What is Dynamic Lock?
Dynamic lock is a major security feature accessible on Windows 11 and 10 devices. The device works by turning itself off when the mobile phone signals weaken to a particular threshold level of Received Signal Strength Indicator (RSSI). When away from their computers, users can better protect themselves because of the fundamental reason behind dynamic locking.
How Dynamic Lock Works
Dynamic lock works only under specific circumstances. It triggers the device to lock only when the following criteria are met:
Bluetooth signal falls below configured RSSI value.
The system is inactive currently.
However, dynamic locking cannot always replace manual locking. Before the Bluetooth signal decreases, the intruder must access the system, or the device will not lock automatically. The dynamic lock is designed to protect users’ computers from getting hacked.
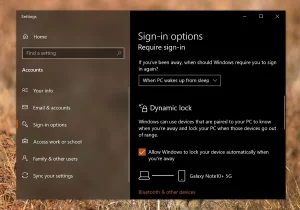
The diagram below explains the use of Dynamic Lock through Group Policy.
A Group Policy Object (GPO) can be used to ease the procedure for configuring dynamic locking on Windows gadgets. Follow these steps to set up dynamic lock using the Group Policy Management Console (GPMC):
a. To apply a domain-based Group Policy to computer accounts in Active Directory using GPMC, scope it. b. Amend the Group Policy object to view policy settings. c. Locate and enable the “Configure dynamic lock factors” policy setting under Computer Configuration > Administrative Templates > Windows Components > Windows Hello for Business. d. Close the Group Policy Management Editor after saving the changes.
Understanding Dynamic Lock Factors
When you enable the “Configure dynamic lock factors” policy setting, the Group Policy Editor creates a default signal rule policy. The given policy lays out predetermined values that dictate the behavior of a dynamic locks. To accurately assess RSSI measurements, Microsoft recommends employing the default values in each situation.
The default signal rule policy consists of the following attributes:
Signal Type: Bluetooth
Scenario: Dynamic Locks
Class of Device: Therefore, phone calls are better.
The ‘class of Device’ attribute identifies the type of Bluetooth device employed in dynamic locking. So far, Phone support is the only one available. The other attribute will be given more values in the future.
The minimum Bluetooth signal strength for a device to be in-range is set by the ‘rssiMin’ attribute. The default value -10 lets users traverse an average-sized office without unintentionally triggering the locks.
The device should lock when the signal strength decreases more than 10 units, as indicated by the ‘rssiMaxDelta’ attribute’s default value of -10.
Remember that RSSI measurements are in comparison and become lower as the Bluetooth signals reduce between the paired devices. The measure of 0 implies a stronger signal than -10, whereas -60 implies that the devices are getting farther away.
By configuring dynamic lock factors in a correct way, Windows users can secure their devices and keep sensitive information from unauthorized access.
Conclusion,
Windows 11 and Windows 10 users can utilize dynamic lock as an efficient security measure. Group Policy can be configured correctly so that Bluetooth signals below a given strength will automatically trigger the device to lock. Manual locking should be paired with dynamic locking to fully secure devices. Dynamic locks are not always a suitable safety approach.