Introduction:
Pilonidal cysts, though common, often remain misunderstood and overlooked. This comprehensive guide aims to shed light on this condition, delving into its causes, symptoms, treatment options, and preventive measures.
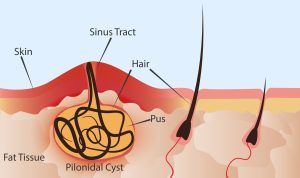
A pilonidal cyst is a round sac filled with air or fluid, typically found in the crease of the buttocks. More than 70,000 cases are reported annually in the U.S. Despite its prevalence, individuals often hesitate to discuss it, even with healthcare providers.
Who is at Risk?:
Understanding the demographic at higher risk is crucial. Men are three to four times more likely to be diagnosed, and individuals between puberty and age 40, particularly those with sedentary jobs like truck drivers and office workers, face elevated risks. Additional risk factors include overweight/obesity, a family history of rough body hair, and wearing tight clothing.

Symptoms and Causes:
Causes of Pilonidal Cysts: Experts are still unraveling the complete set of causes, but they link the condition to ingrown hairs in the buttock crease, leading to skin infections. It’s akin to getting a sliver of wood stuck in the skin, with an ingrown hair causing the issue.
Symptoms of Pilonidal Cysts:
- Pain: Often worsens when sitting.
- Dimple or Swollen Area: A small dimple or a large swollen area between the buttocks, usually red and tender.
- Abscess with Drainage: Pus or blood drainage with a foul smell.
- General Discomfort: Nausea, fever, and extreme fatigue.
Can Pilonidal Cysts Occur During Pregnancy? While more common in men, pregnant women can also develop pilonidal cysts. If buttock pain arises during pregnancy, it’s essential to consider this possibility and seek medical attention.
Diagnosis and Tests:
Healthcare providers employ a thorough physical examination to diagnose pilonidal cysts. The examination focuses on the buttock crease, where signs of the cyst, such as a pimple or oozing fluid, may be visible. Questions regarding changes in appearance, fluid drainage, and additional symptoms are crucial in the diagnostic process. In rare cases, CT or MRI scans may be ordered to identify sinus cavities beneath the skin surface.
Management and Treatment:
Upon diagnosis, a tailored treatment plan is devised based on individual cases. Factors such as previous occurrences, concurrent skin issues, and recovery speed influence the chosen approach. Treatment options include:
- Draining the Cyst: In-office procedure involving a small incision to drain fluid.
- Injections: Using phenol, an acidic compound, to treat and prevent mild to moderate cysts.
- Antibiotics: Addressing skin inflammation; however, they are not standalone treatments.
- Laser Therapy: Removing hair to prevent ingrown hairs and recurrent cysts.
- Surgery: Essential for chronic cases or when sinus cavities form. Wound management post-surgery is crucial, with options like leaving it open for packing or closing with sutures or a skin flap.
Surgical Intervention:
Chronic or worsened pilonidal cysts may necessitate surgery. The procedure involves excising the cyst entirely, with options to leave the wound open for packing or close it with sutures or a skin flap. Post-surgery care is vital to prevent infections, and healthcare providers provide guidance on wound hygiene and recognizing signs of infection.
Can Pilonidal Cysts Go Away on Their Own?:
In some cases, pilonidal cysts may spontaneously drain and disappear. However, chronic cases may exhibit intermittent symptoms over time, even after surgery. treatment for other medical problems The recurring nature is especially notable if the condition has worsened or if there’s a family history of pilonidal cysts.
Prevention Strategies:
Taking proactive steps can help prevent pilonidal cysts or reduce their recurrence:
- Hygiene Practices: Regularly washing and drying the buttocks maintains cleanliness.
- Weight Management: Losing weight, especially if overweight, lowers the risk.
- Avoiding Prolonged Sitting: When possible, avoiding extended periods of sitting alleviates pressure on the buttock area.
- Hair Removal: Shaving the hair around the buttocks weekly or using hair removal products reduces the likelihood of ingrown hairs.

Conclusion:
Arming yourself with knowledge about pilonidal cysts, from understanding their origins to recognizing symptoms, seeking timely diagnosis, exploring treatment options, and adopting preventive measures, is crucial. This comprehensive guide aims to empower individuals to navigate the complexities of this common but often overlooked condition.












