Understanding Heart Failure
Heart failure, despite its name, does not mean the heart has stopped beating; rather, it signifies that the heart is not functioning as effectively as it should. This condition develops gradually over time as the heart’s pumping action weakens or stiffens. Consequently, the body does not receive sufficient oxygen and nutrients, leading to a plethora of symptoms that should not be overlooked. Explore More About (Common Mouth Problem)

Recognizing Symptoms Early On
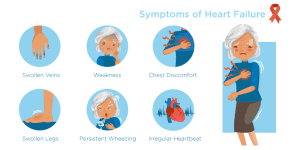
1. Shortness of Breath (Dyspnea)
One of the primary symptoms of heart failure is difficulty breathing or shortness of breath, especially during physical exertion or when lying down flat. This occurs because fluid builds up in the lungs, making it challenging to breathe deeply.
2. Fatigue and Weakness
Individuals with heart failure often experience persistent fatigue and weakness due to the heart’s inability to pump enough blood to meet the body’s demands. Tasks that were once routine may become arduous, and even simple activities can leave one feeling exhausted.
3. Swelling (Edema)
Fluid retention, commonly manifested as swelling in the legs, ankles, feet, or abdomen, is another common symptom of heart failure. This occurs when the heart cannot pump blood efficiently, causing fluid to accumulate in the body’s tissues.
4. Persistent Coughing
A chronic cough, especially one that produces white or pink blood-tinged phlegm, may indicate heart failure. Fluid accumulation in the lungs can trigger coughing, particularly when lying down.
5. Increased Heart Rate
Heart palpitations or a rapid or irregular heartbeat can occur as the heart attempts to compensate for its decreased pumping ability. This heightened heart rate may be noticeable, especially during physical activity or while resting.
6. Reduced Exercise Tolerance
Individuals with heart failure may find that they tire more easily during physical activity or exercise. This reduced tolerance for exertion is due to the heart’s diminished capacity to deliver oxygen-rich blood to the muscles.
7. Loss of Appetite or Nausea
Heart failure can lead to digestive disturbances such as a loss of appetite, feelings of fullness, or nausea. These symptoms may arise as a result of fluid buildup in the abdomen, which can affect digestion and reduce the desire to eat.
8. Difficulty Concentrating or Mental Confusion
In advanced stages of heart failure, reduced blood flow to the brain can cause cognitive impairments such as difficulty concentrating, memory problems, or confusion. These symptoms may be subtle at first but can worsen over time if left unaddressed.
Seeking Prompt Medical Attention
Given the potentially serious nature of heart failure, it is imperative to seek medical attention promptly upon experiencing any of the aforementioned symptoms. Early diagnosis and intervention can significantly improve outcomes and quality of life for individuals living with this condition.
Treatment and Management Strategies
1. Medication Management
Medications such as angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors, beta-blockers, diuretics, and vasodilators are commonly prescribed to manage heart failure symptoms and improve cardiac function. It is essential to adhere to the prescribed medication regimen and attend regular follow-up appointments with healthcare providers.
2. Lifestyle Modifications
In addition to medication, lifestyle modifications play a crucial role in managing heart failure. These may include adopting a heart-healthy diet low in sodium and saturated fats, engaging in regular physical activity, maintaining a healthy weight, limiting alcohol consumption, and quitting smoking.
3. Monitoring Fluid Intake and Weight
Individuals with heart failure are often advised to monitor their fluid intake and weight closely. Consuming too much fluid can exacerbate fluid retention and worsen symptoms, while sudden weight gain may indicate fluid buildup and necessitate adjustments to medication or dietary restrictions.
4. Cardiac Rehabilitation
Cardiac rehabilitation programs offer structured exercise training, education, and support to individuals with heart failure. These programs aim to improve cardiovascular fitness, optimize medication adherence, and enhance overall quality of life through a multidisciplinary approach.
5. Surgical Interventions
In some cases, surgical interventions such as coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG), heart valve repair or replacement, or implantation of a pacemaker or defibrillator may be necessary to treat underlying cardiac issues and alleviate heart failure symptoms.
Medication Options for Heart Failure
| Medication Type | Purpose | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme (ACE) Inhibitors | Improve cardiac function by relaxing blood vessels and reducing blood pressure | Lisinopril, Enalapril |
| Beta-Blockers | Decrease heart rate and blood pressure | Metoprolol, Carvedilol |
| Diuretics | Reduce fluid buildup in the body | Furosemide, Hydrochlorothiazide |
| Vasodilators | Dilate blood vessels to improve blood flow | Hydralazine, Isosorbide dinitrate |
Conclusion
In conclusion, recognizing and addressing the early signs of heart failure is paramount for optimal outcomes and quality of life. By familiarizing oneself with the symptoms and seeking prompt medical attention when necessary, individuals can effectively manage this condition and minimize its impact on daily life. Through a combination of medication, lifestyle modifications, and ongoing medical care, individuals living with heart failure can lead fulfilling and active lives.