ChatGPT: Optimizing Language Models for Dialogue
Artificial intelligence (AI) has made remarkable strides, revolutionizing numerous sectors, ranging from healthcare to finance. Among the most significant advancements in AI is the development of chatbots, capable of simulating human-like conversations.
One such frontrunner in this field is ChatGPT, a potent language model explicitly designed to facilitate seamless and meaningful dialogue. In this article, we will explore the intricacies of optimizing language models like ChatGPT for dialogue and how this cutting-edge technology is transforming the way we communicate.
Understanding ChatGPT
ChatGPT, also known as Chatbot Generative Pre-trained Transformer, represents a state-of-the-art language model built upon the GPT-4 architecture by OpenAI. Its primary purpose is to generate human-like text based on input text, making it an ideal candidate for creating conversational agents or chatbots.
This model’s design revolves around context comprehension, generating coherent responses, and maintaining a natural conversational flow. The technology has found applications in customer service, virtual assistants, and even content generation.

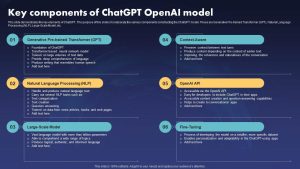
Key Components of ChatGPT
The efficacy of ChatGPT as a conversational agent lies in its ability to optimize language models for dialogue. The optimization process involves three key components:
Pre-training: ChatGPT undergoes pre-training on vast amounts of text data, enabling it to grasp grammar, syntax, and semantics. This process empowers the model to generate coherent and contextually relevant responses.
Fine-tuning: Following pre-training, ChatGPT goes through fine-tuning on specific dialogue datasets, allowing it to adapt better to conversational contexts. This step is crucial for ensuring that the model provides accurate and useful responses.
Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF): To further enhance its performance, ChatGPT undergoes reinforcement learning from human feedback. This step involves training the model using conversations between humans, helping it learn the nuances of natural dialogue and improve its interaction capabilities.
Optimizing Language Models for Dialogue
To optimize language models like ChatGPT for dialogue, researchers and developers need to focus on several key aspects:
Context Understanding: For a model to generate meaningful responses, it must grasp the conversation’s context. Training the model on a diverse range of conversational data and incorporating techniques like attention mechanisms can prioritize contextually relevant information.
Coherence and Consistency: Ensuring that the generated responses are coherent and consistent is crucial in maintaining a natural conversational flow. Techniques like beam search, nucleus sampling, and temperature control can improve the coherence of the model-generated text.
Safety and Ethical Considerations: As AI-powered chatbots become more prevalent, addressing potential issues like harmful content generation, bias, and privacy concerns is essential. Regularly updating training data, employing content filters, and involving human moderators can mitigate these challenges.
Personalization: Enhancing user experience requires personalizing chatbot responses based on user preferences, history, and context. Advanced techniques like transfer learning, meta-learning, and user embeddings can be employed to create a more personalized and engaging conversational agent.

The Conclusion
The optimization of language models like ChatGPT for dialogue has transformed the way businesses and individuals communicate, providing a more efficient, personalized, and engaging conversational experience.
By focusing on context understanding, coherence, safety, and personalization, researchers and developers can further enhance these models’ performance, paving the way for a new era of AI-powered communication. ChatGPT’s role in dialogue optimization marks a significant milestone in the evolution of AI, opening doors to innovative and seamless interactions between humans and technology.












