated with POTS or address underlying mechanisms contributing to autonomic dysfunction:
- Beta-Blockers: Help reduce heart rate and minimize palpitations.
- Fludrocortisone: Increases sodium retention and expands blood volume.
- Midodrine: Constricts blood vessels to improve blood pressure regulation.
- Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs): Can be used to manage symptoms of fatigue and improve overall well-being.
Physical Therapy
Physical therapy plays a vital role in managing POTS by improving cardiovascular fitness, muscle strength, and flexibility. A structured exercise program tailored to individual capabilities can help enhance orthostatic tolerance and reduce symptom severity over time.
Psychological Support
Living with a chronic condition like POTS can take a toll on mental health and emotional well-being. Seeking support from mental health professionals, joining support groups, or participating in cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) can provide valuable coping strategies and emotional support.
Lifestyle Modifications vs. Medications
| Lifestyle Modifications | Medications |
|---|---|
| Hydration: Maintain adequate fluid intake | Beta-Blockers: Reduce heart rate and palpitations |
| Salt Intake: Increase sodium intake | Fludrocortisone: Increase sodium retention and expand blood volume |
| Physical Counterpressure Maneuvers | Midodrine: Constrict blood vessels to improve blood pressure |
| Compression Garments: Wear as directed | SSRIs: Manage symptoms of fatigue and improve overall well-being |
Conclusion
Coping with POTS requires a comprehensive approach that addresses both the physical and emotional aspects of the condition. By understanding the symptoms, pursuing an accurate diagnosis, and implementing tailored treatment strategies, individuals with POTS can effectively manage their symptoms and improve their quality of life. It’s essential to work closely with healthcare providers to develop a personalized treatment plan that meets individual needs and goals. With proper management and support, individuals with POTS can lead fulfilling and active lives.